MicroRNA Expression Analyses in Preoperative Pancreatic Juice Samples of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Context Cytological assessment of pancreatic juice is commonly used to diagnose pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; however, the sensitivity of cytological assessment has been reported to be low. MicroRNAs are small RNAs regulating various cellular processes and have recently been identified as possible markers of malignant diseases including pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Objective The purposes of this study were to prove the existence of microRNAs in pancreatic juice and to determine whether specific microRNAs in pancreatic juice could be used for detecting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Methods Relative expression levels of microRNA-21 and microRNA-155 in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues of resected specimens (no. 13) and pancreatic juice samples collected using preoperative endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (no. 21) were quantified and their expression levels were then compared to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis. Results Relative expression levels of microRNA-21 in tissue and pancreatic juice samples were significantly higher in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma than those in chronic pancreatitis (P=0.009 and P=0.021, respectively). The same results were obtained in the expression levels of microRNA-155 in tissue and pancreatic juice between pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and chronic pancreatitis (P=0.014 and P=0.021, respectively). Expression levels of microRNA-21 and microRNA-155 did not correlate with the preoperative cytological results of pancreatic juice. Conclusion MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-155 in pancreatic juice have the potential of becoming biomarkers for diagnosing pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
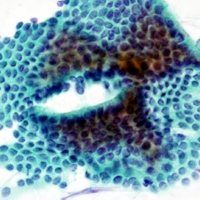
Image: Non-atypical cells in pancreatic juice.
Downloads
References
Hirata K, Egawa S, Kimura Y, Nobuoka T, Oshima H, Katsuramaki T, et al. Current status of surgery for pancreatic cancer. Dig Surg 2007; 24:137-47. [PMID 17476103]
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 2009; 59:225-49. [PMID 19474385]
Fujita N, Noda Y, Kobayashi G, Kimura K, Ito K. Endoscopic approach to early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2004; 28:279-81. [PMID 15084971]
Wakatsuki T, Irisawa A, Bhutani MS, Hikichi T, Shibukawa G, Takagi T, et al. Comparative study of diagnostic value of cytologic sampling by endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration and that by endoscopic retrograde pancreatography for the management of pancreatic mass without biliary stricture. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 20:1707-11. [PMID 16246190]
Pillai RS. MicroRNA function: multiple mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA 2005; 11:1753-61. [PMID 16314451]
Szafranska AE, Davison TS, John J, Cannon T, Sipos B, Maghnouj A, et al. MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2007; 26:4442-52. [PMID 17237814]
Wang J, Chen J, Chang P, LeBlanc A, Li D, Abbruzzesse JL, et al. MicroRNAs in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2009; 2:807-13. [PMID 19723895]
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, et al. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 2007; 297:1901-8. [PMID 17473300]
Moriyama T, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Yu J, Sato N, Nabae T, et al. MicroRNA-21 modulates biological functions of pancreatic cancer cells including their proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance. Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8:1067-74. [PMID 19435867]
Habbe N, Koorstra JB, Mendell JT, Offerhaus GJ, Ryu JK, Feldmann G, et al. MicroRNA miR-155 is a biomarker of early pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Biol Ther 2009; 8:340-6. [PMID 19106647]
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Yu J, Yamaguchi H, Konomi H, Nagai E, et al. S100A6 is increased in a stepwise manner during pancreatic carcinogenesis: clinical value of expression analysis in 98 pancreatic juice samples. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2007; 16:649-54. [PMID 17416753]
Peltier HJ, Latham GJ. Normalization of microRNA expression levels in quantitative RT-PCR assays: identification of suitable reference RNA targets in normal and cancerous human solid tissues. RNA 2008; 14:844-52. [PMID 18375788]
Nakashima A, Murakami Y, Uemura K, Hayashidani Y, Sudo T, Hashimoto Y, et al. Usefulness of human telomerase reverse transcriptase in pancreatic juice as a biomarker of pancreatic malignancy. Pancreas 2009; 38:527-33. [PMID 19342980]
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103:2257-61. [PMID 16461460]
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 2005; 65:7065-70. [PMID 16103053]
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM, Kosik KS. MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65:6029-33. [PMID 16024602]
Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, Wehbe H, Maheshwari S, Mendell JT, et al. Involvement of human micro-RNA in growth and response to chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Gastroenterology 2006; 130:2113-29. [PMID 16762633]
Kluiver J, Poppema S, de Jong D, Blokzijl T, Harms G, Jacobs S, et al. BIC and miR-155 are highly expressed in Hodgkin, primary mediastinal and diffuse large B cell lymphomas. J Pathol 2005; 207:243-9. [PMID 16041695]
Kluiver J, Haralambieva E, de Jong D, Blokzijl T, Jacobs S, Kroesen BJ, et al. Lack of BIC and microRNA miR-155 expression in primary cases of Burkitt lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2006; 45:147-53. [PMID 16235244]
Lu LF, Thai TH, Calado DP, Chaudhry A, Kubo M, Tanaka K, et al. Foxp3-dependent microRNA155 confers competitive fitness to regulatory T cells by targeting SOCS1 protein Immunity 2009; 30:80-91. [PMID 19144316]
Chen DF, Gong BD, Xie Q, Ben QW, Liu J, Yuan YZ. MicroRNA155 is induced in activated CD4(+) T cells of TNBS-induced colitis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16:854-61. [PMID 20143464]
Copyright (c) 2010 Yoshihiko Sadakari, Takao Ohtsuka, Kenoki Ohuchida, Kosuke Tsutsumi, Shunichi Takahata, Masafumi Nakamura, Kazuhiro Mizumoto, Masao Tanaka

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.