The Radiological Management of Pseudoaneurysms Complicating Pancreatitis
Abstract
Context Pseudoaneurysms associated with pancreatitis are rare, and bleeding pseudoaneurysms are associated with a high mortality. Objective The aim of this study was to report the outcomes of endovascular and percutaneous therapy in the management of pseudoaneurysms secondary to pancreatitis. Patients Patients who underwent angiography for pseudoaneurysms associated with pancreatitis from 2005 to 2011 were identified from the angiography database. Main outcome measures Patient demographics, clinical presentation, radiological findings, treatment, and outcomes were retrospectively reviewed. Results Nineteen pseudoaneurysms associated with pancreatitis in 13 patients were identified. The diagnosis of a pseudoaneurysm was made by computerised tomography angiography in seven patients, followed by portal venous phase contrast enhanced CT (n=4), duplex ultrasound (n=1) and angiography (n=1). At angiography, coil embolisation was attempted in 11 patients with an initial success rate of 82% (n=9). One patient underwent successful embolisation with percutaneous thrombin injection. The recurrence rate following initial successful embolisation was 11% (n=1). There were no episodes of re-bleeding following embolisation but re-bleeding following thrombin injection was observed in one case. The morbidity and mortality rate in the 12 patients that were successfully treated was 25% (n=3) and 8% (n=1), respectively. All 12 patients that were successfully treated demonstrated radiological resolution of their pseudoaneurysms, with a median follow-up of 20 months. Conclusion Endovascular embolisation is a suitable first-line management strategy associated with low recurrence rates. The role of percutaneous thrombin injection is yet to be defined.
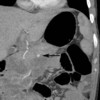
Image: Arterial phase computed tomography demonstrates a small pseudoaneurysm.
Downloads
References
Roberts SE, Williams JG, Meddings D, Goldacre MJ. Incidence and case fatality for acute pancreatitis in England: geographical variation, social deprivation, alcohol consumption and aetiology--a record linkage study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2008;28(7): 931-941.
Gurusamy KS, Farouk M, Tweedie JH. UK guidelines for management of acute pancreatitis: is it time to change? Gut 2005;54(9): 1344-1345.
Whitcomb DC. Clinical practice. Acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2006;354(20): 2142-2150.
Mendelson RM, Anderson J, Marshall M, Ramsay D. Vascular complications of pancreatitis. ANZ J Surg 2005;75(12): 1073-1079.
White AF, Baum S, Buranasiri S. Aneurysms secondary to pancreatitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1976;127(3): 393-396.
Kiviluoto T, Kivisaari L, Kivilaakso E, Lempinen M. Pseudocysts in chronic pancreatitis. Surgical results in 102 consecutive patients. Arch Surg 1989;124(2): 240-243.
Fankhauser GT, Stone WM, Naidu SG, Oderich GS, Ricotta JJ, Bjarnason H, Money SR. The minimally invasive management of visceral artery aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Surg;53(4): 966-970.
Sethi H, Peddu P, Prachalias A, Kane P, Karani J, Rela M, Heaton N. Selective embolization for bleeding visceral artery pseudoaneurysms in patients with pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int;9(6): 634-638.
Bergert H, Hinterseher I, Kersting S, Leonhardt J, Bloomenthal A, Saeger HD. Management and outcome of hemorrhage due to arterial pseudoaneurysms in pancreatitis. Surgery 2005;137(3): 323-328.
Dasgupta R, Davies NJ, Williamson RC, Jackson JE. Haemosuccus pancreaticus: treatment by arterial embolization. Clin Radiol 2002;57(11): 1021-1027.
Balachandra S, Siriwardena AK. Systematic appraisal of the management of the major vascular complications of pancreatitis. Am J Surg 2005;190(3): 489-495.
Stabile BE, Wilson SE, Debas HT. Reduced mortality from bleeding pseudocysts and pseudoaneurysms caused by pancreatitis. Arch Surg 1983;118(1): 45-51.
Mortele KJ, Mergo PJ, Taylor HM, Wiesner W, Cantisani V, Ernst MD, Kalantari BN, Ros PR. Peripancreatic vascular abnormalities complicating acute pancreatitis: contrast-enhanced helical CT findings. Eur J Radiol 2004;52(1): 67-72.
El Hamel A, Parc R, Adda G, Bouteloup PY, Huguet C, Malafosse M. Bleeding pseudocysts and pseudoaneurysms in chronic pancreatitis. Br J Surg 1991;78(9): 1059-1063.
Sessa C, Tinelli G, Porcu P, Aubert A, Thony F, Magne JL. Treatment of visceral artery aneurysms: description of a retrospective series of 42 aneurysms in 34 patients. Ann Vasc Surg 2004;18(6): 695-703.
Horowitz MB, Purdy PD, Valentine RJ, Morrill K. Remote vascular catastrophes after neurovascular interventional therapy for type 4 Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000;21(5): 974-976.
Freeman RK, Swegle J, Sise MJ. The surgical complications of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Am Surg 1996;62(10): 869-873.
Hall RI, Lavelle MI, Venables CW. Chronic pancreatitis as a cause of gastrointestinal bleeding. Gut 1982;23(3): 250-255.
Gadacz TR, Trunkey D, Kieffer RF, Jr. Visceral vessel erosion associated with pancreatitis. Case reports and a review of the literature. Arch Surg 1978;113(12): 1438-1440.
Maus TP. Pseudoaneurysm hemorrhage as a complication of pancreatitis. Mayo Clin Proc 1993;68(9): 895-896.
Kahn LA, Kamen C, McNamara MP, Jr. Variable color Doppler appearance of pseudoaneurysm in pancreatitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1994;162(1): 187-188.
de Perrot M, Berney T, Buhler L, Delgadillo X, Mentha G, Morel P. Management of bleeding pseudoaneurysms in patients with pancreatitis. Br J Surg 1999;86(1): 29-32.
Hsu JT, Yeh CN, Hung CF, Chen HM, Hwang TL, Jan YY, Chen MF. Management and outcome of bleeding pseudoaneurysm associated with chronic pancreatitis. BMC Gastroenterol 2006;6: 3.
Balthazar EJ, Fisher LA. Hemorrhagic complications of pancreatitis: radiologic evaluation with emphasis on CT imaging. Pancreatology 2001;1(4): 306-313.
Nicholson AA, Patel J, McPherson S, Shaw DR, Kessel D. Endovascular treatment of visceral aneurysms associated with pancreatitis and a suggested classification with therapeutic implications. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2006;17(8): 1279-1285.
Bharwani N, Patel S, Prabhudesai S, Fotheringham T, Power N. Acute pancreatitis: the role of imaging in diagnosis and management. Clin Radiol;66(2): 164-175.
Perez C, Llauger J, Pallardo Y, Sanchis E, Sabate JM. Radiologic diagnosis of pseudoaneurysms complicating pancreatitis. Eur J Radiol 1993;16(2): 102-106.
Kirby JM, Vora P, Midia M, Rawlinson J. Vascular complications of pancreatitis: imaging and intervention. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2008;31(5): 957-970.
Hyare H, Desigan S, Brookes JA, Guiney MJ, Lees WR. Endovascular management of major arterial hemorrhage as a complication of inflammatory pancreatic disease. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2007;18(5): 591-596.
Paci E, Antico E, Candelari R, Alborino S, Marmorale C, Landi E. Pseudoaneurysm of the common hepatic artery: treatment with a stent-graft. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2000;23(6): 472-474.
Golzarian J, Nicaise N, Deviere J, Ghysels M, Wery D, Dussaussois L, Van Gansbeke D, Struyven J. Transcatheter embolization of pseudoaneurysms complicating pancreatitis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 1997;20(6): 435-440.
Gambiez LP, Ernst OJ, Merlier OA, Porte HL, Chambon JP, Quandalle PA. Arterial embolization for bleeding pseudocysts complicating chronic pancreatitis. Arch Surg 1997;132(9): 1016-1021.
Bergert H, Dobrowolski F, Caffier S, Bloomenthal A, Hinterseher I, Saeger HD. Prevalence and treatment of bleeding complications in chronic pancreatitis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2004;389(6): 504-510.
Waslen T, Wallace K, Burbridge B, Kwauk S. Pseudoaneurysm secondary to pancreatitis presenting as GI bleeding. Abdom Imaging 1998;23(3): 318-321.
Lina JR, Jaques P, Mandell V. Aneurysm rupture secondary to transcatheter embolization. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1979;132(4): 553-556.
Beattie GC, Hardman JG, Redhead D, Siriwardena AK. Evidence for a central role for selective mesenteric angiography in the management of the major vascular complications of pancreatitis. Am J Surg 2003;185(2): 96-102.
Morita R, Muto N, Konagaya M, Honda T, Miyazawa M, Nakazawa S, Kondo N, Kimura N, Miura T, Harasawa S, et al. Successful transcatheter embolization of pseudoaneurysm associated with pancreatic pseudocyst. Am J Gastroenterol 1991;86(9): 1264-1267.
Deshmukh H, Rathod K, Garg A, Sheth R, Kulkarni S. Transcatheter embolization as primary treatment for visceral pseudoaneurysms in pancreatitis: clinical outcome and imaging follow up. Indian J Gastroenterol 2004;23(2): 56-58.
Boudghene F, L'Hermine C, Bigot JM. Arterial complications of pancreatitis: diagnostic and therapeutic aspects in 104 cases. J Vasc Interv Radiol 1993;4(4): 551-558.
Mauro MA, Jaques P. Transcatheter management of pseudoaneurysms complicating pancreatitis. J Vasc Interv Radiol 1991;2(4): 527-532.
Kudelko PE, 2nd, Alfaro-Franco C, Diethrich EB, Krajcer Z. Successful endoluminal repair of a popliteal artery aneurysm using the Wallgraft endoprosthesis. J Endovasc Surg 1998;5(4): 373-377.
Burger T, Meyer F, Tautenhahn J, Halloul Z, Fahlke J. Initial experiences with percutaneous endovascular repair of popliteal artery lesions using a new PTFE stent-graft. J Endovasc Surg 1998;5(4): 365-372.
Parodi JC, Schonholz C, Ferreira LM, Bergan J. Endovascular stent-graft treatment of traumatic arterial lesions. Ann Vasc Surg 1999;13(2): 121-129.
Plagnol P, Diard N, Bruneteau P, Roncheau V. Case report: pseudoaneurysm of popliteal artery complicating a total knee replacement: a successful percutaneous endovascular treatment. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2001;21(1): 81-83.
Saad NE, Saad WE, Davies MG, Waldman DL, Fultz PJ, Rubens DJ. Pseudoaneurysms and the role of minimally invasive techniques in their management. Radiographics 2005;25 Suppl 1: S173-189.
Liau CS, Ho FM, Chen MF, Lee YT. Treatment of iatrogenic femoral artery pseudoaneurysm with percutaneous thrombin injection. J Vasc Surg 1997;26(1): 18-23.
Taylor BS, Rhee RY, Muluk S, Trachtenberg J, Walters D, Steed DL, Makaroun MS. Thrombin injection versus compression of femoral artery pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Surg 1999;30(6): 1052-1059.
Armstrong EM, Edwards A, Kingsnorth AN, Freeman S, Roobottom CA. Ultrasound guided thrombin injection to treat a pseudoaneurysm secondary to chronic pancreatitis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2003;26(4): 448-449.
Manazer JR, Monzon JR, Dietz PA, Moglia R, Gold M. Treatment of pancreatic pseudoaneurysm with percutaneous transabdominal thrombin injection. J Vasc Surg 2003;38(3): 600-602.
Puri S, Nicholson AA, Breen DJ. Percutaneous thrombin injection for the treatment of a post-pancreatitis pseudoaneurysm. Eur Radiol 2003;13 Suppl 4: L79-82.
McErlean A, Looby S, Lee MJ. Percutaneous ultrasound-guided thrombin injection as first-line treatment of pancreatic pseudoaneurysm. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2007;30(3): 526-528.
Roach H, Roberts SA, Salter R, Williams IM, Wood AM. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided thrombin injection for the treatment of pancreatic pseudoaneurysm. Endoscopy 2005;37(9): 876-878.
Robinson M, Richards D, Carr N. Treatment of a splenic artery pseudoaneurysm by endoscopic ultrasound-guided thrombin injection. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2007;30(3): 515-517.
Lameris R, du Plessis J, Nieuwoudt M, Scheepers A, van der Merwe SW. A visceral pseudoaneurysm: management by EUS-guided thrombin injection. Gastrointest Endosc;73(2): 392-395.
Copyright (c) 2014 Antonella De Rosa, Dhanwant Gomez, John G Pollock, Peter Bungay, Mario De Nunzio, Richard I Hall, Peter Thurley

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.