Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm (IPMN) and Chronic Pancreatitis: Overlapping Pathological Entities? Two Case Reports
Abstract
Context Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) are a recently classified pancreatic neoplasm with an increasing incidence. IPMN is often misdiagnosed as chronic pancreatitis because of symptoms of relapsing abdominal pain, pancreatitis, and steatorrhea and imaging findings of a dilated pancreatic duct of cystic lesions that are frequently confused with pseudocysts. Early recognition of IPMN allows for prompt surgical resection before malignant transformation. Case reports We report two cases of patients with long histories of chronic pancreatitis (more than 15 years) that went on to develop IPMN. Both patients presented with symptoms of abdominal pain, nausea, steatorrhoea and eventually weight loss. Biochemical and radiological findings were suggestive of chronic pancreatitis although no clear causes for this were identified. Both patients were followed up with multiple repeat scans with no reported sinister findings. Many years after the initial diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis, radiological investigations identified pathological changes suggestive of neoplastic development and histology confirmed IPMN. Conclusions The cases demonstrate the ongoing challenges in diagnosing and managing IPMN effectively; highlights the important aspects of epidemiology in differentiating chronic pancreatitis and IPMN; continues the discussion surrounding the relationship between IPMN and chronic pancreatitis.
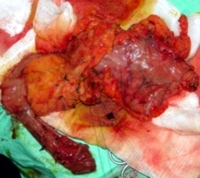
Image: Intraoperative findings of the Whipple surgical specimen.
Downloads
References
Klöppel G, Solcia E, Longnecker DS, Capella C, Sobin LH. Histological typing of tumours of the exocrine pancreas. In: World Health Organization International Classification of Tumors, 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer, 1996:11-20.
Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Hruban RH, Fukushima N, Campbell KA, Lillemoe KD. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an updated experience. Ann Surg 2004; 239:788-97. [PMID 15166958]
Cho KR, Vogelstein B. Genetic alterations in the adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Cancer 1992; 70:1727-31. [PMID 1516027]
Bassi C, Sarr MG, Lillemoe KD, Reber HA. Natural history of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN): current evidence and implications for management. J Gastrointest Surg 2008; 12:645-50. [PMID 18097728]
Chari ST, Yadav D, Smyrk TC, DiMagno EP, Miller LJ, Raimondo M, et al. Study of recurrence after surgical resection of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Gastroenterology 2002; 123:1500-7. [PMID 12404225]
Talamini G, Zamboni G, Salvia R, Capelli P, Sartori N, Casetti L, et al. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms and Chronic Pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2006; 6:626-34. [PMID 17135772]
Klöppel G, Adsay NV. Chronic pancreatitis and the differential diagnosis versus pancreatic cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009; 133:382-7. [PMID 19260744]
Abu-Hilal M, Salvia R, Casaril A, Pearce NW, Bassi C, Capelli P, Nicoli N. Obstructive chronic pancreatitis and/or intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs): a 21-year long case report. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2006; 7:218-21. [PMID 16525207]
Longnecker DS. Observations on the etiology and pathogenesis of intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Hepatogastroenterology 1998; 45:1973-80. [PMID 9951850]
Andrejevic-Blant S, Kosmahl M, Sipos B, Klöppel G. Pancreatic intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms: a new and evolving entity. Virchows Arch 2007; 451:863-9. [PMID 17899180]
Warshaw AL. Mucinous cystic tumors and mucinous ductal ectasia of the pancreas. Gastrointest Endosc 1991; 37:199-201. [PMID 1851710]
Traverso LW, Peralta EA, Ryan JA Jr, Kozarek RA. Intraductal neoplasms of the Pancreas. Am J Surg 1998; 175:426-32. [PMID 9600293]
Salvia R, Fernández-del Castillo C, Bassi C, Thayer SP, Falconi M, Mantovani W, et al. Main-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: clinical predictors of malignancy and long-term survival following resection. Ann Surg 2004; 239:678-85. [PMID 15082972]
Kalaitzakis E, Braden B, Trivedi P, Sharifi Y, Chapman R. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm in chronic calcifying pancreatitis: egg or hen. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15:1273-5. [PMID 19291831]
Falconi M, Salvia R, Bassi C, Zamboni G, Talamini G, Pederzoli P. Clinicopathological features and treatment of intraductal papillary mucinous tumour of the pancreas. Br J Surg 2001; 88:376-81. [PMID 11260102]
A-Cienfuegos J, Rotellar F, Martí-Cruchaga P, Valentí V, Zozaya G, Bueno A, et al. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN) of the pancreas: clinico-pathologic results. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2010; 102:314-20. [PMID 20524759]
Correa-Gallego C, Warshaw AL, Fernandez-del Castillo C. Fluid CEA in IPMNs: A useful test or the flip of a coin? Am J Gastroenterol 2009; 104:796-7. [PMID 19223886]
Pais SA, Attasaranya S, Leblanc J, Sherman S, Mchenry L, Schmidt M, Dewitt J. Utility of EUS-FNA and cyst fluid analysis in the diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous tumors: correlation with histopathology in 74 patients. Gastrointest Endosc 2006; 63:AB268.
Maker AV, Brennan MF, DeMatteo RP, D'Angelica MI, Fong Y, Jarnagin WR, Allen P. Cyst fluid cytokines to distinguish low- and high-risk intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMN). 2010 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium. Abstract No. 133.
Ikemoto T, Shimada M, Utsunomiya T, Imura S, Morine Y, Hanaoka J, et al. Evaluation of Foxp3/CD4/CD25/t cell (Treg) in peripheral blood as a biomarker for the aggressiveness of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm. 2010 ASCO Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium. Abstract No. 148.
Copyright (c) 2011 Athanasios Petrou, Alexandros Papalambros, Nicholas Brennan, Evangelos Prassas, Thoedora Margariti, Konstadinos Bramis, Theofilos Rozemberg, Efstathios Papalambros

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.