Prevention and Management of Post-ERCP Pancreatitis
Abstract
Pancreatitis remains as one of the most frequent and serious complications of ERCP. Research has identified several patient-related and procedural risk factors, which help guide the endoscopist in prophylaxis and management of pancreatitis. Recent studies have had a major impact on both procedural techniques and pharmacological methods for prophylaxis of post-ERCP pancreatitis. The purpose of this article is to review the relevant literature and describe the most recent and effective approaches in prevention and management of post-ERCP pancreatitis.
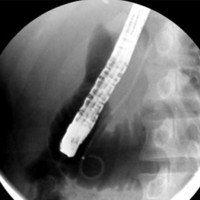
Image: Pancreas stenting.
Downloads
References
Andriulli A, Loperfido S, Napolitano G, et al. Incidence rates of post-ERCP complications: a systematic survey of prospective studies. Am J Gastroenterol 2007;102: 1781-8. [PMID: 17509029]
Freeman ML, DiSario JA, Nelson DB, et al. Risk factors for post-ERCP pancreatitis: a prospective, multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 2001;54: 425-34. [PMID: 11577302]
Vandervoort J, Soetikno RM, Tham TC, et al. Risk factors for complications after performance of ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc 2002;56:652-6. [PMID: 12397271]
Wang P, Li ZS, Liu F, et al. Risk factors for ERCP-related complications: a prospective multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:31-40. [PMID: 19098846]
Sherman S, Blaut U, Watkins JL, et al. Does prophylactic administration of corticosteroid reduce the risk and severity of post-ERCP pancreatitis: a randomized, prospective, multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 2003;58:23-9. [PMID: 12838216]
Cotton PB, Lehman G, Vennes J, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy complications and their management: an attempt at consensus. Gastrointest Endosc 1991;37:383-93. [PMID: 2070995]
Testoni PA, Bagnolo F. Pain at 24 hours associated with amylase levels greater than 5 times the upper normal limit as the most reliable indicator of post-ERCP pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2001;53:33-9. [PMID: 11154486]
Badalov N, Tenner S, Baillie J. The Prevention, recognition and treatment of post-ERCP pancreatitis. JOP 2009;10:88-97. [PMID: 19287099]
Buxbaum J, Yan A, Yeh K, et al. Aggressive hydration with lactated ringer's solution reduces pancreatitis after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;12:303-7 e1. [PMID: 23920031]
Elmunzer BJ, Scheiman JM, Lehman GA, et al. A randomized trial of rectal indomethacin to prevent post-ERCP pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2012;366:1414-22. [PMID: 22494121]
de-Madaria E, Soler-Sala G, Lopez-Font I, et al. Update of the Atlanta Classification of severity of acute pancreatitis: should a moderate category be included? Pancreatology 2010;10:613-9. [PMID: 21042037]
Bradley EL, 3rd. A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta, Ga, September 11 through 13, 1992. Arch Surg 1993;128:586-90. [PMID: 8489394]
Vege SS, Gardner TB, Chari ST, et al. Low mortality and high morbidity in severe acute pancreatitis without organ failure: a case for revising the Atlanta classification to include "moderately severe acute pancreatitis". Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:710-5. [PMID: 19262525]
Cheng CL, Sherman S, Watkins JL, et al. Risk factors for post-ERCP pancreatitis: a prospective multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol 2006;101:139-47. [PMID: 16405547]
Cotton PB, Garrow DA, Gallagher J, et al. Risk factors for complications after ERCP: a multivariate analysis of 11,497 procedures over 12 years. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;70:80-8. [PMID: 19286178]
Masci E, Toti G, Mariani A, et al. Complications of diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP: a prospective multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:417-23. [PMID: 11232684]
Loperfido S, Angelini G, Benedetti G, et al. Major early complications from diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP: a prospective multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc 1998;48:1-10. [PMID: 9684657]
Masci E, Mariani A, Curioni S, et al. Risk factors for pancreatitis following endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a meta-analysis. Endoscopy 2003;35:830-4. [PMID: 14551860]
Singh P, Gurudu SR, Davidoff S, et al. Sphincter of Oddi manometry does not predispose to post-ERCP acute pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;59:499-505. [PMID: 15044885]
Lukens FJ, Howell DA, Upender S, et al. ERCP in the very elderly: outcomes among patients older than eighty. Dig Dis Sci 2010;55:847-51. [PMID: 19337836]
Freeman ML, Nelson DB, Sherman S, et al. Complications of endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy. N Engl J Med 1996;335:909-18. [PMID: 8782497]
Cennamo V, Fuccio L, Zagari RM, et al. Can early precut implementation reduce endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography-related complication risk? Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Endoscopy 2010;42:381-8. [PMH0029208]
Gong B, Hao L, Bie L, et al. Does precut technique improve selective bile duct cannulation or increase post-ERCP pancreatitis rate? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Surg Endosc 2010;24:2670-80. [PMID: 20414680]
Manes G, Di Giorgio P, Repici A, et al. An analysis of the factors associated with the development of complications in patients undergoing precut sphincterotomy: a prospective, controlled, randomized, multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:2412-7. [PMID: 19550413]
Disario JA, Freeman ML, Bjorkman DJ, et al. Endoscopic balloon dilation compared with sphincterotomy for extraction of bile duct stones. Gastroenterology 2004;127:1291-9. [PMID: 15520997]
Ersoz G, Tekesin O, Ozutemiz AO, et al. Biliary sphincterotomy plus dilation with a large balloon for bile duct stones that are difficult to extract. Gastrointest Endosc 2003;57:156-9. [PMID: 12556775]
Stefanidis G, Viazis N, Pleskow D, et al. Large balloon dilation vs. mechanical lithotripsy for the management of large bile duct stones: a prospective randomized study. Am J Gastroenterol 2011;106:278-85. [PMID: 21045816]
Itoi T, Itokawa F, Sofuni A, et al. Endoscopic sphincterotomy combined with large balloon dilation can reduce the procedure time and fluoroscopy time for removal of large bile duct stones. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:560-5. [PMID: 19174779]
Maydeo A, Bhandari S. Balloon sphincteroplasty for removing difficult bile duct stones. Endoscopy 2007;39:958-61. [PMID: 17701853]
Freeman ML. Complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: avoidance and management. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2012;22:567-86. [PMID: 22748249]
Choudhary A, Bechtold ML, Arif M, et al. Pancreatic stents for prophylaxis against post-ERCP pancreatitis: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Gastrointest Endosc 2011;73:275-82. [PMID: 21295641]
Mazaki T, Masuda H, Takayama T. Prophylactic pancreatic stent placement and post-ERCP pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy 2010;42:842-53. [PMID: 20886403]
Singh P, Das A, Isenberg G, et al. Does prophylactic pancreatic stent placement reduce the risk of post-ERCP acute pancreatitis? A meta-analysis of controlled trials. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;60:544-50. [PMID: 15472676]
Andriulli A, Forlano R, Napolitano G, et al. Pancreatic duct stents in the prophylaxis of pancreatic damage after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a systematic analysis of benefits and associated risks. Digestion 2007;75:156-63. [PMH: 0024820]
Tarnasky PR, Palesch YY, Cunningham JT, et al. Pancreatic stenting prevents pancreatitis after biliary sphincterotomy in patients with sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gastroenterology 1998;115:1518-24. [PMID: 9834280]
Harewood GC, Pochron NL, Gostout CJ. Prospective, randomized, controlled trial of prophylactic pancreatic stent placement for endoscopic snare excision of the duodenal ampulla. Gastrointest Endosc 2005;62:367-70. [PMID: 16111953]
Cha SW, Leung WD, Lehman GA, et al. Does leaving a main pancreatic duct stent in place reduce the incidence of precut biliary sphincterotomy-associated pancreatitis? A randomized, prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc 2013;77:209-16. [PMID: 23084272]
Sofuni A, Maguchi H, Mukai T, et al. Endoscopic pancreatic duct stents reduce the incidence of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis in high-risk patients. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;9:851-8; quiz e110. [PMID: 17509029]
Das A, Singh P, Sivak MV, Jr., et al. Pancreatic-stent placement for prevention of post-ERCP pancreatitis: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2007;65:960-8. [PMID: 17331513]
Zolotarevsky E, Fehmi SM, Anderson MA, et al. Prophylactic 5-Fr pancreatic duct stents are superior to 3-Fr stents: a randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy 2011;43:325-30. [PMID: 21455872]
Kozarek RA. Pancreatic stents can induce ductal changes consistent with chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc 1990;36:93-5. [PMID: 2335298]
Rashdan A, Fogel EL, McHenry L, Jr., et al. Improved stent characteristics for prophylaxis of post-ERCP pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;2:322-9. [PMID: 15067627]
Freeman ML, Overby C, Qi D. Pancreatic stent insertion: consequences of failure and results of a modified technique to maximize success. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;59:8-14. [PMID: 14722540]
Lella F, Bagnolo F, Colombo E, et al. A simple way of avoiding post-ERCP pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;59:830-4. [PMID: 15173796]
Lee TH, Park do H, Park JY, et al. Can wire-guided cannulation prevent post-ERCP pancreatitis? A prospective randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;69:444-9. [PMID: 19007927]
Artifon EL, Sakai P, Cunha JE, et al. Guidewire cannulation reduces risk of post-ERCP pancreatitis and facilitates bile duct cannulation. Am J Gastroenterol 2007;102:2147-53. [PMID: 17581267]
Tse F, Yuan Y, Moayyedi P, et al. Guidewire-assisted cannulation of the common bile duct for the prevention of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) pancreatitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012;12:CD009662. [PMID: 23235679]
Tse F, Yuan Y, Moayyedi P, et al. Guide wire-assisted cannulation for the prevention of post-ERCP pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy 2013;45:605-18. [PMID: 23807804]
Cheung J, Tsoi KK, Quan WL, et al. Guidewire versus conventional contrast cannulation of the common bile duct for the prevention of post-ERCP pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2009;70:1211-9. [PMID: 19962504]
Cennamo V, Fuccio L, Zagari RM, et al. Can a wire-guided cannulation technique increase bile duct cannulation rate and prevent post-ERCP pancreatitis?: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:2343-50. [PMID: 19532133]
Mariani A, Giussani A, Di Leo M, et al. Guidewire biliary cannulation does not reduce post-ERCP pancreatitis compared with the contrast injection technique in low-risk and high-risk patients. Gastrointest Endosc 2012;75:339-46. [PMID: 22075192]
Kawakami H, Maguchi H, Mukai T, et al. A multicenter, prospective, randomized study of selective bile duct cannulation performed by multiple endoscopists: the BIDMEN study. Gastrointest Endosc 2012;75:362-72, 372 e1. [PMID: 22248605]
Shao LM, Chen QY, Chen MY, et al. Nitroglycerin in the prevention of post-ERCP pancreatitis: a meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci 2010;55:1-7. [PMID: 19160042]
Schwartz JJ, Lew RJ, Ahmad NA, et al. The effect of lidocaine sprayed on the major duodenal papilla on the frequency of post-ERCP pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;59:179-84. [PMID: 14745389]
Xu LH, Qian JB, Gu LG, et al. Prevention of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis by epinephrine sprayed on the papilla. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;26:1139-44. [PMID: 21392105]
Chen B, Fan T, Wang CH. A meta-analysis for the effect of prophylactic GTN on the incidence of post-ERCP pancreatitis and on the successful rate of cannulation of bile ducts. BMC Gastroenterol 2010;10:85. [PMID: 20673365]
Bai Y, Xu C, Yang X, et al. Glyceryl trinitrate for prevention of pancreatitis after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Endoscopy 2009;41:690-5. [PMH: 0028515]
Dumonceau JM, Andriulli A, Deviere J, et al. European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline: prophylaxis of post-ERCP pancreatitis. Endoscopy 2010;42:503-15. [PMID: 20506068]
Andriulli A, Leandro G, Federici T, et al. Prophylactic administration of somatostatin or gabexate does not prevent pancreatitis after ERCP: an updated meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2007;65:624-32. [PMID: 17383459]
Zheng M, Chen Y, Bai J, et al. Meta-analysis of prophylactic allopurinol use in post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis. Pancreas 2008;37:247-53. [PMID: 18815544]
Katsinelos P, Kountouras J, Paroutoglou G, et al. Intravenous N-acetylcysteine does not prevent post-ERCP pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2005;62:105-11. [PMID: 15990827]
Sherman S, Cheng CL, Costamagna G, et al. Efficacy of recombinant human interleukin-10 in prevention of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis in subjects with increased risk. Pancreas 2009;38:267-74. [PMID: 19214137]
Oh HC, Cheon YK, Cho YD, et al. Use of udenafil is not associated with a reduction in post-ERCP pancreatitis: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Gastrointest Endosc 2011;74:556-62. [PMID: 21802079]
Rabenstein T, Fischer B, Wiessner V, et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin does not prevent acute post-ERCP pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2004;59:606-13. [PMID: 15114301]
Elmunzer BJ, Waljee AK, Elta GH, et al. A meta-analysis of rectal NSAIDs in the prevention of post-ERCP pancreatitis. Gut 2008;57:1262-7. [PMID: 18375470]
Sotoudehmanesh R, Khatibian M, Kolahdoozan S, et al. Indomethacin may reduce the incidence and severity of acute pancreatitis after ERCP. Am J Gastroenterol 2007;102:978-83. [PMID: 17355281]
Murray B, Carter R, Imrie C, et al. Diclofenac reduces the incidence of acute pancreatitis after endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Gastroenterology 2003;124:1786-91. [PMID: 12806612]
Brown A, Baillargeon JD, Hughes MD, et al. Can fluid resuscitation prevent pancreatic necrosis in severe acute pancreatitis? Pancreatology 2002;2:104-7. [PMID: 12123089]
Muddana V, Whitcomb DC, Khalid A, et al. Elevated serum creatinine as a marker of pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2009;104:164-70. [PMID: 19098865]
Wu BU, Johannes RS, Sun X, et al. Early changes in blood urea nitrogen predict mortality in acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2009;137:129-35. [PMID: 19344722]
Gardner TB, Vege SS, Chari ST, et al. Faster rate of initial fluid resuscitation in severe acute pancreatitis diminishes in-hospital mortality. Pancreatology 2009;9:770-6. [PMID: 20110744]
Wu BU, Hwang JQ, Gardner TH, et al. Lactated Ringer's solution reduces systemic inflammation compared with saline in patients with acute pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;9:710-717 e1. [PMID: 21645639]
Reddy N, Wilcox CM, Tamhane A, et al. Protocol-based medical management of post-ERCP pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008;23:385-92. [PMID: 18318823]
Madacsy L, Kurucsai G, Joo I, et al. Rescue ERCP and insertion of a small-caliber pancreatic stent to prevent the evolution of severe post-ERCP pancreatitis: a case-controlled series. Surg Endosc 2009;23:1887-93. [PMID: 19057957]
Copyright (c) 2014 Ara B Sahakian, James L Buxbaum, Jacques Van Dam

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.