Pancreatic Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm Size Using CT Volumetry, Spherical and Ellipsoid Formulas: Validation Study
Abstract
Context The accuracy for determining pancreatic cyst volume with commonly used spherical and ellipsoid methods is unknown. The role of CT volumetry in volumetric assessment of pancreatic cysts needs to be explored. Objectives To compare volumes of the pancreatic cysts by CT volumetry, spherical and ellipsoid methods and determine their accuracy by correlating with actual volume as determined by EUS-guided aspiration. Setting This is a retrospective analysis performed at a tertiary care center. Patients Seventy-eight pathologically proven pancreatic cysts evaluated with CT and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) were included. Design The volume of fourteen cysts that had been fully aspirated by EUS was compared to CT volumetry and the routinely used methods (ellipsoid and spherical volume). Two independent observers measured all cysts using commercially available software to evaluate inter-observer reproducibility for CT volumetry. Main outcome measures The volume of pancreatic cysts as determined by various methods was compared using repeated measures analysis of variance. Bland-Altman plot and intraclass correlation coefficient were used to determine mean difference and correlation between observers and methods. The error was calculated as the percentage of the difference between the CT estimated volumes and the aspirated volume divided by the aspirated one. Results CT volumetry was comparable to aspirated volume (P=0.396) with very high intraclass correlation (r=0.891, P<0.001) and small mean difference (0.22 mL) and error (8.1%). Mean difference with aspirated volume and error were larger for ellipsoid (0.89 mL, 30.4%; P=0.024) and spherical (1.73 mL, 55.5%; P=0.004) volumes than CT volumetry. There was excellent inter-observer correlation in volumetry of the entire cohort (r=0.997, P<0.001). Conclusions CT volumetry is accurate and reproducible. Ellipsoid and spherical volume overestimate the true volume of pancreatic cysts.
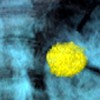
Image: 3-D CT image of a pancreatic tail mucinous cystic neoplasm
Downloads
References
Laffan TA, Horton KM, Klein AP, Berlanstein B, Siegelman SS, Kawamoto S, et al. Prevalence of unsuspected pancreatic cysts on MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008; 191:802-807. [PMID 18716113]
Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Falconi M, Shimizu M, et al. International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2006; 6:17-32. [PMID 16327281]
Sahani DV, Miller JC, del Castillo CF, Brugge WR, Thrall JH, Lee SI. Cystic pancreatic lesions: classification and management. J Am Coll Radiol 2009; 6:376-380. [PMID 19394581]
Allen PJ, D'Angelica M, Gonen M, Jaques DP, Coit DG, Jarnagin WR, et al. A selective approach to the resection of cystic lesions of the pancreas: results from 539 consecutive patients. Ann Surg 2006; 244:572-582. [PMID 16998366]
Singh AK, Hiroyuki Y, Sahani DV. Advanced postprocessing and the emerging role of computer-aided detection. Radiol Clin North Am 2009; 47:59-77. [PMID 19195534]
Buckler AJ, Mulshine JL, Gottlieb R, Zhao B, Mozley PD, Schwartz L. The Use of Volumetric CT as an Imaging Biomarker in Lung Cancer. Academic Radiology 2010; 17:100-106. [PMID 19969253]
Lee SM, Kim SH, Lee JM, Im S-A, Bang Y-J, Kim WH, et al. Usefulness of CT volumetry for primary gastric lesions in predicting pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. Abdominal Imaging 2008; 34:430-440. [PMID 18546037]
Mozley PD, Bendtsen C, Zhao B, Schwartz LH, Thorn M, Rong Y, et al. Measurement of Tumor Volumes Improves RECIST-Based Response Assessments in Advanced Lung Cancer. Translational oncology 2012; 5:19-25. [PMID 22348172]
Chalian H, Tochetto SM, Tore HG, Rezai P, Yaghmai V. Hepatic tumors: region-of-interest versus volumetric analysis for quantification of attenuation at CT. Radiology 2012; 262:853-861. [PMID 22357887]
Galizia MS, Tore HG, Chalian H, McCarthy R, Salem R, Yaghmai V. MDCT necrosis quantification in the assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma response to yttrium 90 radioembolization therapy: comparison of two-dimensional and volumetric techniques. Acad Radiol 2012; 19:48-54. [PMID 22054801]
Zhao B, Schwartz LH, Moskowitz CS, Ginsberg MS, Rizvi NA, Kris MG. Lung cancer: computerized quantification of tumor response--initial results. Radiology 2006; 241:892-898. [PMID 17114630]
Keil S, Plumhans C, Behrendt FF, Stanzel S, Suehling M, Muhlenbruch G, et al. Semi-automated quantification of hepatic lesions in a phantom. Invest Radiol 2009; 44:82-88. [PMID 19104439]
Aghaei Lasboo A, Rezai P, Yaghmai V. Morphological analysis of pancreatic cystic masses. Acad Radiol 2010; 17:348-351. [PMID 20005746]
Walsh RM, Zuccaro G, Dumot JA, Vargo J, Biscotti CV, Hammel J, Brown N. Predicting success of endoscopic aspiration for suspected pancreatic cystic neoplasms. JOP : Journal of the pancreas 2008; 9:612-617. [PMID 18762692]
Rkein A, Harrigal C, Friedman A, Persky D, Krupinski E. Comparison of the Accuracy of CT Volume Calculated by Circumscription to Prolate Ellipsoid Volume (Bidimensional Measurement Multiplied by Coronal Long Axis). Academic Radiology 2009; 16:181-186. [PMID 19124103]
Nishino M, Jagannathan JP, Ramaiya NH, Van den Abbeele AD. Revised RECIST Guideline Version 1.1: What Oncologists Want to Know and What Radiologists Need to Know. American Journal of Roentgenology 2010; 195:281-289. [PMID 20651182]
Marten K, Auer F, Schmidt S, Kohl G, Rummeny EJ, Engelke C. Inadequacy of manual measurements compared to automated CT volumetry in assessment of treatment response of pulmonary metastases using RECIST criteria. Eur Radiol 2006; 16:781-790. [PMID 16331462]
Keil S, Behrendt FF, Stanzel S, Suhling M, Koch A, Bubenzer J, et al. Semi-automated measurement of hyperdense, hypodense and heterogeneous hepatic metastasis on standard MDCT slices. Comparison of semi-automated and manual measurement of RECIST and WHO criteria. Eur Radiol 2008; 18:2456-2465. [PMID 18523775]
Instruments M. Particle size and shape measurement. Malvern Instruments. http://www.fei.com/uploadedFiles/ Documents/Content/particle_morphology.pdf
Kimura W, Nagai H, Kuroda A, Muto T, Esaki Y. Analysis of small cystic lesions of the pancreas. Int J Pancreatol 1995; 18:197-206. [PMID 8708390]
Fritz S, Klauss M, Bergmann F, Hackert T, Hartwig W, Strobel O, et al. Small (Sendai negative) branch-duct IPMNs: not harmless. Ann Surg. 2012; 256:313-320. [PMID 22791105]
Sahani DV, Kadavigere R, Saokar A, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Brugge WR, Hahn PF. Cystic pancreatic lesions: a simple imaging-based classification system for guiding management. Radiographics 2005; 25:1471-1484. [PMID 16284129]
Pitman MB, Lewandrowski K, Shen J, Sahani D, Brugge W, Fernandez-del Castillo C. Pancreatic cysts: preoperative diagnosis and clinical management. Cancer Cytopathol 2010; 118:1-13. [PMID 20043327]
Jaffe CC. Measures of response: RECIST, WHO, and new alternatives. J Clin Oncol 2006; 24:3245-3251. [PMID 16829648]
van Klaveren RJ, Aerts JG, de Bruin H, Giaccone G, Manegold C, van Meerbeeck JP. Inadequacy of the RECIST criteria for response evaluation in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2004; 43:63-69. [PMID 14698538]
Gietema HA, Wang Y, Xu D, van Klaveren RJ, de Koning H, Scholten E, et al. Pulmonary nodules detected at lung cancer screening: interobserver variability of semiautomated volume measurements. Radiology 2006; 241:251-257. [PMID 16908677]
Buerke B, Puesken M, Muter S, Weckesser M, Gerss J, Heindel W, Wessling J. Measurement accuracy and reproducibility of semiautomated metric and volumetric lymph node analysis in MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2010; 195:979-985. [PMID 20858828]
Wormanns D, Kohl G, Klotz E, Marheine A, Beyer F, Heindel W, Diederich S. Volumetric measurements of pulmonary nodules at multi-row detector CT: in vivo reproducibility. Eur Radiol 2004; 14:86-92. [PMID 14615902]
Revel MP, Lefort C, Bissery A, Bienvenu M, Aycard L, Chatellier G, Frija G. Pulmonary nodules: preliminary experience with three-dimensional evaluation. Radiology 2004; 231:459-466. [PMID 15128991]
Gavrielides MA, Kinnard LM, Myers KJ, Petrick N. Noncalcified lung nodules: volumetric assessment with thoracic CT. Radiology 2009; 251:26-37. [PMID 19332844]
Goodman LR, Gulsun M, Washington L, Nagy PG, Piacsek KL. Inherent variability of CT lung nodule measurements in vivo using semiautomated volumetric measurements. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2006; 186:989-994. [PMID 16554568]
Das M, Muhlenbruch G, Katoh M, Bakai A, Salganicoff M, Stanzel S, et al. Automated volumetry of solid pulmonary nodules in a phantom: accuracy across different CT scanner technologies. Invest Radiol 2007; 42:297-302. [PMID 17414525]
Honda O, Sumikawa H, Johkoh T, Tomiyama N, Mihara N, Inoue A, et al. Computer-assisted lung nodule volumetry from multi-detector row CT: influence of image reconstruction parameters. Eur J Radiol 2007; 62:106-113. [PMID: 17161571]
Yoon SH, Lee JM, Cho JY, Lee KB, Kim JE, Moon SK, et al. Small (= 20 mm) pancreatic adenocarcinomas: analysis of enhancement patterns and secondary signs with multiphasic multidetector CT. Radiology 2011; 259:442-452. [PMID 21406627]
Ogawa H, Itoh S, Nagasaka T, Suzuki K, Ota T, Naganawa S. CT findings of intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct: assessment with multiphase contrast-enhanced examination using multi-detector CT. Clinical radiology 2012; 67:224-231. [PMID 21944774]
Leung KK, Ross WA, Evans D, Fleming J, Lin E, Tamm EP, Lee JH. Pancreatic cystic neoplasm: the role of cyst morphology, cyst fluid analysis, and expectant management. Ann Surg Oncol 2009; 16:2818-2824. [PMID 19536601]
Sadakari Y, Ienaga J, Kobayashi K, Miyasaka Y, Takahata S, Nakamura M, et al. Cyst size indicates malignant transformation in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas without mural nodules. Pancreas 2010; 39:232-236. [PMID 19752768]
Bose D, Tamm E, Liu J, Marcal L, Balachandran A, Bhosale P, et al. Multidisciplinary management strategy for incidental cystic lesions of the pancreas. J Am Coll Surg 2010; 211:205-215. [PMID 20670858]
Copyright (c) 2014 Hamid Chalian, Adeel Rahim Seyal, Pedram Rezai, Hüseyin Gürkan Töre, Frank H Miller, David J Bentrem, Vahid Yaghmai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.