Rationale for Inhibition of the Hedgehog Pathway Paracrine Loop in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
The role of hedgehog pathway in the biology of pancreatic adenocarcinoma is an emerging area of investigation and provides a novel field for treatment intervention. Recent studies have shown the activation of the hedgehog pathway in pancreatic cancer. Despite the initial assumption of an autocrine mechanism, it seems that the hedgehog pathway contributes to the molecular conversation between tumor and its microenvironment through a paracrine loop. Furthermore, members of the hedgehog pathway crosstalk with other pathways; they regulate tumor angiogenesis and are associated with cancer stem cells. In addition, there is preclinical evidence about the efficiency of hedgehog inhibitors both in vitro and in vivo and the first clinical trials with those compounds in the treatment of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma, are already under way.
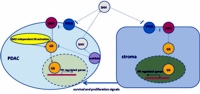
Image: Sonic hedgehog (SHH) ligand is produced from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells and acts mainly in a paracrine way to release SMO from PTCH control, in the tumor microenvironment
Downloads
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 2009; 59:225-49. [PMID 19474385]
Feldmann G, Beaty R, Hruban RH, Maitra A. Molecular genetics of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2007; 14:224-32. [PMID 17520196]
Huangfu D, Anderson KV. Signaling from Smo to Ci/Gli: conservation and divergence of Hedgehog pathways from Drosophila to vertebrates. Development 2006; 133:3-14. [PMID 16339192]
Lees C, Howie S, Sartor RB, Satsangi J. The hedgehog signalling pathway in the gastrointestinal tract: implications for development, homeostasis, and disease. Gastroenterology 2005; 129:1696-710. [PMID 16285967]
Lupi O. Correlations between the Sonic Hedgehog pathway and basal cell carcinoma. Int J Dermatol 2007; 46:1113-7. [PMID 17988327]
Yang ZJ, Ellis T, Markant SL, Read TA, Kessler JD, Bourboulas M, et al. Medulloblastoma can be initiated by deletion of Patched in lineage-restricted progenitors or stem cells. Cancer Cell 2008; 14:135-45. [PMID 18691548]
Watkins DN, Berman DM, Baylin SB. Hedgehog signaling: progenitor phenotype in small-cell lung cancer. Cell Cycle 2003; 2:196-8. [PMID 12734424]
Alcedo J, Noll M. Hedgehog and its patched-smoothened receptor complex: a novel signaling mechanism at the cell surface. Biol Chem 1997; 378:583-90. [PMID 9278137]
ThayThayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW, Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY, et al. Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature 2003; 425:851-6. [PMID 14520413]
Prasad NB, Biankin AV, Fukushima N, Maitra A, Dhara S, Elkahloun AG, et al. Gene expression profiles in pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia reflect the effects of Hedgehog signaling on pancreatic ductal epithelial cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65:1619-26. [PMID 15753353]
Nagai S, Nakamura M, Yanai K, Wada J, Akiyoshi T, Nakashima H, et al. Gli1 contributes to the invasiveness of pancreatic cancer through matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation. Cancer Sci 2008; 99:1377-84. [PMID 18410405]
Hwang JH, Lee SH, Lee KH, Lee KY, Kim H, Ryu JK, et al. Cathepsin B is a target of Hedgehog signaling in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett 2009; 273:266-72. [PMID 19004543]
Feldmann G, Dhara S, Fendrich V, Bedja D, Beaty R, Mullendore M, et al. Blockade of hedgehog signaling inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion and metastases: a new paradigm for combination therapy in solid cancers. Cancer Res 2007; 67:2187-96. [PMID 17332349]
Yauch RL, Gould SE, Scales SJ, Tang T, Tian H, Ahn CP, et al. A paracrine requirement for hedgehog signalling in cancer. Nature 2008; 455:406-10. [PMID 18754008]
Xu XF, Guo CY, Liu J, Yang WJ, Xia YJ, Xu L, et al. Gli1 maintains cell survival by up-regulating IGFBP6 and Bcl-2 through promoter regions in parallel manner in pancreatic cancer cells. J Carcinog 2009; 8:13. [PMID 19736394]
Nolan-Stevaux O, Lau J, Truitt ML, Chu GC, Hebrok M, Fernández-Zapico ME, Hanahan D. GLI1 is regulated through Smoothened-independent mechanisms in neoplastic pancreatic ducts and mediates PDAC cell survival and transformation. Genes Dev 2009; 23:24-36. [PMID 19136624]
Pasca di Magliano M, Sekine S, Ermilov A, Ferris J, Dlugosz AA, Hebrok M. Hedgehog/Ras interactions regulate early stages of pancreatic cancer. Genes Dev 2006; 20:3161-73. [PMID 17114586]
Kasai K, Inaguma S, Yoneyama A, Yoshikawa K, Ikeda H. SCL/TAL1 interrupting locus derepresses GLI1 from the negative control of suppressor-of-fused in pancreatic cancer cell. Cancer Res 2008; 68:7723-9. [PMID 18829525]
Ji Z, Mei FC, Xie J, Cheng X. Oncogenic KRAS activates hedgehog signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2007; 282:14048-55. [PMID 17353198]
Lauth M, Bergström A, Shimokawa T, Tostar U, Jin Q, Fendrich V, et al. DYRK1B-dependent autocrine-to-paracrine shift of Hedgehog signaling by mutant RAS. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2010; 17:718-25. [PMID 20512148]
Tian H, Callahan CA, DuPree KJ, Darbonne WC, Ahn CP, Scales SJ, de Sauvage FJ. Hedgehog signaling is restricted to the stromal compartment during pancreatic carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009; 106:4254-9. [PMID 19246386]
Bailey JM, Mohr AM, Hollingsworth MA. Sonic hedgehog paracrine signaling regulates metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 2009; 28:3513-25. [PMID 19633682]
Walter K, Omura N, Hong SM, Griffith M, Vincent A, Borges M, Goggins M. Overexpression of smoothened activates the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer-associated fibroblasts. Clin Cancer Res 2010; 16:1781-9. [PMID 20215540]
Bailey JM, Swanson BJ, Hamada T, Eggers JP, Singh PK, Caffery T, et al. Sonic hedgehog promotes desmoplasia in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14:5995-6004. [PMID 18829478]
Yamazaki M, Nakamura K, Mizukami Y, Ii M, Sasajima J, Sugiyama Y, Nishikawa T, et al. Sonic hedgehog derived from human pancreatic cancer cells augments angiogenic function of endothelial progenitor cells. Cancer Sci 2008; 99:1131-8. [PMID 18422746]
Nakamura K, Sasajima J, Mizukami Y, Sugiyama Y, Yamazaki M, Fujii R, et al. Hedgehog promotes neovascularization in pancreatic cancers by regulating Ang-1 and IGF-1 expression in bone-marrow derived pro-angiogenic cells. PLoS One 2010; 5:e8824. [PMID 20098680]
Yamasaki A, Kameda C, Xu R, Tanaka H, Tasaka T, Chikazawa N, et al. Nuclear factor kappaB-activated monocytes contribute to pancreatic cancer progression through the production of Shh. Cancer Immunol Immunother 2010; 59:675-86. [PMID 19862523]
Stanton BZ, Peng LF. Small-molecule modulators of the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway. Mol Biosyst 2010; 6:44-54. [PMID 20024066]
Shafaee Z, Schmidt H, Du W, Posner M, Weichselbaum R. Cyclopamine increases the cytotoxic effects of paclitaxel and radiation but not cisplatin and gemcitabine in Hedgehog expressing pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 2006; 58:765-70. [PMID 16552573]
Hu WG, Liu T, Xiong JX, Wang CY. Blockade of sonic hedgehog signal pathway enhances antiproliferative effect of EGFR inhibitor in pancreatic cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2007; 28:1224-30. [PMID 17640486]
Chun SG, Zhou W, Yee NS. Combined targeting of histone deacetylases and hedgehog signaling enhances cytoxicity in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 2009; 8:1328-39. [PMID 19421011]
Olive KP, Jacobetz MA, Davidson CJ, Gopinathan A, McIntyre D, Honess D, et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Science 2009; 324:1457-61. [PMID 19460966]
Jimeno A, Feldmann G, Suárez-Gauthier A, Rasheed Z, Solomon A, Zou GM, et al. A direct pancreatic cancer xenograft model as a platform for cancer stem cell therapeutic development. Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8:310-4. [PMID 19174553]
Feldmann G, Fendrich V, McGovern K, Bedja D, Bisht S, Alvarez H, et al. An orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of Hedgehog signaling inhibits tumor initiation and metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7:2725-35. [PMID 18790753]
Fan L, Pepicelli CV, Dibble CC, Catbagan W, Zarycki JL, Laciak R, et al. Hedgehog signaling promotes prostate xenograft tumor growth. Endocrinology 2004; 145:3961-70. [PMID 15132968]
Copyright (c) 2011 Anastasios Dimou, Kostas Syrigos, Muhammad Wasif Saif

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.