Unusual Cause of Massive Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding: A Pancreatic Arteriovenous Malformation
Abstract
Context Upper gastrointestinal bleeding is one of the most common emergencies in gastroenterology. The common causes of the upper gastrointestinal bleeding include peptic ulcer disease, gastric erosive mucosal disease and portal hypertension. Gastrointestinal arteriovenous malformation is a less common cause of gastrointestinal bleeding and these arteriovenous malformation are most commonly located in the large and small intestine. Pancreatic arteriovenous malformation is a rare condition in which there is tumor-like formation or vascular anomaly built up via an aberrant bypass anastomosis of the arterial and venous systems in the pancreas. Splenic artery is most commonly involved (42%), followed by gastroduodenal artery (22%) and small pancreatic arteries (25%). Clinically it may present as gastrointestinal hemorrhage which is occasionally fatal. Other presentations are abdominal pain, pancreatitis, duodenal ulcer, jaundice, and portal hypertension. Case report We present a rare case of pancreatic arteriovenous malformation presenting as massive upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Conclusion Since early surgery is a life saving treatment for such cases, hence, a high index of suspicion should be maintained especially when massive bleeding is detected from the medial wall of second part of duodenum.
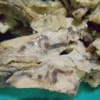
Image: Gross specimen of the pancreatic arteriovenous malformation.
Downloads
References
Halpern M, Turner AF, Citron BP. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. An angiographic study of abdominal visceral angiodysplasias associated with gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Radiology 1968; 90:1143-9. PubMed PMID: 5656734.
Sawabu N, Ishida Y, Toya D, Yoneshima M, Hattori N, Kadoya M. Pancreatic arteriovenous malformation presenting as interesting findings on endoscopic retrograde pancreatography. Dig Dis Sci 1984; 29:678-82. PubMed PMID: 6734376.
Nishiyama R, Kawanishi Y, Mitsuhashi H, Kanai T, Ohba K, Mori T, Hamabe N, Watahiki Y, Nakamura S. Management of pancreatic arteriovenous malformation. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2000; 7:438-42. PubMed PMID: 11180867.
Uda O, Aoki T, Tsuchida A, Asami K, Inoue K, Masuhara S, Koyanagi Y, Hakamada Y, Yasuda D. Pancreatic arteriovenous malformation observed to bleed from the bile duct and a duodenal ulcer: report of a case. Surg Today 1999; 29:462-6. PubMed PMID: 10333421.
Kanno A, Satoh K, Kimura K, Masamune A, Asakura T, Egawa S, Sunamura M, Watanabe M, Shimosegawa T. Acute pancreatitis due to pancreatic arteriovenous malformation: 2 case reports and review of the literature. Pancreas 2006; 32:422-5. PubMed PMID: 16670626.
Song KB, Kim SC, Park JB, Kim YH, Jung YS, Kim MH, Lee SK, Lee SS, Seo DW, Park do H, Kim JH, Han DJ. Surgical outcomes of pancreatic arteriovenous malformation in a single center and review of literature. Pancreas 2012; 41:388-96. PubMed PMID: 22129532.
Zinner MJ, Schwartz SI, Ellis H, Maingot R. Maingot’s abdominal operations. 10th ed. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, 1997:156-158.
Chuang VP, Pulmano CM, Walter JF, Cho KJ. Angiography of pancreatic arteriovenuos malformation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1977; 129:1015-8. PubMed PMID: 413351.
Trapp RG, Breuer RI, Crampton AR, Davis JH, Derman RE, Larson RH, Victor TA. Pancreatic duct arteriovenous fistula and the metastatic fat necrosis syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 1979; 24:403-8. PubMed PMID: 456226.
Ponsky JL, Hoffman M, Rhodes RS. Arteriovenous fistula and portal hypertension secondary to islet-cell tumor of the pancreas. Surgery 1979; 85:408-11. PubMed PMID: 219555.
Gincul R, Dumortier J, Ciocirlan M, Adham M, Queneau PE, Ponchon T, Pilleul F. Treatment of arteriovenous malformation of the pancreas: a case report. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010; 22:116-20. PubMed PMID: 19687743.
Grasso, R. F., Cazzato, R. L., Luppi, G., Faiella, E., Del Vescovo, R., Giurazza, F., Zobel, B. B. (2012). Pancreatic arteriovenous malformation involving the duodenum embolized with ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (onyx). Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology, 35(4), 958-962
Sato M, Kishi K, Shirai S, Suwa K, Kimura M, Kawai N, Tanihata H, Yamada K, Terada M, Yamaue H. Radiation therapy for a massive arteriovenous malformation of the pancreas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003; 181:1627-8. PubMed PMID: 14627586.
Hayashi N, Sakai T, Kitagawa M, Inagaki R, Yamamoto T, Ishii Y, Maehara M, Nakagawara G. Intractable gastrointestinal bleeding caused by pancreatic arteriovenous malformation: successful treatment with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Eur J Radiol 1998; 28:164-6. PubMed PMID: 9788023.
Copyright (c) 2014 Anil Arora, Pankaj Tyagi, Vijendra Kirnake, Vikas Singla, Praveen Sharma, Naresh Bansal, Samarjit Singh Ghuman, Deepali Jain, Ashish Kumar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.