Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Succinct Overview
Abstract
Autoimmune pancreatitis is a rare type of chronic pancreatitis with characteristic clinical, radiologic, and histopathologic findings. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis is often challenging due to its low incidence and nonspecific clinical and radiologic findings. Patients with autoimmune pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer share similar clinical presentations, including obstructive jaundice, abdominal pain and weight loss. Due to these overlapping features, autoimmune pancreatitis patients are often misdiagnosed with pancreatic cancer and undergo unnecessary surgery. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis lists 5 cardinal features to establish the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. These features include imaging, serology, other organ involvement, histopathology of the pancreas, and response to steroid therapy. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration is a routine diagnostic tool for pancreatic lesions. It is usually utilized to exclude a malignant process in autoimmune pancreatitis patients, since its role to establish a definitive diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis is often limited. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided-tru-cut biopsy and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle using a large gauge needle (19 to 22 gauges) have been the preferred methods to obtain tissue samples for histologic evaluation. Lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates, fibrotic stroma, mildly atypical epithelial cells, periphlebitis, and obliterative periphlebitis are the common histologic findings of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. Meanwhile, granulocytic pancreatic ductal epithelial damage and ductal obliteration are the histologic characteristics of type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. Immunohistochemical and molecular studies may be helpful to support the diagnosis of AIP in biopsy materials.
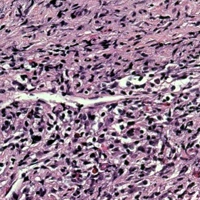
Image: Permanent section of the fine needle aspirate showing venulitis.
Downloads
References
Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T, Watanabe S, Shiratori K, Hayashi N. Chronic pancreatitis caused by an autoimmune abnormality: proposal of the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 1995; 40:1561-68. [PMID: 7628283]
Hart PA, Kamisawa T, Brugge W, et al. Long-term outcomes of autoimmune pancreatitis: a multicentre, international analysis. Gut 2013; 62:1771-6. [PMID: 2323048]
Sarles H, Sarles JC, Muratoren R, Guien C. Chronic inflammatory sclerosing of the pancreas-an autonomous pancreatic disease? Am J Dig Dis 1961; 6:688-98. [PMID: 13746542]
Gardner TB, Levy MJ, Takahashi N, Smyrk TC, Chari ST. Misdiagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis: a caution to clinicians. Am J Gastroenterol 2009; 104:1620-3. [PMID: 19574965]
Hardacre JM, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Sohn TA, et al. Results of pancreaticoduodenectomy for lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis. Ann Surg 2003; 237:853-9. [PMID: 12796582]
Kim KP, Kim MH, Song MH, Lee SS, Seo DW, Lee SK. Autoimmune chronic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2004; 99:1605-16. [PMID: 15307882]
Pearson RK, Longnecker DS, Chari ST, et al. Controversies in clinical pancreatology: autoimmune pancreatitis: does it exist? Pancreas 2003; 27:1-13. [PMID: 12826899]
Park DH, Kim MH, Chari ST. Recent advances in autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 2009; 58:1680-9. [PMID: 19240063]
Sah RP, Chari ST, Pannala R, et al. Differences in clinical profile and relapse rate of type 1 versus type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2010; 139:140-8. [PMID: 20353791]
Chari ST, Kloeppel, Zhang L, et al. Histopathologic and clinical subtypes of autoimmune pancreatitis: the Honolulu Consensus Document. Pancreatology 2010; 10:664-72. [PMID: 21242705]
Agrawal S, Daruwala C, Khurana J. Distinguishing autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreaticobiliary cancers. Ann Surg 2012; 255:248-58. [PMID: 21997803]
Deshpande V, Mino-Kenudson M, Brugge W, Lauwers GY. Autoimmune pancreatitis: more than just a pancreatic disease? A contemporary review of its pathology. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005; 129:1148-54. [PMID: 16119989]
Finkelberg DL, Sahani D, Deshpande V, Brugge W. Autoimmune pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2006; 355:2670-6. [PMID: 17182992]
Sah RP, Chari ST. Autoimmune pancreatitis: an update on classification, diagnosis, natural history and management. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2012; 14:95-105. [PMID: 22350841]
Chari ST, Takahashi N, Levy MJ, et al. A diagnostic strategy to distinguish autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009; 7:1089-96. [PMID: 19410017]
Shimosegawa T, Chari ST, Frulloni L, et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria (ICDC) for autoimmune pancreatitis: guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas 2011; 40:352-8. [PMID: 21412117]
Farrell JJ, Garber J, Sahani D, Brugge WR. EUS findings in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastrointes Endosc 2004; 60:927-36. [PMID: 15605008]
Hoki N, Mixuno N, Sawaki A, et al. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis using endoscopic ultrasonography. J Gastroenterol 2009; 44:154-9. [PMID: 19214678]
Kamisawa T, Ohara H, Kim MH, Kanno A, Okazaki K, Fujita N. Role of endoscopy in the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis and immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing cholangitis. Dig Endosc 2014; 26:627-35. [PMID: 24712522]
Imai K, Matsubayashi H, Fukutomi A, et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy using 22-gauge needle in diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Liver Dis 2011; 43:869-74. [PMID: 21733766]
Zhang X, Liu X, Joseph L, et al. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with autoimmune pancreatitis-like histologic and immunohistochemical features. Hum Pathol 2014; 45:621-7. [PMID: 24457081]
Dhall D, Suriawinata AA, Tang LH, Shia J, Klimstra DS. Use of immunohistochemistry for IgG4 in the distinction of autoimmune pancreatitis from peritumoral pancreatitis. Hum Pathol 2010; 41:643-52. [PMID:20149413]
Resheq YJ, Quaas A, von Renteln D, Schramm C, Lohse AW, Luth S. Infiltration of peritumoral but tumour-free parenchyma with IgG4-positive plasma cells in hilar cholangiocarcinoma and pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Dig Liver Dis 2013; 45:859-65. [PMID: 23602806]
Cai G, Mahooti S, Lipata FM, Chhieng D, Hui P. Diagnostic value of k-ras mutation analysis for pancreaticobiliary cytology specimens with indeterminate diagnosis. Cancer Cytopathol 2012; 120:313-8. [PMID: 22367918]
Kamisawa T, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A, et al. Frequent and significant K-ras mutation in the pancreas, the bile duct, and the gallbladder in autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 2009; 38:890-5. [PMID: 19752775]
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, et al. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 2007; 297:1901-8. [PMID: 17473300]
Xue Y, Abou Tayoun AN, Abo KM, Pipas JM, Gordon SR, Gardner TB, et al. MicroRNAs as diagnostic markers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its precursor, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasm. Cancer Genet 2013; 206:217-21. [PMID: 23933230]
Szafranska AE, Doleshal M, Edmunds HS, et al. Analysis of microRNAs in pancreatic fine-needle aspirates can classify benign and malignant tissues. Clin Chem 2008; 54:1716-24. [PMID: 18719196]
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, et al. Japanese clinical guidelines for autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 2009; 38:849-66. [PMID: 19745774]
Maire F, Baleur YL, Rebours V, et al. Outcome of patients with type 1 or 2 autoimmune pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2011; 106:151-6. [PMID: 20736934]
Hart PA, Topazian MD, Witzig TE, et al. Treatment of relapsing autoimmune pancreatitis with immunomodulators and rituximab: the Mayo Clinic experience. Gut 2013; 62:1607-15. [PMID: 22936672]
Copyright (c) 2015 Juan Putra, Xiaoying Liu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.