“Vascular Lock” Causing Splenic Perfusion Defects During Irreversible Electroporation of a Locally Advanced Pancreatic Tumor
Abstract
Context There is little reported experience of irreversible electroporation (IRE) of locally advanced pancreatic tumors (LAP). In literature, few data reported complications. In particular vascular vasoconstriction miming splenic infarcts in humans has never been found. Case report This report describes the onset of asymptomatic multiple little splenic perfusion defects after the treatment of a LAP localized in the boby-tail portion of the pancreas with the application of five percutaneous probes for IRE, in a 79 year-old man. Splenic artery was regularly patent but entirely trapped in the tumor. Conclusion To the best of our knowledge, until now, no experience concerning percutaneous IRE of pancreatic cancer described that phenomenon. The cause could not be established with certainty and “vascular lock" may be a valid hypothesis. Additional studies are necessary to evaluate its frequency and its exact pathophysiological cause in humans.
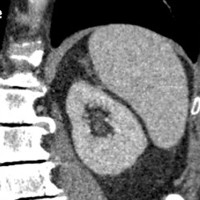
Image: Splenic parenchyma before irreversible electroporation at coronal CT.
Downloads
References
Martin RC 2nd, McFarland K, Ellis S, Velanovich V. Irreversible electroporation in locally advanced pancreatic cancer: potential improved overall survival. Ann Surg Oncol 2013; 20: S443-449. [PMID: 23128941]
Callery MP, Chang KJ, Fishman EK, Talamonti MS, William Traverso L, Linehan DC. Pretreatment assessment of resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: expert consensus statement. Ann Surg Oncol 2009; 16: 1727–1733. [PMID: 19396496]
Varadhachary GR, Tamm EP, Abbruzzese JL, Xiong HQ, Crane CH, Wang H, Lee JE, et al. Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: definitions, management, and role of preoperative therapy. Ann Surg Oncol 2006; 13: 1035–1046. [PMID: 16865597]
Bagla S, Papadouris D. Percutaneous irreversible electroporation of surgically unresectable pancreatic cancer: a case report. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2012; 23: 142-145. [PMID: 22221480]
Lee EW, Loh CT, Kee ST. Imaging guided percutaneous irreversible electroporation: ultrasound and immunohistological correlation. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2007; 6: 287–294. [PMID: 17668935]
Ierardi AM, Lucchina N, Petrillo M, Floridi C, Piacentino F, Bacuzzi A, Fonio P, et al. Systematic review of minimally invasive ablation treatment for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Radiol Med 2014. [PMID: 24981482]
Thomson KR, Cheung W, Ellis SJ, Federman D, Kavnoudias H, Loader-Oliver D, Roberts S, et al. Investigation of the safety of irreversible electroporation in humans. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2011; 22: 611–621. [PMID: 21439847]
Martin RC 2nd, McFarland K, Ellis S, Velanovich V. Irreversible electroporation therapy in the management of locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Am Coll Surg. 2012; 215: 361-369. [PMID: 22726894]
Narayanan G, Hosein PJ, Arora G, Barbery KJ, Froud T, Livingstone AS, Franceschi D, et al. Percutaneous irreversible electroporation for downstaging and control of unresectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Vasc Interv Radiol 2012; 23: 1613-1621. [PMID: 23177107]
Hawker GA, Mian S, Kendzerska T, French M. Measures of adult pain. Arthritis care and Res 2011; 63: S240-S252. [PMID: 22588748]
Grahm AL, Andren-Sandberg A. Prospective evaluation of pain in exocrine pancreatic cancer. Digestion 1997; 58: 542–549. [PMID: 9438600]
Markman JD, Philip A. Interventional Approaches to Pain Management. Med Clin North Am 2007; 91: 271-286. [PMID: 17321286]
Yan BM, Myers RP. Neurolytic celiac plexus block for pain control in unresectable pancreatic cancer. Am J Gastroenterol 2007; 102: 430-438. [PMID: 17100960]
Orlowski S, Mir LM. Cell electropermeabilization: a new tool for biochemical and pharmacological studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1993; 1154: 51–63. [PMID: 8507646]
Maor E, Ivorra A, Leor J, Rubinsky B. The effect of irreversible electroporation on blood vessels. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2007; 6: 307–312. [PMID: 17668938]
Au JT, Wong J, Mittra A, Carpenter S, Haddad D, Carson J, Jayaraman S, et al. Irreversible electroporation is a surgical ablation technique that enhances gene transfer. Surgery 2011; 150: 474–479. 19. [PMID: 21878233]
Jose´ A, Sobrevals L, Ivorra A, Fillat C. Irreversible electroporation shows efficacy against pancreatic carcinoma without systemic toxicity in mouse models. Cancer Lett 2012; 317: 16–23. [PMID: 22079741]
Månsson C, Bergenfeldt M, Brahmstaedt R, Karlson BM, Nygren P, Nilsson A. Safety and preliminary efficacy of ultrasound-guided percutaneous irreversible electroporation for treatment of localized pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res 2014; 34: 289-293. [PMID: 24403476]
Markelc B, Sersa G, Cemazar M. Differential Mechanisms Associated with Vascular Disrupting Action of Electrochemotherapy: Intravital Microscopy on the Level of Single Normal and Tumor Blood Vessels. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e59557.
Bellard E, Markelc B, Pelofy S, Le Guerroué F, Sersa G, Teissié J, Cemazar M, et al. Intravital microscopy at the single vessel level brings new insights of vascular modification mechanisms induced by electropermeabilization. J Control Release 2012; 163: 396–403. [PMID: 23017380]
Gehl J, Skovsgaard T, Mir LM. Vascular reactions to in vivo electroporation: characterization and consequences for drug and gene delivery. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002; 1569: 51–58. [PMID: 11853957]
Markelc B, Bellard E, Sersa G, Pelofy S, Teissie J, Coer A, Golzio M, et al. In vivo molecular imaging and histological analysis of changes induced by electric pulses used for plasmid DNA electrotransfer to the skin: a study in a dorsal window chamber in mice. J Membr Biol 2012; 245: 545–554. [PMID: 22644389]
Al-Sakere B, André F, Bernat C, Connault E, Opolon P, Davalos RV, Rubinsky B, et al. Tumor ablation with irreversible electroporation. PLoS One 2007; 2: e1135. [PMID: 17989772]
Copyright (c) 2014 Anna Maria Ierardi, Natalie Lucchina, Ejona Duka, Alessandro Bacuzzi, Gianlorenzo Dionigi, Gianpaolo Carrafiello

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.