Alternative Arterial Reconstruction After Extended Pancreatectomy. Case Report and Some Considerations of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
Context The clinical benefits of distal pancreatectomy with en bloc celiac axis resection for locally advanced pancreatic body cancer remains controversial and, therefore, declared unresectable in most cases. Appleby first described extended distal pancreatectomy with celiac axis resection for locally advanced gastric cancer. Case report We report a case of a 65-year-old female who presented a locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma with infiltration of celiac axis. After radio-chemo neoadjuvant treatment, the patient underwent exploratory laparoscopy and subsequent distal pancreatectomy with en bloc resection of celiac axis. Arterial reconstruction was necessary as hepatic flow was not adequate, determined by intraoperative Doppler ultrasonography. It consisted of end to end anastomosis with prosthetic graft between hepatic artery directly to the aorta, as an atheromatous plaque was at the origin of the celiac axis. The postoperative course was uneventful with a perfect relief of pain. She presents a long term survival of 36 months, very exceptional for this type of disease. Conclusion The particularity of this case is not only the surgical treatment, rarely offered to these patients, but also and especially the subsequent vascular reconstruction. To our knowledge, this is the first report of this type of arterial reconstruction. Besides, we briefly discuss the recent advances in results of extended distal pancreatectomy with arterial resection for locally advanced pancreatic carcinoma.
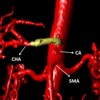
Image: 3D reconstruction with the stump of the celiac axis.
Downloads
References
Harrison LE, Klimstra DS, Brennan MF. Isolated portal vein involvement in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. A contraindication for resection? Ann Surg 1996; 224: 342-47.
Sasson AR, Hoffman JP, Ross EA, et al. En bloc resection for locally advanced cancer of the pancreas: is it worthwhile? J Gastrointest Surg 2002; 6: 147-157.
Tseng JF, Raut CP, Lee JE, el al. Pancreatoduodenectomy with vascular resection: margin status and survival duration. J Gastrointest Surg 2004; 8: 935-49.
Kondo S, Katoh H, Hirano S, et al. Results of radical distal pancreatectomy with en bloc resection of the celiac artery for locally advanced cancer of the pancreatic body. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2003; 388: 101-6.
Mollberg N, Rahbari NN, Koch M, et al. Arterial resection during pancreatectomy for pancreatic cancer. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Surg 2011; 254: 882-93.
Appleby LH. The coeliac axis in the expansion of the operation for gastric. Cancer 1953; 6: 704-7.
Mayumi T, Nimura Y, Kamiya, et al. Distal pancreatectomy with en bloc resection of the celiac artery for carcinoma of the body and tail of the pancreas. Int J Pancr 1997; 22: 15-21.
Gagandeep S, Artinyan A, Jabbour N, Mateo R, et al. Extended pancreatectomy with resection of the celiac axis: the modified Appleby operation. Am J Surg 2006; 192: 330-35.
Muller SA, Hartel A, Mehrabi A, et al. Vascular resection in pancreatic cáncer surgery: survival determinants. J Gastrointest Surg 2009; 13: 784-92.
Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, et al. Resected adenocarcinoma of the pancreas-616 patients: results, outcome, and prognostic indicators. J Gastrointest Surg 2000; 4: 567-79.
Almano H, Miura F, Toyota N, et al. Is pancreatectomy with arterial recontsruction a safe and useful procedure for locally advanced pancreatic cancer? J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2009; 16: 850-57
Denecke T, Andreou A, Podrabsky P, et al. Distal pancreatectomy with en bloc resection of the celiac trunk for extended pancreatic tumor disease: an interdisciplinary approach. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2010; 34: 1058-64
Hartwig W, Hackert T, Hinz T, et al. Multivisceral resection for pancreatic malignancies: risk-analysis and long-term outcome. Ann Surg 2009; 250: 81-7.
Wu X, Tao R, Lei R, et al. Distal pancreatectomy combined combined with celiac axis resection in treatment of carcinoma of the body/tail of the pancreas: a single-center experience. Ann Surg Oncol 2010; 17: 1359-66.
Goff SL, Chabot JA. A neoadjuvant strategy for the management of nonmetastatic pancreatic cancer. Cancer J 2012; 18: 602-8.
Duran H. Vicente E, Quijano Y, Ielpo B, et al Study of degree of tumor regression in resected adenocarcinoma of pancreas following a neoadjuvant treatment (Gemcitabine and Abraxane). Predictive value of the endosonographic elastography. 10th World congress of the IHPBA 2012; 104.
Yamamoto Y, Sakamoto Y, Ban D, et al. Is celiac axis resection justified for T4 pancreatic body cancer? Surgery 2012; 151: 61-9.
Kondo S, Katoh H, Shimizu T, Omi M, et al. Preoperative embolization of the common hepatic artery in preparation for radical pancreatectomy for pancreas body cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 2000; 47: 1447-9.
Tzakis AG, Gordon RD, Makowka L, et al. Clinical considerations in orthotopic liver transplantation. Radiol ClinNoth Am 1987; 25: 289-97.
Kondo S, Katoh H, Shimizu T, Omi M, et al. Radical distal pancreatectomy with en bloc resection of the celiac artery, plexus, and ganglions for advanced cancer of the pancreatic body: a preliminary report on perfect pain relief. JOP 2001; 2; 93-7.
Copyright (c) 2014 Benedetto Ielpo, Valentina Ferri, Riccardo Caruso, Hipolito Duran, Eduardo Diaz, Isabel Fabra, Catalina Oliva, Sergio Olivares, Yolanda Quijano, Emilio Vicente

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.