A Foregut Cystic Neoplasm with Diagnostic and Therapeutic Similarities to Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas
Abstract
Context Greater utilization of cross-sectional abdominal imaging has increased the diagnostic frequency of cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. The “International Consensus Guidelines 2012 for the Management of IPMN and MCN of the Pancreas” illustrates a diagnostic and therapeutic algorithm for these lesions based on current knowledge. Case report We present a case of a 49-year-old woman with two years of intermittent epigastric pain found to have an 8.5 cm head of the pancreas mass on CT. Evaluation was consistent with a mucinous cystic neoplasm for which she underwent an uneventful pancreaticoduodenectomy. Histology revealed a bronchogenic cyst of the head of the pancreas. Discussion Bronchogenic cysts are congenital anomalies of the ventral foregut that can migrate into the abdomen prior to fusion of the diaphragm. They can easily be misdiagnosed for other benign and malignant retroperitoneal lesions. Similarly to mucinous cystic neoplasms, bronchogenic cysts have been reported to undergo malignant transformation. They can also become infected and hemorrhage. Therefore, resection should be performed in appropriate risk candidates. It is possible, with increased use of high resolution cross-sectional imaging, that these lesions may be identified with greater frequency in the abdomen and confused with other pancreatic neoplasms. The presence of ciliated respiratory epithelium and cartilage on pathology provides for definitive diagnosis.
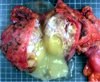
Image: Gross pancreaticoduodenectomy specimen.
Downloads
References
Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, et al. International Consensus Guidelines for Management of Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms and Mucinous Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas. Pancreatology 2006;6:17–32.
Zhang XM, Mitchell DG, Dohke M, Holland GA, Parker L. Pancreatic cysts: depiction on single-shot fast spin-echo MR images. Radiology 2002;223(2):547-53.
Laffan TA, Horton KM, Klein AP, et al. Prevalence of unsuspected pancreatic cysts on MDCT. Am J Roentgenol 2008 Sep;191(3):802-7.
Brugge WR, Lauwers GY, Sahani D, et al. Cystic Neoplasms of the Pancreas. NEJM 2004;351:1218-26.
Tanaka M, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Adsay V, et al. International Consensus Guidelines 2012 for the Management of IPMN and MCN of the Pancreas. Pancreatology 2012;12:183-197.
Maurea S, Fusari M, Imbriaco M et al. Pitfalls in diagnostic imaging of cystic pancreatic masses: a case of true cystic lesion mimicking a mucinous cystadenoma. JOP. 2012;13(1):83-6.
Andersson R, Lindell G, Cwikiel W, Dawiskiba S. Retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst as a differential diagnosis of pancreatic mucinous cystic tumor. Dig Surg 2003;20(1):55-7.
Liang MK, Yee HT, Song JW, et al. Subdiaphragmatic bronchogenic cysts: a comprehensive review of the literature. Am Surg 2005;71(12):1034-41.
Coselli MP, de Ipolyi P, Bloss RS, et al. Bronchogenic cysts above and below the diaphragm: Report of eight cases. Ann Thorac Surg 1987;44:491–494.
Sumiyoshi K, Shimizu S, Enjoji M, et al. Bronchogenic cyst in the abdomen. Virchows Arch. A Pathol Anat Histopathol 1985; 408: 93–8.
Cetinkursun S, Ozturk H, Celasun B, et al. Isolate abdominal bronchogenic cyst: A case report. Eur J Pediatr Surg 1997;7:103–105.
Miller RF, Graub M, Pashuck ET. Bronchogenic cyst: Anomalies resultingfrom maldevelopment of primitive foregut and midgut. Am J Roentgenol 1953;70:771–785.
Fusari M, Maurea S, Imbriaco M, et al. Comparison between multislice CT and MR imaging in the diagnostic evaluation of patients with pancreatic masses. Radiol Med. 2010;115(3):453-66.
McAdams HP, Kirejczyk WM, Rosado-de-Christenson ML et al. Bronchogenic cyst: imaging features with clinical and histopathologic correlation. Radiology. 2000;217(2):441-6.
Wilentz RE, Albores-Saavedra J, Zahurak M, et al. Pathologic examination accurately predicts prognosis in mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Am J Surg Pathol 1999;23:1320-7.
Sullivan SM, Okada S, Kudo M, et al. A retroperitoneal bronchogenic cyst with malignant change. Pathol Int 1999;49:338–341.
Fievet L, D'Journo XB, Guys JM et al. Bronchogenic cyst: best time for surgery? Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;94(5):1695-9.
Copyright (c) 2014 Michael D Kluger, Claude Tayar, Andrea Belli, Juan A Salceda, Jeanne T van Nhieu, Alain Luciani, Daniel Cherqui

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.