CT Attenuation of Unilocular Pancreatic Cystic Lesions to Differentiate Pseudocysts from Mucin-Containing Cysts
Abstract
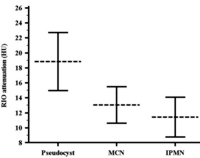
Context There is extensive overlap among the imaging characteristics of pseudocyst, mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN) and side branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) on CT images. Objective The purpose of this study was to evaluate the usefulness of attenuation measurement in differentiating pseudocysts from MCN and IPMN of pancreas on CT images. Patients Seventy-five pathologically proven unilocular pancreatic cysts including 31 pseudocysts, 29 MCN and 15 IPMN imaged with multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) before resection were evaluated. Main outcome measures Attenuation values were measured by conventional region of interest (ROI) method. Design Attenuation values (in Hounsfield unit, HU) were compared between the cyst pathologies. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to obtain the best attenuation threshold between mucin-containing cysts and pseudocysts. Correlation between attenuation values and cyst size was assessed. Results Maximum transaxial diameters of pseudocysts (4.5 cm), MCNs (3.7 cm) and IPMNs (4.0 cm) were comparable (P=0.919). Mean attenuation was 18.9 HU, 13.0 HU and 11.4 HU for pseudocyst, MCNs and IPMNs, respectively. Attenuations were significantly higher in pseudocysts versus mucin-containing (MCN+IPMN) cysts (P=0.001) and comparable between MCNs and IPMNs (P=0.390). ROC curve showed 14.5 HU the best cut-off (accuracy: 73.5%) for differentiating pseudocysts from mucin-containing cysts (P<0.001). Pancreatic cyst attenuation measurement did not significantly correlate with cyst size (r=-0.03, P=0.772). Conclusion Attenuation measurement may help in differentiating pseudocysts from unilocular mucin-containing simple cysts of the pancreas on CT images.
Image: Mean and 95%CI of the attenuation in pseudocyst, MCN and IPMN.
Downloads
References
Kimura W, Nagai H, Kuroda A, Muto T, Esaki Y. Analysis of small cystic lesions of the pancreas. Int J Pancreatol 1995;18:197-206.
Laffan TA, Horton KM, Klein AP, Berlanstein B, Siegelman SS, Kawamoto S, et al. Prevalence of unsuspected pancreatic cysts on MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008; 191:802-7.
Boerma D, Obertop H, Gouma DJ. Pancreatic pseudocysts in chronic pancreatitis. Surgical or interventional drainage? Ann Ital Chir 2000;71:43-50.
Habashi S, Draganov PV. Pancreatic pseudocyst. World J Gastroenterol 2009;15:38-47.
Brugge WR, Lauwers GY, Sahani D, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Warshaw AL. Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1218-1226.
Sahani DV, Kadavigere R, Blake M, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Lauwers GY, Hahn PF. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of pancreas: Multi-detector row ct with 2d curved reformations--correlation with mrcp. Radiology 2006;238:560-569.
Curry CA, Eng J, Horton KM, Urban B, Siegelman S, Kuszyk BS, Fishman EK. CT of primary cystic pancreatic neoplasms: Can ct be used for patient triage and treatment? AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000; 175:99-103.
Macari M, Finn ME, Bennett GL, Cho KC, Newman E, Hajdu CH, Babb JS. Differentiating pancreatic cystic neoplasms from pancreatic pseudocysts at mr imaging: Value of perceived internal debris. Radiology 2009;251:77-84.
Siegelman SS, Copeland BE, Saba GP, Cameron JL, Sanders RC, Zerhouni EA. CT of fluid collections associated with pancreatitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1980; 134:1121-32.
Pezzilli R, Billi P, Miniero R, Fiocchi M, Cappelletti O, Morselli-Labate AM, et al. Serum interleukin-6, interleukin-8, and beta 2-microglobulin in early assessment of severity of acute pancreatitis. Comparison with serum C-reactive protein. Dig Dis Sci 1995; 40:2341-8.
Fernandez-del Castillo C, Targarona J, Thayer SP, Rattner DW, Brugge WR, Warshaw AL. Incidental pancreatic cysts: Clinicopathologic characteristics and comparison with symptomatic patients. Arch Surg 2003;138:427-423; discussion 433-424.
Sahani D, Prasad S, Saini S, Mueller P. Cystic pancreatic neoplasms evaluation by ct and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 2002;12:657-672.
Fernandez-del Castillo C, Warshaw AL. Cystic tumors of the pancreas. Surg Clin North Am 1995;75:1001-1016.
Sahani DV, Kadavigere R, Saokar A, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Brugge WR, Hahn PF. Cystic pancreatic lesions: A simple imaging-based classification system for guiding management. Radiographics 2005;25:1471-1484.
Farnell MB. Surgical management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (ipmn) of the pancreas. J Gastrointest Surg 2008;12:414-416.
Sadakari Y, Ienaga J, Kobayashi K, Miyasaka Y, Takahata S, Nakamura M, Mizumoto K, Tanaka M. Cyst size indicates malignant transformation in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas without mural nodules. Pancreas 2010;39:232-236.
Cohen-Scali F, Vilgrain V, Brancatelli G, Hammel P, Vullierme MP, Sauvanet A, Menu Y. Discrimination of unilocular macrocystic serous cystadenoma from pancreatic pseudocyst and mucinous cystadenoma with ct: Initial observations. Radiology 2003;228:727-733.
Moparty B, Logrono R, Nealon WH, Waxman I, Raju GS, Pasricha PJ, Bhutani MS. The role of endoscopic ultrasound and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration in distinguishing pancreatic cystic lesions. Diagn Cytopathol 2007;35:18-25.
Pais SA, Attasaranya S, Leblanc JK, Sherman S, Schmidt CM, DeWitt J. Role of endoscopic ultrasound in the diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: Correlation with surgical histopathology. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:489-495.
Procacci C, Biasiutti C, Carbognin G, Accordini S, Bicego E, Guarise A, Spoto E, Andreis IA, De Marco R, Megibow AJ. Characterization of cystic tumors of the pancreas: Ct accuracy. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1999;23:906-912.
Miller FH, Keppke AL, Dalal K, Ly JN, Kamler VA, Sica GT. MRI of pancreatitis and its complications: Part 1, acute pancreatitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004; 183:1637-44.
Birnbaum BA, Hindman N, Lee J, Babb JS. Multi-detector row ct attenuation measurements: Assessment of intra- and interscanner variability with an anthropomorphic body CT phantom. Radiology 2007; 242:109-119.
Copyright (c) 2011 Hamid Chalian, Hüseyin Gürkan Töre, Frank H Miller, Vahid Yaghmai

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.