Splenic Parenchymal Complications in Pancreatitis
Abstract
Context The close proximity of splenic hilum to the tail of pancreas makes it vulnerable to complications in both acute and chronic pancreatitis. In this article, we examine the clinical course of these potentially fatal complications. Case reports Citing three clinical cases, we present the spectrum of splenic complications in pancreatitis and explore the anatomical causal relationships and pathological basis of such complications. A literature review was carried out to inform on the incidence, morbidity and mortality rates, and clinical course especially diagnostic and management options for these patients. The spectrum of splenic complications in pancreatitis is wide ranging from pseudo cysts to haematomas, haemorrhages, infarctions and life threatening splenic rupture. Although a contrast enhanced helical CT scan is the investigation of choice a high index of clinical suspicion is essential in their early identification. Splenic complications in pancreatitis incur a high morbidity (79%) and a significant mortality (8%). Conclusions Splenic parenchymal complications in pancreatitis are an increasingly recognised entity and should be suspected in patients with inflammation and or necrosis involving the tail of pancreas. Conservative management is feasible with close radiological monitoring for most patients in a tertiary referral centre with appropriate expertise and surgery may be reserved for haemodynamically unstable patients.
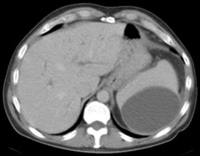
Image: Splenic sub-capsular haematoma.
Downloads
References
Malka D, Hammel P, Lévy P, Sauvanet A, Ruszniewski P, Belghiti J, Bernades P. Splenic complications in chronic pancreatitis: prevalence and risk factors in a medical-surgical series of 500 patients. Br J Surg 1998; 85:1645-9. [PMID 9876067]
Heider R, Behrns KE. Pancreatic pseudocysts complicated by splenic parenchymal involvement: results of operative and percutaneous management. Pancreas 2001; 23:20-5. [PMID 11451143]
Siu TL. Percutaneous drainage of spontaneous subcapsular haematoma of the spleen complicating chronic pancreatitis. Surgeon 2004; 2:52-5. [PMID 15570808]
Thompson JE Jr, Ashley SW. Subcapsular hematoma of the spleen associated with acute pancreatitis. Surgery 1997; 121:231-3. [PMID 9037239]
Mortele KJ, Mergo PJ, Taylor HM, Ernst MD, Ros PR. Splenic and perisplenic involvement in acute pancreatitis: determination of prevalence and morphologic helical CT features. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2001; 25:50-4. [PMID 11176293]
Toussi HR, Cross KS, Sheehan SJ, Bouchier-Hayes D, Leahy AL. Spontaneous splenic rupture: a rare complication of acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg 1996; 83:632. [PMID 8689204]
Fishman EK, Soyer P, Bliss DF, Bluemke DA, Devine N. Splenic involvement in pancreatitis: spectrum of CT findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1995; 164:631-5. [PMID 7863884]
Rypens F, Deviere J, Zalcman M, Braude P, Van de Stadt J, Struyven J, et al. Splenic parenchymal complications of pancreatitis: CT findings and natural history. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1997; 21:89-93. [PMID 9022775]
Lankisch PG. The spleen in inflammatory pancreatic disease. Gastroenterology 1990; 98:509-16. [PMID 2403954]
Hastings OM, Jain KM, Khademi M, Lazaro EJ. Intrasplenic pancreatic pseudocyst complicating severe acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 1978; 69:182-6. [PMID 665640]
Warshaw AL, Chesney TM, Evans GW, McCarthy HF. Intrasplenic dissection by pancreatic pseudocysts. N Engl J Med 1972; 287:72-5. [PMID 5040037]
Sitzmann JV, Imbembo AL. Splenic complications of a pancreatic pseudocyst. Am J Surg 1984; 147:191-6. [PMID 6696192]
Wang SJ, Chen JJ, Changchien CS, Chiou SS, Tai DI, Lee CM, et al. Sequential invasions of pancreatic pseudocysts in pancreatic tail, hepatic left lobe, caudate lobe, and spleen. Pancreas 1993; 8:133-6. [PMID 8419901]
Vujic I. Vascular complications of pancreatitis. Radiol Clin North Am 1989; 27:81-91. [PMID 2642279]
Miller FH, Keppke AL, Dalal K, Ly JN, Kamler VA, Sica GT. MRI of pancreatitis and its complications: Part 1, Acute pancreatitis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004; 183:1637-44. [PMID 15547203]
Patel VG, Eltayeb OM, Zakaria M, Fortson JK, Weaver WL. Spontaneous subcapsular splenic hematoma: a rare complication of pancreatitis. Am Surg 2005; 71:1066-9. [PMID 16447482]
Copyright (c) 2011 Pradeep V Patil, Ahmed Khalil, Mohamed A Thaha

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.