Large Duodenal Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Presenting with Acute Bleeding Managed by a Whipple Resection. A Review of Surgical Options and the Prognostic Indicators of Outcome
Abstract
Context Duodenal gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are uncommon and constitute a relatively small subset of GISTs which presents a unique dilemma having various surgical options. A case of a large ulcerating duodenal GIST arising from the second and third parts of the duodenum and involving the pancreas which was managed by a Whipple resection is presented. The literature is also reviewed to present the current status on surgical options, outcome, prognostic indicators and the role of imatinib mesylate in its management. Case report A 58-year-old patient presented with acute gastrointestinal bleeding which was diagnosed to be due to a duodenal GIST following CT scan and endoscopic biopsy. The mass which measured about 10x9 cm originated from the 2nd part and extended into the 3rd part of the duodenum. He underwent a Whipple resection, and histopathology confirmed a duodenal GIST having a greater than 10 mitotic count per fifty high power field and areas of necrosis. Postoperatively, he received imatinib mesylate 400 mg bid; however, 4 months later, he presented with multiple disseminated peritoneal metastases and succumbed to the disease 2 months later. Conclusion GISTs of the duodenum which are small in size and do not involve the papilla of Vater are better resolved using a limited resection of the duodenum since the outcome in terms of operative risk or disease recurrence is not influenced in these cases. However, large tumors with more extensive involvement would require a pancreaticoduodenectomy to achieve adequate tumor clearance. Even though duodenal GISTs have a relatively better prognosis as compared to GISTs at other sites, their aggressiveness ranges from small indolent tumors to aggressive sarcomas. Following tumor resection, a recurrence rate of about 40% has been reported. A more favorable prognosis in duodenal GISTs is attributed to a lower prevalence of P53 loss, the duodenal location of the tumor, a smaller size of the lesion and a low mitotic count. Imatinib mesylate is reported to play a role in neoadjuvant therapy as well as in the management of metastatic and recurrent disease, although some of these tumors may fail to respond.
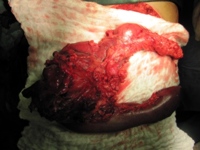
Image: Specimen after Whipple resection revealing a large duodenal GIST tumor.
Downloads
References
Miettinen M, Kopczynski J, Makhlouf HR, Sarlomo-Rikala M, Gyorffy H, Burke A, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours, intramural leiomyomas, and leiomyosarcomas in the duodenum. A clinicopathological, immunohistochemical and molecular genetic study of 167 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2003; 27:625-41. [PMID 12717247]
Chung JC, Chu CW, Cho GS, Shin EJ, Lim CW, Kim HC, Song OP. Management and outcome of gastrointestinal stromal tumours of the duodenum. J Gastrointest Surg 2010; 14:880-3. [PMID 20140534]
Mennigen R, Wolters HH, Schulte B, Pelster FW. Segmental resection of the duodenum for gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST). World J Surg Oncol 2008; 6:105. [PMID 18826622]
Gervaz P, Huber O, Morel P. Surgical management of gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Br J Surg 2009; 96:567-78. [PMID 19434705]
Yang WL, Yu JR, Wu YJ, Zhu KK, Ding W, Gao Y, et al. Duodenal gastrointestinal stromal tumour: clinical, pathologic, immunohistochemical characteristics, and surgical prognosis. J Surg Oncol 2009; 100:606-10. [PMID 19697360]
Asakawa M, Sakamoto Y, Kajiwara T, Nara S, Esaki M, Shimada K, et al. Simple segmental resection of the second portion of the duodenum for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2008; 393:605-9. [PMID 18026747]
Bucher P, Egger JF, Gervaz P, Ris F, Weintraub D, Villiger P, et al. An audit of surgical management of gastrointestinal stromal tumours(GIST). Eur J Surg Oncol 2006; 32:310-14. [PMID 16414236]
Cohen MH, Cortazar P, Justice R, Pazdur R. Approval summary: Imatinib mesylate in the adjuvant treatment of malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Oncologist 2010; 15:300-7. [PMID 20200041]
Corless CL, Schroeder A, Griffich D, Town A, McGreeevery L, Harrell P, et al. PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumours: frequency, spectrum and in vitro sensitivity to imatinib. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23:5357-64. [PMID 15928335]
Goettsch WG, Bos SD, Breekveldt-Postma N, Casparie M, Herings RM, Hogendoorn PC. Incidence of gastrointestinal stromal tumours is underestimated : results of a nationwide study. Eur J Cancer 2005; 41:2868-72. [PMID 16293410]
Tran T, Davila JA, El-Serag HB. The epidemiology of malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumours: an analysis of 1,458 cases from 1992 to 2000. Am J Gastroenterol 2005; 100:162-8. [PMID 15654796]
Aydin A, Tekin F, Günşar F, Güler A, Tunçyürek M, Ilter T. Value of endoscopic ultrasonography for upper gastrointestinal stromal tumours. A single center experience. Turk J Gastroenetrol 2004; 15:233-7. [PMID 16249977]
Ghanem N, Altehoefer C, Furtwängler A, Winterer J, Schäfer O, Springer O, et al. Computed tomography in gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Eur Radiol 2003; 13:1669-78. [PMID 12835984]
Sandrasegaran K, Rajesh A, Rushing DA, Rydberg J, Akisik FM, Henley JD. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour. CT &MRI finding. Eur Radiol 2005; 15:1407-14. [PMID 15761716]
Blay JY, Bonvalot S, Casali P, Choi H, Debiec-Richter M, Dei Tos AP, et al. Consensus meeting for the management of gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Report of the GIST consensus conference of 20-21 march 2004 under the auspicies of ESMO. Ann Oncol 2005; 16:566-78. [PMID 15781488]
Goh BK, Chow PK, Ong HS, Wong WK. Gastroinetstinal stromal tumour involving the second and third portion of the duodenum: treatment by partial duodenectomy and Roux-en-Y duodenojejunostomy. J Surg Oncol 2005; 91:273-5. [PMID 16121353]
Cavallini M, Cecera A, Ciardi A, Caterino S, Ziparo V. Small periampullary duodenal gastrointestinal stromal tumour treated by local excision: report of a case. Tumori 2005; 91:264-6. [PMID 16206653]
Pennacchioli E, Colombo C, Berselli M, Gronchi A. Update on management of GIST and post surgical use of imatinib. Open Access Surgery 2010; 3:63-71.
Demetri GD, van Mehren M, Blanke CD, Van den, Abbeele AD, Eisenberg B, et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours. N Engl J Med 2002; 347:472-80. [PMID 12181401]
Gold JS, van der Zwan SM, Gonen M, Maki RG, Singer S, Brennan MF, et al. Outcome of metastatic GIST in the era before tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann Surg Oncol 2007; 14:134-42. [PMID 17080234]
Eisenber BL, Judson I. Surgery and Imatinib in the management of GIST: emerging approaches to adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy. Ann surg Oncol 2004; 11:465-75. [PMID 15123459]
Mohiuddin K, Nizami S, Munir A, Memon B, Memon MA. Metastatic duodenal GIST: role of surgery combined with imatinib mesylate. Int Semin Surg Oncol 2007; 9:1-6. [PMID 17391535]
Fletcher CDM, Bermar JJ, Corless C, Gorstein F, Lasota J, Longley BJ, et al. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumour a consensus approach. Hum Pathol 2002; 33:459-65. [PMID 12094370]
De Matteo RP, Gold JS, Saran L, Gonen M, Liau KH, Maki KH, et al. Tumour mitotic rate , size and location independently predict recurrence after resection of primary gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST). Cancer 2008; 112:608-15. [PMID 18076015]
Copyright (c) 2011 Norman Oneil Machado, Pradeep J Chopra, Ibrahim Hassan Al-Haddabi, Hani Al-Qadhi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.