Predictors of Malignancy in Branch Duct Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of the Pancreas
Abstract
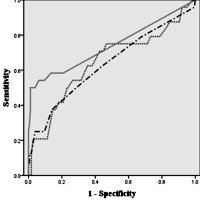
Objective Indication of surgery for branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (BD-IPMN) proposed by the consensus guidelines revised in 2012 was too complex to refer to in clinical practice. This study aimed to identify simple predictors of malignancy in BD-IPMN. Methods Consecutive 202 patients with BD-IPMNs were enrolled. They comprised 35 patients that underwent surgery and 167 that were followed up without surgery by being regarded as benign neoplasms. Cutoff values of cyst size, main pancreatic duct (MPD) diameter, and mural nodule size were determined by receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve. Factors that may discriminate benign from malignant BD-IPMNs were analyzed by multivariate logistic regression model. Results Cutoff values of cyst size, MPD diameter, and mural nodule size were determined to be 30 mm, 6 mm, and 10 mm, respectively. Multivariate analysis demonstrated that mural nodule ≥10 mm (OR 198, 95% CI 23.1-1690, P<0.0001) and positive cytology (OR 634, 95% CI 49.1-8,190, P<0.0001) were predictors of malignancy in BD-IPMN. When BD-IPMNs with mural nodules ≥10 mm or positive cytology were diagnosed as malignant, sensitivity, specificity, and overall accuracy were 88%, 98%, and 97%, respectively. Conclusions Mural nodule ≥10mm and positive cytology were demonstrated to be simple predictors of malignancy in BD-IPMN.
Image: ROC curves of cyst size, main pancreatic duct diameter, and nodule size.
Downloads
References
Hruban RH, Takaori K, Klimstra DS, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J, Biankin AV, Biankin SA, Compton C, et al. An illustrated consensus on the classification of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs). Am J Surg Pathol. 2004; 28: 977-987. [PMID: 15252303].
Ohhashi K, Murakami Y, Maruyama M. Four cases of mucous secreting pancreatic cancer [in Japanese]. Prog Dig Endosc. 1982; 20: 348-351.
Adsay NV, Kloppel G, Fukushima N, et al. Intraductal neoplasms of the pancreas. In: World Health Organization classification of tumours of the digestive system. 2010; 304-310.
Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Falconi M, Shimizu M, Yamaguchi K, Yamao K, et al. International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2006; 6:17–32. [PMID: 16327281].
Pelaez-Luna M, Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Takahashi N, Clain JE, Levy MJ, Pearson RK, et al. Do consensus indications for resection in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm predict malignancy? A study of 147 patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:1759–1764. [PMID: 17686073].
Tang RS, Weinberg B, Dawson DW, Reber H, Hines OJ, Tomlinson JS, Chaudhari V, Raman S, Farrell JJ. Evaluation of the guidelines for management of pancreatic branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008; 6: 815-819. [PMID: 18602036].
Woo SM, Ryu JK, Lee SH, Yoon WJ, Kim YT, Yoon YB. Branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms in a retrospective series of 190 patients. Br J Surg. 2009; 96: 405–411. [PMID: 19283746].
Tanaka M, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Adsay V, Chari S, Falconi M, Jang JY, Kimura W, et al. International consensus guidelines 2012 for the management of IPMN and MCN of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2012; 12: 183–197. [PMID: 22687371].
Sugiyama M, Izumisato Y, Abe N, Masaki T, Mori T, Atomi Y. Predictive factors for malignancy in intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas. Br J Surg. 2003; 90: 1244- 1249. [PMID: 14515294].
Serikawa M, Sasaki T, Fujimoto Y, Kuwahara K, Chayama K. Management of intraductal papillary- mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: treatment strategy based on morphologic classification. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2006; 40: 856-862. [PMID: 17016145].
Schmidt CM, White PB, Waters JA, Yiannoutsos CT, Cummings OW, Baker M, Howard TJ, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Predictors of malignant and invasive pathology. Ann Surg. 2007; 246: 644-654. [PMID: 17893501].
Rodriguez JR, Salvia R, Crippa S, Warshaw AL, Bassi C, Falconi M, Thayer SP, et al. Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: observations in 145 patients who underwent resection. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133: 72-79. [PMID: 17631133].
Schnelldorfer T, Sarr MG, Nagorney DM, Zhang L, Smyrk TC, Qin R, Chari ST, Farnell MB. Experience with 208 resections for Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Arch Surg. 2008; 143: 639-646. [PMID: 18645105].
Mimura T, Masuda A, Matsumoto I, Shiomi I, Yoshida S, Sugimoto M, Sanuki T, et al. Predictors of malignant intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010; 44: 224-229. [PMID: 20453661].
Akita H, Takeda Y, Hoshino H, Wada H, Kobayashi S, Marubashi S, Eguchi H, et al. Mural nodule in branch duct-type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas is a marker of malignant transformation and indication for surgery. Am J Surg. 2011; 202: 214–219. [PMID: 21376305].
Uehara H, Ishikawa O, Katayama K, Kawada N, Ikezawa K, Fukutake N, Takakura R, et al. Size of mural nodule as an indicator of surgery for branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas during follow-up. J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46: 657–663. [PMID: 21085997].
Kim KW, Park SH, Pyo J, Yoon SH, Byun JH, Lee MG, Krajewski KM, Ramaiya NH. Imaging features to distinguish malignant and benign branch-duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. A meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 2014; 259: 72–81. [PMID: 23657084].
Kubo H, Chijiiwa Y, Akahoshi K, Hamada S, Harada N, Sumii T, Takashima M, Nawata H. Intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas: differential diagnosis between benign and malignant tumors by endoscopic ultrasonography. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001; 96: 1429-1434. [PMID: 11374678].
Choi BS, Kim TK, Kim AY, Kim KW, Park SW, Kim PN, Ha HK, Lee MG, Kim SC. Differential diagnosis of benign and malignant intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas: MR cholangiopancreatography and MR angiography. Korean J Radiol. 2003; 4: 157- 162. [PMID: 14530644].
Kawai M, Uchiyama K, Tani M, Onishi H, Kinoshita H, Ueno M, Hama T, Yamaue H. Clinicopathological features of malignant intraductal papillary mucinous tumors of the pancreas: the differential diagnosis from benign entities. Arch Surg. 2004; 139: 188-192. [PMID: 14769579].
Ogawa H, Itoh S, Ikeda M, Suzuki K, Naganawa S. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas: assessment of the likelihood of invasiveness with multisection CT. Radiology. 2008; 248: 876–886. [PMID: 18632526].
Shimizu Y, Yamaue H, Maguchi H, Yamao K, Hirono S, Osanai M, Hijioka S, et al. Predictors of malignancy in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Analysis of 310 pancreatic resection patients at multiple high-volume centers. Pancreas. 2013; 42: 883-888. [PMID: 23508017].
Kobayashi N, Sugimori K, Shimamura T, Hosono K, Watanabe S, Kato S, Ueda M, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonographic findings predict the risk of carcinoma in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2012;12: 141-145. [PMID: 22487524].
Hirono S, Tani M, Kawai M, Okada K, Miyazawa M, Shimizu A, Kitahata Y, Yamaue H. The carcinoembryonic antigen level in pancreatic juice and mural nodule size are predictors of malignancy for branch duct type intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Ann Surg. 2012; 255: 517–522. [PMID: 22301608].
Zhang HM, Yao F, Liu GF, Wang XB, Xiu DH, Gen I. The differences in imaging features of malignant and benign branch duct type of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor. Eur J Radiol. 2011; 80: 744-748. [PMID: 21454028].
Uehara H, Nakaizumi A, Iishi H, Tatsuta M, Kitamra T, Okuda S, Ohigashi H, et al. Cytologic examination of pancreatic juice differential diagnosis of benign and malignant mucin-producing tumors of the pancreas. Cancer 1994; 74: 826-833. [PMID: 8039110].
Uehara H, Nakaizumi A, Tatsuta M, Iishi H, Kitamura T, Ohigashi H, Ishikawa O, Takenaka A. Diagnosis of carcinoma in situ of the pancreas by peroral pancreatoscopy and pancreatoscopic cytology. Cancer. 1997; 79: 454-461. [PMID: 9028354].
Murakami Y, Uemura K, Hayashidani Y, Sudo T, Sueda T. Predictive factors of malignant or invasive intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. J Gastrointest Surg. 2007; 11: 338–344. [PMID: 17458608].
Yamaguchi T, Shira Y, Ishiharai T, Sudo K, Nakagawa A, Ito H, Miyazaki M, Nomura F, Saisho H. Pancreatic juice cytology in the diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Cancer. 2005; 104: 2830-2836. [PMID: 16287152].
Yamaguchi K, Nakamura M, Shirahane K, Kawamoto M, Konomi H, Ohta M, Tanaka M. Pancreatic juice cytology in IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology. 2005; 5: 416-421. [PMID: 15985766].
Ohtsuka T, Kono H, Nagayoshi Y, Mori Y, Tsutsumi K, Sadakari Y, Takahata S, et al. An increase in the number of predictive factors augments the likelihood of malignancy in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Surgery. 2012; 151:76-83. [PMID: 21875733].
Copyright (c) 2014 Natsuko Kawada, Hiroyuki Uehara, Shigenori Nagata, Mutsumi Tsuchishima, Mikihiro Tsutsumi, Yasuhiko Tomita

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.