Dysregulation of Hnf1b Gene Expression in Cultured Beta-Cells in Response to Cytotoxic Fatty Acid
Abstract
Context Increased levels of circulating fatty acids deriving from over-nutrition are thought to contribute to the progressive beta-cell failure associated with type 2 diabetes. Pancreatic beta-cells in culture are sensitive to exposure to long-chain saturated fatty acids (e.g. palmitate) which cause cytotoxicity, whereas the monounsaturated equivalents (e.g. palmitoleate) are cytoprotective. Objectives In this study we sought to determine whether of members of the hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF) family of transcription factors, which are mutated in familial, young-onset, monogenic beta-cell diabetes, could play a role in fatty acid-mediated cytotoxicity in cultured beta-cells. Design We used real-time PCR to determine whether hepatocyte nuclear factor gene expression was altered in response to palmitate exposure in the BRIN-BD11 beta-cell line. Results We found that the Hnf isoforms expressed in BRIN-BD11 cells are dysregulated by palmitate exposure. The expression of Hnf1b is specifically reduced by exposure to palmitate, and this response is prevented by co-incubation with palmitoleate. Conclusions Down-regulation of Hnf1b gene expression accompanies palmitate-mediated cytotoxicity in cultured beta-cells.
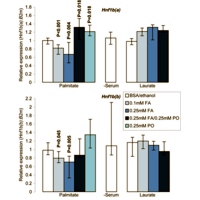
Image: Hnf1b expression is downregulated in response to cytotoxic fatty acid.
Downloads
References
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J. Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 2001; 414:782-7. [PMID 11742409]
Unger RH. Lipotoxicity in the pathogenesis of obesity-dependent NIDDM. Genetic and clinical implications. Diabetes 1995; 44:863-70. [PMID 7621989]
Carpentier AC. Postprandial fatty acid metabolism in the development of lipotoxicity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab 2008; 34:97-107. [PMID 18353699]
Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003; 52:102-10. [PMID 12502499]
Poitout V, Robertson RP. Glucolipotoxicity: fuel excess and beta-cell dysfunction. Endocr Rev 2008; 29:351-66. [PMID 18048763]
Zhou YP, Grill V. Long term exposure to fatty acids and ketones inhibits b-cell functions in human pancreatic islets of Langerhans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1995; 80:1584-90. [PMID 7745004]
Cnop M, Hannaert JC, Hoorens A, Eizirik DL, Pipeleers DG. Inverse relationship between cytotoxicity of free fatty acids in pancreatic islet cells and cellular triglyceride accumulation. Diabetes 2001; 50:1771-7. [PMID 11473037]
Maedler K, Spinas GA, Dyntar D, Moritz W, Kaiser N, Donath MY. Distinct effects of saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids on beta-cell turnover and function. Diabetes 2001; 50:69-76. [PMID 11147797]
Morgan NG, Dhayal S, Diakogiannaki E, Welters HJ. The cytoprotective actions of long-chain mono-unsaturated fatty acids in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Soc Trans 2008; 36:905-8. [PMID 18793159]
Maedler K, Oberholzer J, Bucher P, Spinas GA, Donath MY. Monounsaturated fatty acids prevent the deleterious effects of palmitate and high glucose on human pancreatic beta-cell turnover and function. Diabetes 2003; 52:726-33. [PMID 12606514]
Welters HJ, Tadayyon M, Scarpello JH, Smith SA, Morgan NG. Mono-unsaturated fatty acids protect against beta-cell apoptosis induced by saturated fatty acids, serum withdrawal or cytokine exposure. FEBS Lett 2004; 560:103-8. [PMID 14988006]
Pegorier JP, Le May C, Girard J. Control of gene expression by fatty acids. J Nutr 2004; 134:2444S-9S. [PMID 15333740]
Hayhurst GP, Lee YH, Lambert G, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (nuclear receptor 2A1) is essential for maintenance of hepatic gene expression and lipid homeostasis. Mol Cell Biol 2001; 21:1393-403. [PMID 11158324]
Yuan X, Ta TC, Lin M, Evans JR, Dong Y, Bolotin E, et al. Identification of an endogenous ligand bound to a native orphan nuclear receptor. PLoS One 2009; 4:e5609. [PMID 19440305]
Owen K, Hattersley AT. Maturity-onset diabetes of the young: from clinical description to molecular genetic characterization. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 15:309-23. [PMID 11554773]
Ferrer J. A genetic switch in pancreatic beta-cells: implications for differentiation and haploinsufficiency. Diabetes 2002; 51:2355-62. [PMID 12145145]
Ryffel GU. Mutations in the human genes encoding the transcription factors of the hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF)1 and HNF4 families: functional and pathological consequences. J Mol Endocrinol 2001; 27:11-29. [PMID 11463573]
McClenaghan NH, Barnett CR, Ah-Sing E, Abdel-Wahab YH, O'Harte FP, Yoon TW, et al. Characterization of a novel glucose-responsive insulin-secreting cell line, BRIN-BD11, produced by electrofusion. Diabetes 1996; 45:1132-40. [PMID 8690162]
Asfari M, Janjic D, Meda P, Li G, Halban PA, Wollheim CB. Establishment of 2-mercaptoethanol-dependent differentiated insulin-secreting cell lines. Endocrinology 1992; 130:167-78. [PMID 1370150]
Dhayal S, Welters HJ, Morgan NG. Structural requirements for the cytoprotective actions of mono-unsaturated fatty acids in the pancreatic beta-cell line, BRIN-BD11. Br J Pharmacol 2008; 153:1718-27. [PMID 18297101]
Welters HJ, Diakogiannaki E, Mordue JM, Tadayyon M, Smith SA, Morgan NG. Differential protective effects of palmitoleic acid and cAMP on caspase activation and cell viability in pancreatic beta-cells exposed to palmitate. Apoptosis 2006; 11:1231-8. [PMID 16703263]
Harries LW, Brown JE, Gloyn AL. Species-specific differences in the expression of the HNF1A, HNF1B and HNF4A genes. PLoS One 2009; 4:e7855. [PMID 19924231]
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001; 25:402-8. [PMID 11846609]
El-Assaad W, Buteau J, Peyot ML, Nolan C, Roduit R, Hardy S, et al. Saturated fatty acids synergize with elevated glucose to cause pancreatic beta-cell death. Endocrinology 2003; 144:4154-63. [PMID 12933690]
Diakogiannaki E, Welters HJ, Morgan NG. Differential regulation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in pancreatic beta-cells exposed to long-chain saturated and monounsaturated fatty acids. J Endocrinol 2008; 197:553-63. [PMID 18492819]
Kharroubi I, Ladriere L, Cardozo AK, Dogusan Z, Cnop M, Eizirik DL. Free fatty acids and cytokines induce pancreatic beta-cell apoptosis by different mechanisms: role of nuclear factor-kappaB and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Endocrinology 2004; 145:5087-96. [PMID 15297438]
Diakogiannaki E, Morgan NG. Differential regulation of the ER stress response by long-chain fatty acids in the pancreatic beta-cell. Biochem Soc Trans 2008; 36:959-62. [PMID 18793169]
Bellanne-Chantelot C, Clauin S, Chauveau D, Collin P, Daumont M, Douillard C, et al. Large genomic rearrangements in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta (TCF2) gene are the most frequent cause of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 5. Diabetes 2005; 54:3126-32. [PMID 16249435]
Wang L, Coffinier C, Thomas MK, Gresh L, Eddu G, Manor T, et al. Selective deletion of the Hnf1beta (MODY5) gene in beta-cells leads to altered gene expression and defective insulin release. Endocrinology 2004; 145:3941-9. [PMID 15142986]
Welters HJ, Senkel S, Klein-Hitpass L, Erdmann S, Thomas H, Harries LW, et al. Conditional expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor-1beta, the maturity-onset diabetes of the young-5 gene product, influences the viability and functional competence of pancreatic beta-cells. J Endocrinol 2006; 190:171-81. [PMID 16837621]
Maestro MA, Boj SF, Luco RF, Pierreux CE, Cabedo J, Servitja JM, et al. Hnf6 and Tcf2 (MODY5) are linked in a gene network operating in a precursor cell domain of the embryonic pancreas. Hum Mol Genet 2003; 12:3307-14. [PMID 14570708]
Copyright (c) 2011 Karen A Johnstone, Eleftheria Diakogiannaki, Shalinee Dhayal, Noel G Morgan, Lorna W Harries

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.