Nonspecific Hyperamylasemia: A Case Report
Abstract
Context The elevation of serum amylase and lipase are generally associated with pancreatic diseases. However they can be associated with different pathologies unrelated with amylase and lipase. Case report This paper aims to report a case of a patient diagnosed with nonspecific hyperamylasemia and warn of this possibility in the differentiation of hyperamylasemia. Conclusion The correct diagnosis of silent hyperamylasemia is important in order to determine whether there is the risk of pancreatic disease or if we are just ahead of a benign hyperenzymemia.
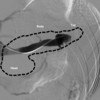
Image: Splenic vein venography.
Downloads
References
Mortelé, K. J., Wiesner, W., Zou, K. H., Ros, P. R., & Silverman, S. G. (2004). Asymptomatic nonspecific serum hyperamylasemia and hyperlipasemia: spectrum of MRCP findings and clinical implications. Abdominal imaging, 29(1),109-14.
Yadav D, Nair S, Norkus EP, Pitchumoni CS (2000) Nonspecific hyperamylasemia and hyperlipasemia in diabetic ketoacidosis: incidence and correlation with biochemical abnormalities. Am J Gastroenterology 95:3123–3128.
Vissers RJ, Abu-Laban RB, McHugh DF (1999) Amylase and lipase in the emergency department: evaluation of acute pancreatitis. J Emerg Med 17:1027–1037.
Gullo L (1996) Chronic nonpathological hyperamylasemia of pancreatic origin. Gastroenterology 110:1905–1908.
Heikius B, Niemela S, Lehtola J, Karttunen TJ (1999) Elevated pancreatic enzymes in inflammatory bowel disease are associated with extensive disease. Am J Gastroenterology 94:1062–1069.
Pezzilli R, Andreone P, Morselli-Labate AM, et al. (1999) Serum pancreatic enzyme concentrations in chronic viral liver diseases. Dig Dis Sci 44:350–355.
Martinez J, Gomez A, Palazon JM, et al. (1997) Asymptomatic chronic hyperamylasemia of unknown origin: an infrequent entity?. Gastroenterology 112:1057.
Forsmark CE, Baillie J; AGA Institute Clinical Practi- ce and Economics Committee; AGA Institute Governing Board. AGA Institute technical review on acute pancreatitis.Gastroenterology. 2007;132(5):2022-44.
Frulloni, L., Patrizi, F., Bernardoni, L., & Cavallini, G. (2005). Pancreatic hyperenzymemia: clinical significance and diagnostic approach. JOP : Journal of the pancreas, 6(6), 536-51.
Castiglione F, Del Vecchio Blanco G, Rispo A, Mazzacca G. Prevention of pancreatitis by weekly amylase assay in patients with Crohn's disease treated with azathioprine. Am J Gastroenterol 2000; 95:2394-5.
Gullo L, Ventrucci M, Barakat B, Migliori M, Tomassetti P, Pezzilli R. Effect of secretin on serum pancreatic enzymes and on the Wirsung duct in chronic nonpathological pancreatic hyperenzymemia. Pancreatology 2003;3:191-4.
Cook LJ, Musa OA, Case RM. Intracellular transport of pancreatic enzymes. Scand J Gastroenterol 1996;31(suppl. 219):1-5.
Gelaye, B., Bekele, T., Khali, a, Haddis, Y., Lemma, S., Berhane, Y., & Williams, M. a. (2011). Laboratory reference values of complete blood count for apparently healthy adults in Ethiopia. Clinical laboratory, 57(7-8),635-40.
Gullo L. benign pancreatic hyperenzymemia. Digestive and liver disease 2007;39:698-702.
Cuckow PM, Foo AY, Jamal A ET al. Familial hyperamylasemia. Gut 1997;40:689-690.
Koda YKL, Vidolin E. Familial hyperamylasemia. Rev Hosp Clín Med S Paulo 2002;57(2):77-82.
Gullo L, Salizzoni E, SerraC, Calculli L, Bastagli L, Migliori M. Can pancreatic steatosis explain the finding of pancreatic hyperenzymemia in subjects with dyslipidemia? Pancreas 2006;33:351-3.
Cavallini G, Frulloni L, Vaona B, Di Francesco V, Bovo P. Is hyperamylasemia related to dyslipidemia? Gastroenterology 1997;112:1058-9.
Hellerhoff, K. J., Iii, H. H., Rösch, T., Settles, M. R., Link, T. M., & Rummeny, E. J. (2002). After Secretin Administration : Image Quality and Diagnostic Accuracy, (July), 121–129.
Testoni PA, Mariani A, Curioni S, Giussani A, Masci E. Pancreatic ductal abnormalities documented by secretin-enhanced MRCP in asymptomatic subjects with chronic pancreatic hyperenzymemia. Am J Gastroenterol 2009; 104:1780-6.
Copyright (c) 2014 Julio Cesar Wiederkehr, Barbara A Wiederkehr, Henrique A Wiederkehr, Caroline A Carvalho

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.