Pancreatic Extragastrointestinal Stromal Tumors, Interstitial Cajal Like Cells, and Telocytes
Abstract
Context The discovery and subsequent ultrastructural characterization of the interstitial Cajal like cells (now called telocytes) in virtually every anatomic sites of the human body, by Laurentiu M Popescu and co-workers, have dramatically improved the understanding the function of these cells and pathogenesis of extragastrointestinal stromal tumors (EGIST). Pancreatic extragastrointestinal stromal tumors (pEGIST), phenotypically similar to pancreatic interstitial Cajal like cells, are extremely rare with an unpredictable biological behavior. Objective To review the clinicopathological, radiological, immunohistochemical, and therapeutic outcome data of all reported cases of pEGIST, and highlight the developments in the field of pancreatic interstitial Cajal like cells/telocytes. Methods A systematic review of English literature (January 2000 to July 2012) was done by using the search engine of PubMed, PubMed Central, Google Scholar, and the Directory of Open Access Journals. Results There have been 19 reported cases of pEGIST during the last decade, over an age range of 31 to 84 years (mean: 56 years) with equal gender predilection ((male:female ratio: 9:10). Preoperative radiological characteristics have been mostly nondiagnostic though these were used, in some, for tissue diagnosis. Majority of pEGIST were localized to pancreatic head (8/19, 42.1%), and 15 of 19 patients (78.9%) were symptomatic at first presentation. The mean size ranged from 2.5 to 35cm (mean: 14 cm). Histomorphological features were that of predominantly spindle cell tumor which consistently expressed c-KIT/CD117 and CD34 by immunohistochemistry, making these two as the most sensitive markers at this site. Results from studies involving discovery on gastrointestinal stromal tumor 1 (DOG-1), the most specific biomarker of GIST/EGIST, has been inconclusive and this was found to be positive in one case only. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with imatinib mesylate and sunitinib were used in few cases, and genetic analysis of c-KIT proto-oncogene was done in two. By univariate analysis, none of the clinicopathological parameters, except surgical resection with microscopic free margin (R0 resection) (P<0.05), were found to be an important indicators of outcome. Conclusion The biological behavior of pEGIST, at present, seems unpredictable which requires indefinite period of follow-up. Large number of such cases with genetic analysis supplemented with immunohistochemistry studies will hopefully throw more light in these tumors.
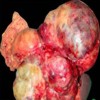
Image: Gross specimen showing a large lobulated tumor in relation to the body and tail of the pancreas.
Downloads
References
Ramon y Cajal S. Histologie du Systeme Nerveux de L’Homme et des Vertebres. Volume 2. Paris: A. Maloine; 1911.
Faussone Pellegrini MS, Cortesini C, Romagnoli P. Ultrastructure of the tunica muscularis of the cardial portion of the human esophagus and stomach, with special reference to the so-called Cajal’s interstitial cells. Arch Ital Anat Embriol. 1977; 82: 157–77.[PMID: 613989]
Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Thuneberg L. Guide to the identification of interstitial cells of Cajal. Microsc Res Tech 1999; 47: 248–66.[PMID: 10602286]
Miettinen M and Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: review on morphology, molecular pathology, prognosis, and differential diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006; 130:1466–78. [ PMID:17090188]
Tan CB, Zhi W, Shahzad G, Mustacchia P. Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: A Review of Case Reports, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Future Directions. ISRN Gastroenterol 2012, Article ID 595968, 1-16, doi:10.5402/2012/595968.
Laurini JA and Carter JE. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010; 134:134–41. [PMID: 20073618]
Levy AD, Remotti HE, Thompson WM, Sobin LH, Miettinen M. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: radiologic features and pathologic correlation. RadioGraphics 2003; 23:283-304. doi: 10.1148/rg.232025146
Miettinen M, Wang ZF, Lasota J. DOG1 antibody in the differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a study of 1840 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2009; 33:1401-8. [PMID:19606013]
West RB, Corless CL, Chen X, Rubin BP, Subramanian S, Montgomery K, Zhu S, et al. The novel marker, DOG-1, is expressed ubiquitously in gastrointestinal stromal tumors irrespective of KIT or PDGFR mutation status. Am J Pathol 2004; 165:107-13.[ PMID: 15215166]
Sun X-W, Feng Z-J, Huang P, Hao W, Sui X-L. Expression of DOG1, CD117 and PDGFRA in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors and Correlations with Clinicopathology. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev, 2012; 13:1389-1393. [PMID: 22799337]
Blay P, Astudillo A, Buesa JM, Campo E, Abad M, Garcia-Garcia J, Miquel R, et al. Protein kinase C theta is highly expressed in gastrointestinal stromal tumors but not in other mesenchymal neoplasias. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10:4089-95. [PMID: 15217944]
Weiss SW, Goldblum JR. Extra gastrointestinal stromal tumors. In: Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors; fifth edition. Mosby Elesevier, 2008; p565-79. [ISBN 978-0-323-04628-2]
Aigaimy A, Wunsch PH. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a regular origin in the muscularis propria, but an extremely diverse gross presentation (a review of 200 cases to critically revaluate the concept of so- called extragastrointestinal stromal tumors). Langenbacks Arch Surg 2006; 391:322-9. [PMID: 16402273]
Miettinen M, Sobin LH, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors presenting as omental masses—a clinicopathologic analysis of 95 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2009; 33:1267–75. [PMID: 19440146]
Rieth JD, Goldblum JR, Lyles RH, Weiss SW. Extragastrointestinal (soft tissue) stromal tumors: an analysis of 48 cases with emphasis on histologic predictors of outcome. Mod Pathol 2000; 13:577–85. [PMID: 10824931]
Popescu LM and Faussone-Pellegrini MS. TELOCYTES – a case of serendipity: the winding way from Interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICC), via Interstitial Cajal-Like Cells (ICLC) to TELOCYTES. J Cell Mol Med 2010; 14 (4):729-40. [PMID: 20367664]
Bussolati G. Of GISTs and EGISTs, ICCs and ICs. Virchows Arch. 2005; 447:907–8. [Epub 2005 Sep 21].
Hinescu ME, Ardeleanu C, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM. Interstitial Cajal like cells in human gallbladder. J Mol Histol 2007; 38:275–84. [PMID: 17541711]
Rasmussen H, Rumessen JJ, Hansen A, Smedts F, Horn T. Ultrastructure of Cajal-like interstitial cells in the human detrusor. Cell Tissue Res 2009; 335:517–27. [PMID: 19142665]
Ahmadi O, de L Nicholson M, Gould ML, Mitchell A, Stringer MD. Interstitial cells of Cajal are present in human extrahepatic bile ducts. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010; 25:277–85. [PMID: 19793166]
Long KB, Butrynski JE, Blank SD, Ebrahim KS, Dressel DM, Heinrich MC, et al. Primary extragastrointestinal stromal tumor of the pleura: report of a unique case with genetic confirmation. Am J Surg Pathol 2010; 34:907-12. [PMID: 20442644]
Petrou A, Alexandrou P, Papalambros A, Saetta A, Fragkou P, Kontos M, et al. A malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the gall bladder immunoreactive for PDGFRA and negative for CD117 (c-KIT). HPB Surgery 2011; Article ID 327192, doi:10.1155/2011/327192.
Terada T. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the uterus: a case report with genetic analyses of c-kit and PDGFRA genes. Int J Gynecol Pathol 2009; 28:29–34. [PMID: 19047911]
Luo XL, Liu D, Yang JJ, Zheng MW, Zhang J, and Zhou XD. Primary gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the liver: a case report. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15 (15):3704–7. [PMID: 19653356]
Popescu LM, Hinescu ME, Ionescu N, Ciontea SM, Cretoiu D, Ardelean C. Interstitial cells of Cajal in pancreas. J Cell Mol Med 2005; 9:169–90. [PMID: 15784175]
Popescu L, Hinescu M, Radu E, et al. CD117/c-kit positive interstitial (Cajal-like) cells in human pancreas. J Cell Mol Med 2005; 9: 738–9. [PMID: 15963268]
Nicolescu MI and Popescu LM. Telocytes in the interstitium of human exocrine pancreas: ultrastructural evidence. Pancreas 2012 Aug; 41(6):949-56. [PMID: 22318257]
Wang XY, Diamant NE, Huizinga JD. Interstitial cells of Cajal: pacemaker cells of the pancreatic duct? Pancreas 2011; 40(1):137-43. [PMID: 21160371]
Yamaura K, Kato K, Miyazawa M, Haba Y, Muramatsu A, Miyata K, Koide N. Stromal tumor of the pancreas with expression of c-kit protein: report of a case. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 19:467-70. [PMID 15012791]
Neto MR, Machuca TN, Pinho RV, Yuasa LD, Bleggi-Torres LF. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor: report of two unusual cases. Virchows Arch 2004; 444:594-6. [PMID 15118853]
Krska Z, Pesková M, Povýsil C, Horejs J, Sedlácková E, Kudrnová Z. GIST of pancreas. Prague Med Rep 2005; 106:201-8. [PMID 16315768]
Daum O, Klecka J, Ferda J, Treska V, Vanecek T, Sima R, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the pancreas: Case report with documentation of KIT gene mutation. Virchows Arch 2005; 446:470-2. [PMID 15756592]
Showalter SL, Lloyd JM, Glassman DT, Berger AC. Extragastrointestinal stromal tumor of the pancreas: case report and a review of the literature. Arch Surg 2008; 143:305-8. [PMID 18347279]
Yan B M, Pai R K, Dam J V. Diagnosis of pancreatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor by EUS guided FNA. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2008; 9:192-6. [PMID 18326928]
Yang F, Long J, Di Y, Fu DL, Jin C, Ni QX, Zhu HG. A giant cystic lesion in the left epigastric region. Pancreatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST).Gut 2008; 57:1494-1636. [PMID: 18941004]
Goh BK, Kesavan SM, Wonk WK. An unusual cause of pancreatic head tumor. Gastroenterol 2009; 137; e5-e6.
Harindhanavudhi T, Tanawuttiwat T, Pyle J, Silva R. Extra- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Presenting as Hemorrhagic Pancreatic Cyst Diagnosed by EUS-FNA. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2009; 10:189-91. [PMID 19287116]
Trabelsi A, Yacoub-Abid L B, Mtimet A, Ben Abdelkrim S, Hammedi F, Ben Ali A, Mokni M. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the pancreas: A case report and review of the literature. North Am J Med Sci 2009; 1:324-6. [PMID: 22666718]
Padhi S, Kongara R, Uppin SG, Uppin MS, Prayaga AK, Sundaram C, Nagari B, and Shastry AR. Extragastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Arising in the Pancreas: A Case Report with a Review of the Literature. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2010; 11(3):244-8. [PMID: 20442520]
Saif MW, Hotchkiss S, Kaley K. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors of the pancreas. JOP. J Pancreas (online) 2010; 11(4):405-406. [PMID: 20601822]
Joshi J and Rustagi T. Pancreatic extragastrointestinal stromal tumor: An unusual presentation of a rare diagnosis. Gastrointest Cancer Res 2010; Suppl 1:S29-S30, Abstr 0917 [PMCID: PMC3047023].
Crisan A, Nicoara E, Cucui V, Cornea G, Laza R. Prolonged fever associated with gastrointestinal stromal tumor-case report. J Exp Med Surg Res 2010; 17 (3):219-224.
Rao RW, Vij M, Singla N, and Kumar A. Malignant pancreatic extra-gastrointestinal stromal tumor diagnosed by ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration cytology. A case report with a review of the literature. JOP. J Pancreas (online) 2011; 12(3):283-86.
Cecka F, John B, Ferko A, Subrt Z, Nikoliv DH, Tycova V. Long term survival of a patient after resection of a gastrointestinal stromal tumor arising from the pancreas. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2011; 10:330-332. [PMID: 21669581]
Soufi M, Bouziane M, Kharrasse G, Bouziane C. An unusual case of a pancreatic head tumor: GIST with pancreatic divisum. P0219. 19th United European Gastroenterology Week, Stockholm, Monday, October 24, 2011.
Kim HH, Koh YS, Park EK, Seoung JS, Hur YH, Kim JC, Cho CK. Primary Extragastrointestinal stromal tumor arising in the pancreas: report of a case. Surgery Today 2012; 42:386-90. [PMID: 22258729]
Babu SR, Kumari S, Zhang Y, Su A, Wang W, Tian B. Extra gastrointestinal stromal tumor arising in the pancreas: a case report and literature review. J Gastroenterol Hepatol Res 2012; 1:80-83. [doi:10.6051/j.issn.2224-3992.2012.01.059]
Kucukardali Y, Oncul O, Cavuslu S, Danaci M, Calangu S, Erdem H, Topcu AW. The spectrum of diseases causing fever of unknown origin in Turkey: a multicenter study. Int J Infect Dis 2008; 12:71-79. [PMID: 17629532 ]
Arnogiannaki N, Martzoukou I, Kountourakis P, Dimitriadis E, Papathanasaki A, Nastoulis E, Gazalidou M. Synchronous presentation of gastrointestinal stromal tumors and other primary neoplasms: A single center experience. In Vivo; 2010; 24 (1):109-15. [PMID: 20133985 ]
Reşorlu B, Baltaci S, Reşorlu M, Kankaya D, Savaş B. Coexistence of papillary renal cell carcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumor in a case. Turk J Gastroenterol 2007; 18(1):47-49. [PMID: 17450496]
Au WY, Ho KM, Shek TW. Papillary renal cell carcinoma and gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a unique association. Ann Oncol 2004; 15 (5):843-44. [PMID: 15111359]
Betigeri AM, Pasupathi P, Bakthavathsalam G, Pugazhenthi B. Co-existence of conventional renal cell carcinoma with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Int J Biolog Med Res 2010; 1 (3): 88-89.
Burgees P, O’Shea M, Gaskin D, Jonnalagadda R. Co-existence of colonic carcinoma, renal cell carcinoma, and gastrointestinal stromal tumor- a case report. Int J Surg Case Report 2010; 1(2):6-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcr.2010.06.002.
Visser BC, Yeh BM, Qayyum A, Way LW, McCulloch CE, Coakley FV. Characterization of cystic pancreatic masses: relative accuracy of CT and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007; 189:648-56. [PMID 17715113]
Anand MKN, Boylan C, Gupta N, Amin Z, Coombs BD, Schmiedl UP, Krasney RM, Karani J. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma imaging. Medscape 2011 (article ID 370909).
Fletcher CD, Berman JJ, Corless C, Gorstein F, Lasota J, Longley BJ, Miettinen M. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: a concensus approach. Human Pathol 2002; 33: 459-65. [PMID: 12094370]
Kindblom LG, Remotti HE, Aldenborg F, Meis-Kindblom JM. Gastrointestinal pacemaker cell tumor (GIPACT): gastrointestinal stromal tumors show phenotypic characteristics of the interstitial cells of Cajal. Am J Pathol 1998; 152:12459-69. [PMID: 9588894]
Erlandson RA, Klimstra DS, Woodruff JM. Subclassification of gastrointestinal stromal tumors based on evaluation by electron microscopy and immunohistochemistry. Ultrastruct Pathol 1996; 20:373-93. [PMID: 8837346]
Ghaffer MA. Large gastrointestinal stromal tumor size does not imply early recurrence. Int Med Case Reports J 2010; 3:13–17.
Demetri GD, vonMehren M, Antonescu CR, et al., “NCCN task force report: Update on the management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors,” JNCCN Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, vol. 8, supplement 2, pp. S1–S44, 2010.
Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Vanderwinden JM, Rumessen JJ. Interstitial cells of Cajal as targets for pharmacological intervention in gastrointestinal motor disorders. Trends Pharmacol Sci 1997; 18:393-403. [PMID: 9357324]
Ardeleanu C and Bussolati G. Telocytes are the common cell of origin of both PEComas and GISTs: an evidence-supported hypothesis. J Cell Mol Med 2011; 15 (12): 2569-74. [PMID: 21977985]
Tirgoviste CI. Pancreatic beta cell clock and telocytes (Editorial). Romanian J Diabetes Nutrn Metabol Dis 2011; 18 (1):
Ardeleanu C, Arsene D, Hinescu M, Andrei F, Gutu D, Luca L, and Popescu LM. Pancreatic expression of DOG1: a novel Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) biomarker. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2009; 17(5): 413-18. [PMID: 19417627]
Bergmann F, Andrulis M, Hartaig W, Penzel R, Gaida MM, Herpel E, Schiracher P, et al. Discovery on gastrointestinal stromal tumor 1 (DOG1) is expressed in pancreatic centroacinar cells and in solid-pseudopapillary neoplasms-novel evidence for a histogenetic relationship. Human Pathol 2011; 42 (6):817-823. [PMID: 21295818]
Copyright (c) 2014 Somanath Padhi, Rajlaxmi Sarangi, Saumyaranjan Mallick

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.