Recurrent Pancreatic Pseudocyst Diagnosed 9 Years After Initial Surgical Drainage
Abstract
Context A pancreatic pseudocyst is defined as a collection of pancreatic juice enclosed by a wall of fibrous or granulation tissue which is not lined by epithelium. Acute pseudocysts occur in acute pancreatitis but can be found after an acute exacerbation of chronic pancreatitis. Chronic pancreatic pseudocysts are typically found in chronic pancreatitis but may develop after an occurrence of acute pancreatitis as well. Most acute fluid collections and pseudocysts will show spontaneous resolution while the remaining may persist with or without symptoms, or progress to produce complications. Treatment is indicated for persistent, symptomatic pseudocysts and, in the case of complications. There is no clear consensus regarding the optimal clinical or radiologic follow-up after treatment. Detection of late recurrence is not common, and the possibility of a cystic neoplasm must be ruled out. Case report We report the case of a 67-year-old female patient who was referred to our institution as the result of a pancreatic pseudocyst. The patient had presented a pancreatic pseudocyst 9 years earlier which had been surgically treated by a cystogastrostomy. No additional acute pancreatic episodes occurred. The diagnostic and treatment approach of this unusual late recurrent pancreatic pseudocyst is herein described. Conclusion The unusual late presentation of a recurrent pancreatic pseudocyst requires clinical, laboratory and radiological evaluation. In the present case, the clinical background, amylase fluid levels and tomographic findings were highly suggestive of a pancreatic pseudocyst.
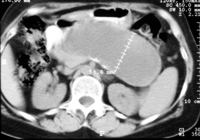
Image: A well-circumscribed unilocular pancreatic pseudocyst.
Downloads
References
Bradley EL 3rd. A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta, Ga, September 11 through 13, 1992. Arch Surg 1993; 1993:586-590. [PMID 8489394]
Rosso E, Alexakis N, Ghaneh P, Lombard M, Smart HL, Evans J, Neoptolemos JP. Pancreatic pseudocyst in chronic pancreatitis: endoscopic and surgical treatment. Dig Surg 2003; 20:397-406. [PMID 12900529]
Bradley EL, Clements JL Jr, Gonzalez AC. The natural history of pancreatic pseudocysts: a unified concept of management. Am J Surg 1979; 137:135-41. [PMID 758840]
Crass RA, Way LW. Acute and chronic pancreatic pseudocysts are different. Am J Surg 1981; 142:660-3. [PMID 7316029]
Sanfey H, Aguilar M, Jones RS. Pseudocysts of the pancreas, a review of 97 cases. Am Surg 1994; 60:661-8. [PMID 8060036]
Warshaw AL, Rattner DW. Timing of surgical drainage for pancreatic pseudocysts. Clinical and chemical criteria. Ann Surg 1985; 202:720-4. [PMID 4073984]
Lerch MM, Stier A, Wahnschaffe U, Mayerle J. Pancreatic pseudocysts: observation, endoscopic drainage, or resection? Dtsch Arztebl Int 2009; 106:614-21. [PMID 19890418]
Eisen GM, Chutkan R, Goldstein JL, Petersen BT, Ryan ME, Sherman S, et al. Endoscopic therapy of chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc 2000; 52:843-8. [PMID 11182688]
Vignesh S, Brugge WR. Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cysts. J Clin Gastroenterol 2008; 42:493-506. [PMID 18344889]
Habashi S, Draganov PV. Pancreatic pseudocyst. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15:38-47. [PMID 19115466]
Shatney CH, Lillehei RC. Surgical treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Analysis of 119 cases. Ann Surg 1979; 189:386-94. [PMID 443893]
Spivak H, Galloway JR, Amerson JR, Fink AS, Branum GD, Redvanly RD, et al. Management of pancreatic pseudocysts. J Am Coll Surg 1998; 186:507-11. [PMID 9583690]
Bradley EL, Gonzalez AC, Clements JL Jr. Acute pancreatic pseudocyst: incidence and implications. Ann Surg 1976; 184:734-7. [PMID 999349]
Hammel P, Levy P, Voitot H, Levy M, Vilgrain V, Zins M, et al. Preoperative cyst fluid analysis is useful for the differential diagnosis of cystic lesions of the pancreas. Gastroenterology 1995; 108:1230-5. [PMID 7535275]
Brugge WR, Lewandrowski K, Lee-Lewandrowski E, Centeno BA, Szydlo T, Regan S, et al. Diagnosis of pancreatic cystic neoplasms: a report of the cooperative pancreatic cyst study. Gastroenterology 2004; 126:1330-6. [PMID 15131794]
Degen L, Wiesner W, Berlinger C. Cystic and solid lesions of the pancreas. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2008; 22:91-103. [PMID 18206815]
Gumaste VV, Aron J. Pseudocyst management. Endoscopic drainage and other emerging techniques. J Clin Gastroenterol 2010; 44:326-31. [PMID 20142757]
Aghdassi AA, Mayerle J, Kraft M, Sielenkämper AW, Heidecke CD, Lerch MM. Pancreatic pseudocysts. When and how to treat? HPB (Oxford) 2006; 8:432-41. [PMID 18333098]
Cannon JW, Callery MP, Vollmer CM Jr. Diagnosis and management of pancreatic pseudocysts: what is the evidence? J Am Coll Surg 2009; 209:385-93. [PMID 19717045]
Grewal HP, London NJM, Carr-Locke D, Wood KF. Endoscopic drainage of a recurrent pancreatic pseudocyst. Postgrad Med J 1990; 66:1081-1083. [PMID 2084661]
Struve CW. Spontaneous resolution of a pancreatic pseudocyst 10 years after detection documented by ultrasound. Pancreas 1993; 8:273-8. [PMID 8460102]
Copyright (c) 2015 Carlos M Nuño-Guzmán, José Arróniz-Jáuregui, José I Gómez-Ontiveros, Haydée Hernández-Estrada, Haydee I Estrada-Castañeda, Juan R Araiza-Navarro, Nereida Esparza-Arias

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.