Microenvironmental Factors and Extracellular Matrix Degradation in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
Pancreatic cancer is a devastating malady with proclivity for early metastasis, accounting for its poor prognosis. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, the most common type of pancreatic malignancy, exhibits an over-expression of several growth factors such as epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor beta, which correlate with a decrease in patient survival. These growth factors as well as hypoxia-reoxygenation conditions have been shown to increase pancreatic tumor cell invasiveness. This review will focus on the signaling pathways used by these distinct microenvironmental factors to promote extracellular matrix degradation and invasion by pancreatic tumor cells.
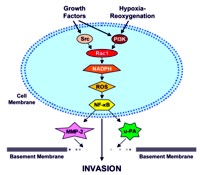
Image: Model for Rac1/ROS/NF-κB-mediated pancreatic cancer invasion.
Downloads
References
Raimondi S, Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: an overview. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009; 6:699-708. [PMID:19806144].
Collins A, Bloomston M. Diagnosis and management of pancreatic cancer. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol 2009; 55:445-54. [PMID:19942828].
Korc M. Pancreatic cancer-associated stroma production. Am J Surg 2007; 194:S84-6. [PMID:17903452].
Spano D, Zollo M. Tumor microenvironment: a main actor in the metastasis process. Clin Exp Metastasis 2012; 29:381-95. [PMID:22322279].
Wilson JS, Pirola RC, Apte MV. Stars and stripes in pancreatic cancer: role of stellate cells and stroma in cancer progression. Front Physiol 2014; 5:52. [PMID:24592240].
Coffelt SB, Lewis CE, Naldini L, Brown JM, Ferrara N, De Palma M. Elusive identities and overlapping phenotypes of proangiogenic myeloid cells in tumors. Am J Pathol 2010; 176:1564-76. [PMID:20167863].
DeNardo DG, Andreu P, Coussens LM. Interactions between lymphocytes and myeloid cells regulate pro- versus anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2010; 29:309-16. [PMID:20405169].
Theoharides TC, Alysandratos KD, Angelidou A, Zhang B. Mast Cells and Tumor Microenvironment. In: Bagley RG, ed. The Tumor Microenvironment, Cancer Drug Discovery and Development. Chapter 17. Springer Science+Business Media, 2010:353-70.
Carpenter G, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem 1990; 265:7709-12. [PMID:2186024].
Ciardiello F, Tortora G. EGFR antagonists in cancer treatment. N Engl J Med 2008; 358:1160-74. [PMID:18337605].
Mimeault M, Brand RE, Sasson AA, Batra SK. Recent advances on the molecular mechanisms involved in pancreatic cancer progression and therapies. Pancreas 2005; 31:301-16. [PMID:16258363].
Wang Z, Sengupta R, Banerjee S, Li Y, Zhang Y, Rahman KM, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein inhibits cell growth and invasion in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 2006; 66:7653-60. [PMID:].
Uegaki K, Nio Y, Inoue Y, Minari Y, Sato Y, Song MM, et al. Clinicopathological significance of epidermal growth factor and its receptor in human pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res 1997; 17:3841-7. [PMID:16885366].
Yeh TS, Jan YY, Chiu CT, Ho YB, Chen TC, Lee KF, et al. Characterisation of oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, trefoil factor 1, and epidermal growth factor and its receptor in pancreatic cystic neoplasms and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gut 2002; 51:712-6. [PMID:12377812].
Pryczynicz A, Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, Kemona A, Czyzewska J. Expression of EGF and EGFR strongly correlates with metastasis of pancreatic ductal carcinoma. Anticancer Res 2008; 28:1399-404. [PMID:18505086].
Massague J. TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell 2008; 134:215-30. [PMID:18662538].
Friess H, Yamanaka Y, Büchler MW, Korc M. Enhanced expression of transforming growth factor-beta isoforms in human pancreatic cancer correlates with decreased survival. Gastroenterology 1993; 105:1846-56. [PMID:8253361].
Doi K, Horiuchi T, Uchinami M, Tabo T, Kimura N, Yokomachi J, et al. Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion promotes liver metastasis of colon cancer. J Surg Res 2002; 105:243-7. [PMID:12121713].
Man K, Ng KT, Lo CM, Ho JW, Sun BS, Sun CK, et al. Ischemia-reperfusion of small liver remnant promotes liver tumor growth and metastases--activation of cell invasion and migration pathways. Liver Transpl 2007; 13:1669-77. [PMID:18044786].
Nicoud IB, Jones CM, Pierce JM, Earl TM, Matrisian LM, Chari RS, Gorden DL. Warm hepatic ischemia-reperfusion promotes growth of colorectal carcinoma micrometastases in mouse liver via matrix metalloproteinase-9 induction. Cancer Res 2007; 67:2720-8. [PMID:17363593].
Rofstad EK. Microenvironment-induced cancer metastasis. Int J Radiat Biol 2000; 76:589-605. [PMID:10866281].
Chaplin DJ, Hill SA. Temporal heterogeneity in microregional erythrocyte flux in experimental solid tumours. Br J Cancer 1995; 71:1210-3. [PMID:].
Bennewith KL, Durand RE. Quantifying transient hypoxia in human tumor xenografts by flow cytometry. Cancer Res 2004; 64:6183-9. [PMID:7779713].
Braun RD, Lanzen JL, Dewhirst MW. Fourier analysis of fluctuations of oxygen tension and blood flow in R3230Ac tumors and muscle in rats. Am J Physiol 1999; 277:H551-68. [PMID:10444480].
Chi JT, Wang Z, Nuyten DS, Rodriguez EH, Schaner ME, Salim A, et al. Gene expression programs in response to hypoxia: cell type specificity and prognostic significance in human cancers. PLoS Med 2006; 3:e47. [PMID:16417408].
Jiang BH, Rue E, Wang GL, Roe R, Semenza GL. Dimerization, DNA binding, and transactivation properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 1996; 271:17771-8. [PMID:8663540].
Wenger RH. Mammalian oxygen sensing, signaling and gene regulation. J Exp Biol 2000; 203:1253-63. [PMID:10729275].
Zhao X, Gao S, Ren H, Sun W, Zhang H, Sun J, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis by activating transcription of the actin-bundling protein fascin. Cancer Res 2014; 74:2455-64. [PMID:24599125].
Xu YF, Yu SN, Lu ZH, Liu JP, Chen J. Fascin promotes the motility and invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2011; 17:4470-8. [PMID:22110277].
Zhu H, Wang D, Liu Y, Su Z, Zhang L, Chen F, et al. Role of the Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha induced autophagy in the conversion of non-stem pancreatic cancer cells into CD133+ pancreatic cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Cell Int 2013; 13:119. [PMID:24505593].
Herreros-Villanueva M, Bujanda L, Billadeau DD, Zhang JS. Embryonic stem cell factors and pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20:2247-54. [PMID:24605024].
Li L, Hao X, Qin J, Tang W, He F, Smith A, et al. Antibody Against CD44s Inhibits Pancreatic Tumor Initiation and Postradiation Recurrence in Mice. Gastroenterology 2014; 146:1108-18. [PMID:24397969].
Bao B, Azmi A, Aboukameel A, Ahmad A, Bolling-Fischer A, Sethi S, et al. Pancreatic cancer stem-like cells display aggressive behavior mediated via activation of FoxQ1. J Biol Chem 2014. [PMID:24719318].
Matthews CP, Colburn NH, Young MR. AP-1 a target for cancer prevention. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2007; 7:317-24. [PMID:17979626].
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR, Li ZW. NF-kappaB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2:301-10. [PMID:12001991].
Björklund M, Koivunen . Gelatinase-mediated migration and invasion of cancer cells, Biochim Biophys Acta 2005; 1755:37-69. [PMID:15907591].
Itoh T, Tanioka M, Yoshida H, Yoshioka T, Nishimoto H, Itohara S. Reduced angiogenesis and tumor progression in gelatinase A-deficient mice. Cancer Res 1998; 58:1048-51. [PMID:9500469].
Yamagata S, Yoshii Y, Suh JG, Tanaka R, Shimizu S. Occurrence of an active form of gelatinase in human gastric and colorectal carcinoma tissues. Cancer Lett 1991; 59:51-5. [PMID:1652352].
Brown PD, Bloxidge RE, Stuart NS, Gatter KC, Carmichael J. Association between expression of activated 72-kilodalton gelatinase and tumor spread in non-small-cell lung carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 1993; 85:574-8. [PMID:8384265].
Gress TM, Muller-Pillasch F, Lerch MM, Friess H, Büchler M, Adler G. Expression and in situ localization of genes coding for extracellular matrix proteins and extracellular matrix degrading proteases in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 1995; 62:407-13. [PMID:7635566].
Koshiba T, Hosotani R, Wada M, Miyamoto Y, Fujimoto K, Lee JU, et al. Involvement of matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity in invasion and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer 1998; 82:642-50. [PMID:9477095].
Ellenrieder V, Alber B, Lacher U, Hendler SF, Menke A, Boeck W, et al. Role of MT-MMPs and MMP-2 in pancreatic cancer progression. Int J Cancer 2000; 85:14-20. [PMID:10585576].
Rauvala M, Aglund K, Puistola U, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T, Horvath G, Willén R, Stendahl U. Matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9 in cervical cancer: different roles in tumor progression. Int J Gynecol Cancer 2006; 16:1297-302. [PMID:16803520].
Jinga DC, Blidaru A, Condrea I, Ardeleanu C, Dragomir C, Szegli G, et al. MMP-9 and MMP-2 gelatinases and TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 inhibitors in breast cancer: correlations with prognostic factors. J Cell Mol Med 2006; 10:499-510. [PMID:16796815].
Nguyen DH, Hussaini IM, Gonias SL. Binding of urokinase-type plasminogen activator to its receptor in MCF-7 cells activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 which is required for increased cellular motility. J Biol Chem 1998; 273:8502-7. [PMID:9525964].
Aguirre Ghiso JA, Kovalski K, Ossowski L. Tumor dormancy induced by down-regulation of urokinase receptor in human carcinoma involves integrin and MAPK signaling. J Cell Biol 1999; 147:89-104. [PMID:10508858].
Mignatti P, Rifkin DB. Plasminogen activators and matrix metalloproteinases in angiogenesis. Enzyme Protein 1996; 49:117-37. [PMID:8797002].
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Dewerchin M, Rosenberg S, Herbert JM, Lupu F, Collen D. Receptor-independent role of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in pericellular plasmin and matrix metalloproteinase proteolysis during vascular wound healing in mice. J Cell Biol 1998; 140:233-45. [PMID:9425170].
Paciucci R, Vila MR, Adell T, Díaz VM, Torà M, Nakamura T, Real FX. Activation of the urokinase plasminogen activator/urokinase plasminogen activator receptor system and redistribution of E-cadherin are associated with hepatocyte growth factor-induced motility of pancreas tumor cells overexpressing Met. Am J Pathol 1998; 153:201-12. [PMID:9665481].
Takeuchi Y, Nakao A, Harada A, Nonami T, Fukatsu T, Takagi H. Expression of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in human pancreatic carcinoma: immunohistochemical study. Am J Gastroenterol 1993; 88:1928-33. [PMID:8237943].
Cantero D, Friess H, Deflorin J, Zimmermann A, Bründler MA, Riesle E, et al. Enhanced expression of urokinase plasminogen activator and its receptor in pancreatic carcinoma. Br J Cancer 1997; 75:388-95. [PMID:9020484].
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 2002; 420:629-35. [PMID:12478284].
Kim KS, Takeda K, Sethi R, Pracyk JB, Tanaka K, Zhou YF, et al. Protection from reoxygenation injury by inhibition of rac1. J Clin Invest 1998; 101:1821-6. [PMID:9576744].
Ng CK, Deshpande SS, Irani K, Alevriadou BR. Adhesion of flowing monocytes to hypoxia-reoxygenation-exposed endothelial cells: role of Rac1, ROS, and VCAM-1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2002; 283:93-102. [PMID:12055077].
Ozaki M, Deshpande SS, Angkeow P, Bellan J, Lowenstein CJ, Dinauer MC, et al. Inhibition of the Rac1 GTPase protects against nonlethal ischemia/reperfusion-induced necrosis and apoptosis in vivo. FASEB J 2000; 14:418-29. [PMID:10657998].
Ozaki M, Deshpande S, Angkeow P, Bellan J, Lowenstein CJ, Dinauer MC, et al. Targeted inhibition of the small GTPase protects against ischemia/reperfusion liver injury in mice, Transplant Proc 2001; 33:863-4. [PMID:11267105].
Harada N, Iimuro Y, Nitta T, Yoshida M, Uchinami H, Nishio T, et al. Inactivation of the small GTPase Rac1 protects the liver from ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. Surgery 2003; 134:480-91. [PMID:14555937].
Bosco EE, Mulloy JC, Zheng Y. Rac1 GTPase: a "Rac" of all trades. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009; 66:370-4. [PMID:19151919].
Heid I, Lubeseder-Martellato C, Sipos B, Mazur PK, Lesina M, Schmid RM, Siveke JT. Early requirement of Rac1 in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2001; 141:719-30. [PMID:21684285].
Yeh MW, Rougier JP, Park JW, Duh QY, Wong M, Werb Z, Clark OH. Differentiated thyroid cancer cell invasion is regulated through epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent activation of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2/gelatinase A. Endocr Relat Cancer 2006; 13:1173-83. [PMID:17158762].
Staun-Ram E, Goldman S, Gabarin D, Shalev E. Expression and importance of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 (MMP-2 and -9) in human trophoblast invasion. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 2004; 2:59-72. [PMID:15294019].
Binker MG, Binker-Cosen AA, Richards D, Oliver B, Cosen-Binker L. EGF promotes invasion by PANC-1 cells through Rac1/ROS-dependent secretion and activation of MMP-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009; 379:445-50. [PMID:19116140].
Ellenrieder V, Hendler SF, Ruhland C, Boeck W, Adler G, Gress TM. TGF-beta-induced invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells is mediated by matrix metalloproteinase-2 and the urokinase plasminogen activator system. Int J Cancer. 2001; 93:204-11. [PMID:11410867].
Teraoka H, Sawada T, Yamashita Y, Nakata B, Ohira M, Ishikawa T, et al. TGF-beta1 promotes liver metastasis of pancreatic cancer by modulating the capacity of cellular invasion. Int J Oncol 2001; 19:709-15. [PMID:11562745].
Binker MG, Binker-Cosen AA, Gaisano HY, de Cosen RH, Cosen-Binker LI. TGF-β1 increases invasiveness of SW1990 cells through Rac1/ROS/NF-κB/IL-6/MMP-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2011; 405:140-5. [PMID:21219858].
Binker MG, Binker-Cosen AA, Richards D, Gaisano HY, de Cosen RH, Cosen-Binker LI. Hypoxia-reoxygenation increase invasiveness of PANC-1 cells through Rac1/MMP-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2010; 393:371-6. [PMID:20153729].
Veit C, Genze F, Menke A, Hoeffert S, Gress TM, Gierschik P, Giehl K. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase is required for glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor-induced migration and invasion of pancreatic carcinoma cells Cancer Res 2004; 64:5291-300. [PMID:15289335].
Ito H, Gardner-Thorpe J, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, Whang EE. Inhibition of tyrosine kinase Src suppresses pancreatic cancer invasiveness. Surgery 2003; 134:221-6. [PMID:12947321].
Wu WS. The signaling mechanism of ROS in tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2006; 25:695-705. [PMID:17160708].
Vaquero EC, Edderkaoui M, Pandol SJ, Gukovsky I, Gukovskaya AS Reactive oxygen species produced by NAD(P)H oxidase inhibit apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2004; 279:34643-54. [PMID:15155719].
Liu J, Ben QW, Yao WY, Zhang JJ, Chen DF, He XY, et al. BMP2 induces PANC-1 cell invasion by MMP-2 overexpression through ROS and ERK. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2012; 17:2541-9. [PMID:22652796].
Li W, Ma Q, Li J, Guo K, Liu H, Han L, Ma G. Hyperglycemia enhances the invasive and migratory activity of pancreatic cancer cells via hydrogen peroxide. Oncol Rep 2011; 25:1279-87. [PMID:21249318].
Kim MH, Yoo HS, Kim MY, Jang HJ, Baek MK, Kim HR, et al. Helicobacter pylori stimulates urokinase plasminogen activator receptor expression and cell invasiveness through reactive oxygen species and NF-kappaB signaling in human gastric carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med 2007; 19:689-97. [PMID:17334646].
Tobar N, Villar V, Santibanez JF. ROS-NFkappaB mediates TGF-beta1-induced expression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator, matrix metalloproteinase-9 and cell invasion. Mol. Cell. Biochem 2010; 340:195-202. [PMID:20204677].
Li L, Gondi CS, Dinh DH, Olivero WC, Gujrati M, Rao JS. Transfection with anti p65 intrabody suppresses invasion and angiogenesis in glioma cells by blocking nuclear factor-kappaB transcriptional activity. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13:2178-90. [PMID:17404102].
Tanno S, Mitsuuchi Y, Altomare DA, Xiao GH, Testa JR. AKT activation up-regulates insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression and promotes invasiveness of human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 2001; 61:589-93. [PMID:11212254].
Bauer TW, Liu W, Fan F, Camp ER, Yang A, Somcio RJ, Bucana et al. Targeting of urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in human pancreatic carcinoma cells inhibits c-Met- and insulin-like growth factor-I receptor-mediated migration and invasion and orthotopic tumor growth in mice. Cancer Res 2005; 65:7775-81. [PMID:16140945].
Hezel AF, Kimmelman AC, Stanger BZ, Bardeesy N, DePinho RA. Genetics and biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Genes & Dev 2006; 20:1218-49. [PMID:16702400].
Copyright (c) 2014 Marcelo G Binker, Makena J Binker-Cosen, Andres A Binker-Cosen, Laura I Cosen-Binker

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.