Pancreatico-Pleural and Bronchial Fistulae and Associated Pseudocysts: Case Series
Abstract
Context Pancreatico-pleural fistula is rare complication of chronic or acute pancreatitis. Previous studies have reported imaging features and various management options of this condition including conservative/medical management, endoscopic treatments and surgery.This article reviews the myriad of imaging appearances of this condition in multimodality imaging and different strategies for the successful management in a short case series. Methods After obtaining the institutional ethics committee approval, retrospective review of the medical records of five patients of pancreatico-pleural fistulae who were diagnosed and successfully managed in our hospital in 2012 and 2013 was done. Follow up with out patient records of these patients was also included.Findings were compared with the current available literature on this entity. Results and discussion Pancreatico-pleural fistulae presents with massive pleural effusion.A high index of suspicion is essential for accurate diagnosis. Demonstration of the fistulous tracts requires cross sectional imaging with contrast enhanced CT being most commonly used and affords accurate diagnosis. MRI demonstrates the tracts and ductal disruptions with greater detail and are helpful in confirming the CT findings. Endoscopic ultrasound and ERCP also offer potential of diagnosis, although being technically demanding and invasive is reserved for interventions. Management of these conditions should be initially conservative with endoscopic stenting being offered in selected cases with favourable anatomy and not responding to conservative management. Surgery is reserved for cases not responding to conservative and endoscopic management. Conclusion In conclusion this case series highlights the clinical and imaging spectrum of pancreatico-pleural fistulae and provides insight into the different management strategies that can be adopted for this condition.
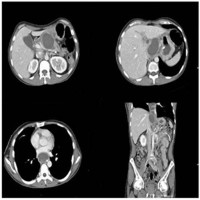
Image: Expansion of the fistulous tract at CT.
Downloads
References
Tombroff M, Loicq A, De Koster JP, Engleholm L, Govaerts JP. Pleural effusion with pancreaticopleural fistula. Br Med J. 1973; 1: 330-331. [PMID: 4685624].
Sakurai T, Fujiyama R, Ohnishi H, Tada K, Tomioka H, Sakamoto H, Iwasaki H, Aoki M. Pancreatic pleural effusion accompanied by bronchopleural fistula. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 1999; 37: 662-666. [PMID: 10496109].
Balasubramanian P, Jeyamani R, Govil S, Chacko A, Kurian G, Subhash HS, Govil S, Thomas K. Pancreatico-pericardial fistula: a rare complication of chronic pancreatitis. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2004; 23: 31-32. [PMID: 15106719].
Poddar U, Kochhar R, Singh A, Nagi B, Singh K. Pancreatico-pleural fistula: successful treatment with octreotide. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1995; 14: 145-146. [PMID: 8868358].
Safadi BY, Marks JM. Pancreatic-pleural fistula: the role of ERCP in diagnosis and treatment. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 51:213-215. [PMID: 10650272].
Machado NO. Pancreaticopleural Fistula: Revisited. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2012. [PMC: 815476].
Dhebri AR, Ferran N. Nonsurgical Management of Pancreaticopleural Fistula. J Pancreas. 2005; 6: 152-161.
Rockey DC, Cello JP. Pancreaticopleural fistula: report of 7 patients and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 1990; 69: 332-344. [PMID: 2233231].
Wronski M, Slodkowski M, Cebulski W, Moronczyk D, Krasnodebski IW. Optimizing management of pancreaticopleural fistulas. World J Gastroenterol. 2011; 17: 4696–4703. [PMC: 3233676].
Lerch MM, Stier A, Wahnschaffe U, Mayerle J. Pancreatic pseudocysts: observation, endoscopic drainage, or resection? Dtsch Arztebl Int 2009; 106: 614-621. [PMID: 19890418].
Aabakken L, Chittom P, McKay DC, Uflacker R, Wilson FA. Percutaneous drainage of a mediastinal pancreatic pseudocyst: a paraspinal, extrapleural CT-guided approach. J Vasc Interv Radiol 1997; 8: 283-285. [PMID: 9083998].
Jacobson BC, Baron TH, Adler DG, Davila RE, Egan J, Hirota WK, Leighton JA, Qureshi W, et al. ASGE guideline: the role of endoscopy in the diagnosis and the management of cystic lesions and inflammatory fluid collections of the pancreas. Gastrointest endosc. 2005; 61: 363-370. [PMID: 15758904].
Amer K, Mahesh B, Ascione R. Pedicled intercostal muscle flap: a simple technique of closing pancreatico-pleural fistula from a thoracic approach. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002; 22: 831-832. [PMID: 12414056].
King JC, Reber HA, Shiraga S, Hines OJ. Pancreatic-pleural fistula is best managed by early operative intervention. Surgery. 2010; 147: 154-159. [PMID: 19744435].
Copyright (c) 2014 Salil Pandey, Shiran A Shetty, Krishnaveni Janarthanan, Devanand Balalakshmoji, Kamal K Sen, Venkat Leelakrishnan

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.