Effect of Protein Kinase C on Glucose-Mediated Insulin Secretion in HIT-T15 Cells
Abstract
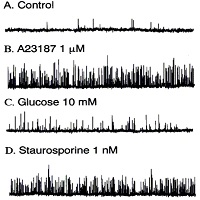
Objective To clarify the regulation of protein kinase C on glucose-mediated insulin secretion. Main outcome measures We examined the effect of protein kinase C on the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) and the activity of Ca2+-activated K+ channels (KCa-channel) in the insulinoma cell line, HIT-T15. Results Glucose at a concentration of 10 mmol/L increased the secretion of insulin. This increase was partly inhibited by 1 nmol/L staurosporine, a protein kinase C inhibitor. Staurosporine (1 nmol/L) also attenuated the glucose-induced elevations in [Ca2+]i. On the contrary, glibenclamide (100 nmol/L) specifically blocked ATP-sensitive K+ channels, and increased both [Ca2+]i and insulin secretion, but staurosporine had no effect on them. Patch clamp studies showed that 10 mmol/L glucose almost completely blocked KCa channel activity, an effect that was reversed by 1 nmol/L staurosporine. Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (1 mmol/L), a protein kinase C activator, also decreased KCa channel activity. Conclusions These results indicate that the activation of protein kinase C is involved in the glucose-induced release of insulin by modulating K+ channel function in HIT-T15 cells.
Image: Inhibitory effects of glucose on KCa channels.
Downloads
References
Ashcroft FM, Harrison DE, Ashcroft SJH. Glucose induces closure of single potassium channels in isolated rat pancreatic beta-cells. Nature 1984; 312:446-8.
Cook DL, Hales CN. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature 1984; 311:271-3.
Rorsman P, Trube G. Glucose dependent K+-channels in pancreatic beta-cells are regulated by intracellular ATP. Pflugers Arch 1985; 405:305-9.
Arkhammar P, Nilsson T, Rorsman P, Berggren PO. Inhibition of ATP-regulated K+ channels precedes depolarization-induced increase in cytoplasmic free Ca2+ concentration in pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem 1987; 262:5448-54.
Schmid-Antomarchi HS, Weille JD, Fosset M, Lazdunski M. The receptor for antidiabetic sulfonylureas controls the activity of the ATP-modulated K+ channel in insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem 1987; 262:15840-4.
Henquin JC, Charles S, Nenquin M, Mathot F, Tamagawa T. Diazoxide and D 600 inhibition of insulin release. Diabetes 1982; 31:776-83.
Gembal M, Gilon P, Henquin JC. Evidence that glucose can control insulin release independently from its action on ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse B cells. J Clin Invest 1992; 89:1288-95.
Gembal M, Detimary P, Gilon P, Gao ZY, Henquin JC. Mechanisms by which glucose can control insulin release independently from its action on adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K+ channels in mouse B cells. J Clin Invest 1993; 91:871-80.
Aizawa T, Sato Y, Ishihara F, Taguchi N, Komatsu M, Suzuki N, et al. ATP-sensitive K+ channel-independent glucose action in rat pancreatic b-cell. Am J Physiol 1994; 266:C622-7.
Berridge MJ, Irvine RF. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature 1984; 312:315-21.
Streb H, Irvine RF, Berridge MJ, Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature 1983; 306:67-9.
Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumor promotion. Nature 1984; 308:693-8.
Tanigawa K, Kuzuya H, Imura H, Taniguchi H, Baba S, Takai Y, et al. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in rat pancreas islets of langerhans. FEBS Lett 1982; 138:183-6.
Thams P, Capito K, Hedeskov CJ. Endogenous substrate proteins for Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent, Ca2+-phospholipid-dependent and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases in mouse pancreatic islets. Biochem J 1984; 221:247-53.
Lord JM, Ashcroft SJH. Identification and characterization of Ca2+-phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in rat islets and hamster beta-cells. Biochem J 1984; 219:547-51.
Hutton JC, Peshavaria M, Brocklehurst KW. Phorbol ester stimulation of insulin release and secretory-granule protein phosphorylation in a transplantable rat insulinoma. Biochem J 1984; 224:483-90.
Deeney JT, Cunningham BA, Chheda S, Bokvist K, Juntti-Berggren L, Lam K, et al. Reversible Ca2+-dependent translocation of protein kinase C and glucose-induced insulin release. J Biol Chem. 1996; 271:18154-60.
Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science 1986; 233:305-12.
Higashida H, Brown DA. Two polyphoshatidylinositide metabolites control two K+ currents in a neuronal cell. Nature 1986; 323:333-5.
Findlay I, Dunne MJ, Petersen OH. ATP-sensitive inward rectifier and voltage- and calcium-activated K+ channels in cultured pancreatic islet cells. J Membr Biol 1985; 88:165-72.
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch 1981; 391:85-100.
Nishizuka Y. The family of protein kinase C for signal transduction. J Am Med Assoc 1989; 262:1826-33.
Malaisse WJ, Sener A, Herchuelz A, Carpinelli AR, Poloczek P, Winand J, et al. Insulinotropic effect of the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in rat pancreatic islets. Cancer Res 1980; 40:3827-31.
Malaisse WJ, Lebrun P, Herchuelz A, Sener A, Malaisselagae F. Synergistic effect of a tumor-promoting phorbol ester and a hypoglycemic sulfonylurea upon insulin release. Endocrinology 1983; 113:1870-7.
Hii CST, Jones PM, Persaud SJ, Howell SL. A re-assessment of the role of protein kinase C in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Biochem J 1987; 246:489-93.
Hughes SJ, Chalk JG, Ashcroft SJH. The role of cytosolic free Ca2+ and protein kinase C in acetylcholine-induced insulin release in the clonal beta-cell line, HIT-T15. Biochem J 1990; 267:227-32.
Wollheim CB, Dunne MJ, Peter-Riesch B, Bruzzone R, Pozzan T, Petersen OH. Activators of protein kinase C depolarize insulin-secreting cells by closing K+ channels. EMBO J 1988; 7:2443-9.
Eddlestone GT, Ribalet B, Ciani S. Comparative study of K channel behavior in beta cell lines with different secretory responses to glucose. J Membr Biol 1989; 109:123-34.
Copyright (c) 2000 Hiroko Akiyoshi, Yutaka Nakaya

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.