Inflammation and Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Potential Scenario for Novel Drug Targets
Abstract
No abstract available.
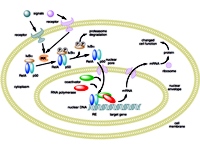
Image: Mechanism of NF-κB action (Author: Boghog2 from Wikimedia Commons)
Downloads
References
Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002; 420:860-7. [PMID 12490959]
Farrow B, Evers BM. Inflammation and the development of pancreatic cancer. Surg Oncol 2002; 10:153-69. [PMID 12020670]
Algül H, Treiber M, Lesina M, Schmid RM. Mechanisms of disease: chronic inflammation and cancer in the pancreas--a potential role for pancreatic stellate cells? Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007; 4:454-62. [PMID 17667994]
Whitcomb DC, Gorry MC, Preston RA, Furey W, Sossenheimer MJ, Ulrich CD, et al. Hereditary pancreatitis is caused by a mutation in the cationic trypsinogen gene. Nat Genet 1996; 14:141-5. [PMID 8841182]
Whitcomb DC, Applebaum S, Martin SP. Hereditary pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1999; 880:201-9. [PMID 10415865]
Howes N, Lerch MM, Greenhalf W, Stocken D, Ellis I, Simon P, et al. Clinical and genetic characteristics of hereditary pancreatitis in Europe. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 2:252-61. [PMID 15017610]
Lowenfels AB, Maissoneuve P, Cavallini G, Amman RW, Lankisch PG, Andersen JR, et al. Pancreatitis and the risk of pancreatic cancer. International Pancreatitis Study Group. N Engl J Med 1993; 328:1433-7. [PMID 8479461]
Rozenblum E, Schutte M, Goggins M, Hahn SA, Panzer S, Zahurak M, et al. Tumor-suppressive pathways in pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer Res 1997; 57:1731-4. [PMID 9135016]
Hruban RH, Wilentz RE, Kern SE. Genetic progression in the pancreatic ducts. Am J Pathol 2000; 156:1821-5. [PMID 10854204]
Greer JB, Whitcomb DC. Inflammation and pancreatic cancer: an evidence-based review. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2009; 9:411-8. [PMID 19589727]
Baldwin AS Jr. Series introduction: the transcription factor NF-kappaB and human disease. j Clin Invest 2001; 107:3-6. [PMID 11134170]
Wiseman H, Haliwell B. Damage to DNA by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: role in inflammatory disease and progression to cancer. Biochem J 1996; 313:17-29. [PMID 8546679]
Woutersen RA, Appel MJ, Van Garderen-Hoetmer A. Modulation of pancreatic carcinogenesis by antioxidants. Food Chem Toxicol 1999; 37:981-4. [PMID 10541454]
Kliewer SA, Wilson TM. The nuclear receptor PPARgamma-bigger than fat. Curr Opin Genet Dev 1998; 8:576-81. [PMID 9794815]
Cho N, Momose Y. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists as insulin sensitizers: from the discovery to recent progress. Curr Top Med Chem 2008; 8:1483-507. [PMID 19075761]
Krentz AJ, Patel MB, Bailey CJ. New drugs for type 2 diabetes mellitus: what is their place in therapy? Drugs 2008; 68:2131-62. [PMID 18840004]
Nakajima A, Tomimoto A, Fujita K, Sugiyama M, Takahashi H, Ikeda I, et al. Inhibition of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activity suppresses pancreatic cancer cell motility. Cancer Sci 2008; 99:1892-900. [PMID 19016747]
Dong YW, Wang XP, Wu K. Suppression of pancreatic carcinoma growth by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma involves angiogenesis inhibition. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 15:441-8. [PMID 19152448]
Eibl G. The role of PPAR-gamma and its interaction with COX-2 in pancreatic cancer. PPAR Res 2008; 2008:326915. [PMID 18615182]
Fesinmeyer MD, Stanford JL, Brentnall TA, Mandelson MT, Farin FM, Srinouanprachanh S, et al. Association between the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma Pro12Ala variant and haplotype and pancreatic cancer in a high-risk cohort of smokers: a pilot study. Pancreas 2009; 38:631-7. [PMID 19436234]
Giaginis C, Katsamangou E, Tsourouflis G, Zizi-Serbetzoglou D, Kouraklis G, Theocharis S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and retinoid X receptor-alpha expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: association with clinicopathological parameters, tumor proliferative capacity, and patients' survival. Med Sci Monit 2009; 15:148-56. [PMID 19396032]
Harris RE, Beebe-Donk J, Doss H, Burr Doss D. Aspirin, ibuprofen, and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in cancer prevention: a critical review of non-selective COX-2 blockade. Oncol Rep 2005; 13:559-83. [PMID 15756426]
Chen YF, Jobanputra P, Barton P, Bryan S, Fry-Smith A, Harris G, Taylor RS. Cyclooxygenase-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (etodolac, meloxicam, celecoxib, rofecoxib, etoricoxib, valdecoxib and lumiracoxib) for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and economic evaluation. Health Technol Assess 2008; 12:1-278. [PMID 18405470]
Seo SW, Jung WS, Piao TG, Hong SH, Yun KJ, Park RK, et al. Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor ameliorates cholecystokinin-octapeptide-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13:2298-304. [PMID 17511027]
Talukdar R, Saikia N, Singal DK, Tandon R. Chronic pancreatitis: evolving paradigms. Pancreatology 2006; 6:440-9. [PMID 16847381]
Hermanova M, Trna J, Nenutil R, Dite P, Kala Z. Expression of COX-2 is associated with accumulation of p53 in pancreatic cancer: analysis of COX-2 and p53 expression in premalignant and malignant ductal pancreatic lesions. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008; 20:732-9. [PMID 18617777]
Albazaz R, Verbeke CS, Rahman SH, McMahon MJ. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression associated with severity of PanIN lesions: a possible link between chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology 2005; 5:361-9. [PMID 15980665]
Whitcomb DC. Clinical practice. Acute pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 2006; 354:2142-5. [PMID 16707751]
Aoki H, Ohnishi H, Hama K, Shinozaki S, Kita H, Osawa H, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 is required for activated pancreatic stellate cells to respond to proinflammatory cytokines. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2007; 292:259-68. [PMID 16837651]
Moses AG, Maingay J, Sangster K, Fearon CH, Ross JA. Pro-inflammatory cytokine release by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: relationship to acute phase response and survival. Oncol Rep 2009; 21:1091-5. [PMID 19288013]
Falconer JS, Fearon KC, Plester CE, Ross JA, Carter DC. Cytokines, the acute-phase response, and resting energy expenditure in cachectic patients with pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg 1994; 219:325-31. [PMID 7512810]
Uomo G, Gallucci F, Rabitti PG. Anorexia-cachexia syndrome in pancreatic cancer: recent development in research and management. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2006; 6:157-62. [PMID 16525199]
Istituto Nazionale di Statistica (National Institute of Statistics). Cause di morte 2001 (Causes of deaths, 2001). Annuario ISTAT 2007.
Raimondi S, Maisonneuve P, Lowenfels AB. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: an overview. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009; 6:699-708. [PMID 19806144]
Whitcomb D, Greer J. Germ-line mutations, pancreatic inflammation, and pancreatic cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2009; 7(11 Suppl):S29-34. [PMID 19896094]
Copyright (c) 2010 Ilaria Uomo, Simona Miraglia, Maurizio Pastorello

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.