Micronutrient Therapy for Chronic Pancreatitis: Rationale and Impact
Abstract
Micronutrient therapy, designed to buttress tissue methyl and thiol groups, curbs attacks and controls background pain in patients with chronic pancreatitis, irrespective of aetiology. This outcome and the premises upon which it is based facilitate an understanding of links with mutations in genes for hereditary pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis, demography, and predisposition to pancreatic cancer. Above all, there is an opportunity for prophylaxis in individuals at high risk of developing the disease.
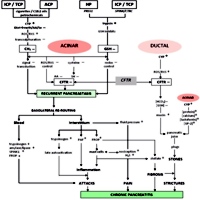
Image: A template for the pathogenesis of chronic pancreatitis.
Downloads
References
Cawley T. A singular case of diabetes, consisting entirely in the quantity of urine: With an inquiry into the different theories of the disease. Lond Med J 1788; 9:286-308.
Ahmad SA, Lowy AM, Wray CJ, D'Alessio D, Choe KA, James LE, et al. Factors associated with insulin and narcotic independence after islet autotransplantation in patients with severe chronic pancreatitis. J Am Coll Surg 2005; 201:680-7. [PMID 16256909] (FULL TEXT: http://www.journalacs.org/article/PIIS1072751505010458/fulltext)
Braganza JM. Pancreatic disease: a casualty of hepatic 'detoxification'? Lancet 1983; ii:1000-3. [PMID 6138545]
Braganza JM. The pancreas. Recent Adv Gastroenterol Lond, Churchill-Livingstone, 1986; 6:251-80.
Guyan PM, Uden S, Braganza JM. Heightened free radical activity in pancreatitis. Free Radic Biol Med 1990; 8:347-54. [PMID 2379863]
Uden S, Bilton D, Nathan L, Hunt LP, Main C, Braganza JM. Antioxidant therapy for recurrent pancreatitis: placebo-controlled trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1990; 4:357-71. [PMID 2103755] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/119377775/PDFSTART)
Uden S, Schofield D, Miller PF, Day JP, Bottiglieri T, Braganza JM. Antioxidant therapy for recurrent pancreatitis: biochemical profiles in a placebo-controlled trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1992; 6:229-40. [PMID 1600043] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/119328110/PDFSTART)
Bilton D, Schofield D, Mei G, Kay PM, Bottiglieri T, Braganza JM. Placebo-controlled trials of antioxidant therapy including S-adenosulmethionine in patients with recurrent non-gallstone pancreatitis. Drug Invest 1994; 8:10-20.
McCloy R. Chronic pancreatitis at Manchester, UK. Focus on antioxidant therapy. Digestion 1998; 59(Suppl 4):36-48. [PMID 9832634] (FULL TEXT: http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=51441&Ausgabe=227780&ProduktNr=223838&filename=51441.pdf)
Bhardwaj P, Garg PK, Maulik SK, Saraya A, Tandon RK, Acharya SK. A randomized controlled trial of antioxidant supplementation for pain relief in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2009; 136:149-59. [PMID 18952082] (FULL TEXT: http://www.gastrojournal.org/article/PIIS0016508508016971/fulltext)
De las Heras Castaño G, García de la Paz A, Fernández MD, Fernández Forcelledo JL. Use of antioxidants to treat pain in chronic pancreatitis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2000; 92;381-85. [PMID 10985097]
Kirk GR, White JS, McKie L, Stevenson M, Young I, Clements WD, Rowlands BJ. Combined antioxidant therapy reduces pain and improves quality of life in chronic pancreatitis. J Gastrointest Surg 2006; 10:499-503. [PMID 16627214] (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/p40h317232701u85/fulltext.pdf)
Dítě P, Prěcechtelová M, Novotný I, Soška V, Źáková A, Lata J. Changes of reactive oxidative substances in patients with morphologically different degrees of chronic pancreatitis and effects of long-term therapy with natural antioxidants. Gastroenterologia Polska 2003; 10: 379-83. (FULL TEXT: http://www.cornetis.com.pl/artykul_en.php?issn=1232-9886&rok=2003&numer=4&str_p=379)
Uomo G, Talamini G, Rabitti PG. Antioxidant treatment in hereditary pancreatitis. A pilot study on three young patients. Dig Liver Dis 2001; 33:58-62. [PMID 11303976] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B7582-4B1WW1V-95-1&_cdi=12914&_user=839424&_pii=S1590865801801365&_orig=browse&_coverDate=02%2F28%2F2001&_sk=999669998&view=c&wchp=dGLzVtz-zSkWA&md5=717e10aab86ee4e72bbeb37033f721a6&ie=/sdarticle.pdf)
Braganza JM. The pathogenesis of chronic pancreatitis. QJM 1996; 89:243-50. [PMID 8733510] (FULL TEXT: http://qjmed.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/reprint/89/4/243)
Mitchell RM, Byrne MF, Baillie J. Pancreatitis. Lancet 2003; 361:1447-55. [PMID 12727412] (FULL TEXT: http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(03)13139-X/fulltext)
Braganza JM. Towards a novel treatment strategy for acute pancreatitis. 1. Reappraisal of the evidence on aetiogenesis. Digestion 2001; 63:69-91. [PMID 11244246] (FULL TEXT: http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=51875&Ausgabe=227804&ProduktNr=223838&filename=51875.pdf)
Lin TM, Grossman MI. Reversal by DL-methionine of acute effect of DL-ethionine on pancreatic enzyme output in dogs. Am J Physiol 1954; 176: 377-80. [PMID 16193325] (FULL TEXT: http://ajplegacy.physiology.org/cgi/reprint/176/3/377)
Cook LJ, Musa OA, Case RM. Intracellular transport of pancreatic enzymes. Scand J Gastroenterol 1996; 31(Suppl 219):1-5. [PMID 8865462]
Rinderknecht H. Acute necrotizing pancreatitis and its complications: an excessive reaction of natural defence mechanisms? In: Braganza JM (ed). The pathogenesis of Pancreatitis Manchester, UK: Manchester University Press, 1990; 86-100.
Gaisano HY, Gorelick FS. New insights into the mechanisms of pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2009; 136:2020-4. [PMID 19379751] (FULL TEXT: http://www.gastrojournal.org/article/PIIS001650850900568X/fulltext)
Halangk W, Krüger B, Ruthenbürger M, Stürzebecher J, Albrecht E, Lippert H, Lerch MM. Trypsin activity is not involved in premature intrapancreatic trypsinogen activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2002; 282: G367-74. [PMID 11804859] (FULL TEXT: http://ajpgi.physiology.org/cgi/content/full/282/2/G367)
Gaiser S, Ahler A, Gundling F, Kruse ML, Savkovic V, Selig L, et al. Expression of mutated cationic trypsinogen reduces cellular viability in AR4-2J cells. Bochim Biophys Res Commun 2005; 334:721- 8. [PMID 16036133] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WBK-4GJV95J-4&_user=839424&_coverDate=08%2F26%2F2005&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000045367&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=839424&md5=4025d8839e6da29b65c0fe5cd7d5be0c)
Mantke R, Schubert D, Röcken C, Paege I, Halangk W, Peters B, et al. Caerulein or taurocholate induced enzymatic and histologic alterations in the isolated perfused rat pancreas. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2009; 394:363-9. [PMID 18690472] (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/h3875811w3l48504/fulltext.html)
Braganza JM. Towards a novel treatment strategy for acute pancreatitis. 2. Principles and potential practice. Digestion 2001; 63:143-62. [PMID 11351142] (FULL TEXT: http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=51884&Ausgabe=227805&ProduktNr=223838&filename=51884.pdf)
Leung PS, Chan YC. Role of oxidative stress in pancreatic inflammation. Antioxid Redox Signal 2009 ;11:135-65. [PMID 18837654] (FULL TEXT: http://www.liebertonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1089/ars.2008.2109)
Braganza JM. A framework for the pathogenesis of chronic pancreatitis. Digestion 1998; 59(Suppl 4):1-12. [PMID 9832631] (FULL TEXT: http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=51438&Ausgabe=227780&ProduktNr=223838&filename=51438.pdf)
Jin CX, Hayakawa T, Kitagawa M, Ishiguro H. Lactoferrin in chronic pancreatitis. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2009; 10:237-41. [PMID 19454813] (FULL TEXT: http://www.joplink.net/prev/200905/04.html)
Houston JM. Cytochromes P450 in chronic pancreatitis. In: Braganza JM (ed). The Pathogenesis of Pancreatitis Manchester, UK: Manchester University Press 1991: 103-14.
Gonzalez FJ. Role of cytochromes P450 in chemical toxicity and oxidative stress: studies with CYP2E1. Mutat Res 2005; 569:101-10. [PMID 15603755] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T2C-4DTSMJG-2&_user=839424&_coverDate=01%2F06%2F2005&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000045367&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=839424&md5=86d7a89376abe3cc2ea623c81fd9f277)
Golden MHN. The exocrine pancreas in severe malnutrition. In: Braganza JM (ed). The Pathogenesis of Pancreatitis Manchester, UK: Manchester University Press 1991: 139-55.
Wallig M. Xenobiotic metabolism, oxidant stress and chronic pancreatitis. Digestion 1998; 59(Suppl 4):13-24. [PMID 9832632] (FULL TEXT: http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=51439&Ausgabe=227780&ProduktNr=223838&filename=51439.pdf)
Segal I. Pancreatitis in Soweto, South Africa. Focus on alcohol-related disease. Digestion 1998; 59(Suppl 4):25-35. [PMID 9832633] (FULL TEXT: http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=51440&Ausgabe=227780&ProduktNr=223838&filename=51440.pdf)
Chowdhury P, Gupta P. Pathophysiology of alcoholic pancreatitis: an overview. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12:7421-7. [PMID 17167828] (FULL TEXT: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/12/7421.asp)
Askari MD, Tsao MS, Cekanova M, Schuller HM. Ethanol and the tobacco-specific carcinogen, NNK, contribute to signaling in immortalized human pancreatic duct epithelial cells. Pancreas 2006; 33:53-62. [PMID 16804413] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2006&issue=07000&article=00008&type=abstract)
Li J, Guo M, Hu B, Liu R, Wang R, Tang C. Does chronic ethanol intake cause chronic pancreatitis?: evidence and mechanism. Pancreas 2008; 37:189-95. [PMID 18665082] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2008&issue=08000&article=00013&type=abstract)
Strubelt O. Interactions between ethanol and other hepatotoxic agents. Biochem Pharmacol 1980; 29: 1445-9. [PMID 6994745] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6T4P-478FNKD-J0-1&_cdi=4980&_user=839424&_pii=0006295280905912&_orig=browse&_coverDate=06%2F01%2F1980&_sk=999709988&view=c&wchp=dGLbVzW-zSkWA&md5=1c37b0f0d0eb85f9c6c80ad4f14fa33c&ie=/sdarticle.pdf)
McNamee R, Braganza JM, Hogg J, Leck I, Rose P, Cherry NM. Occupational exposure to hydrocarbons and chronic pancreatitis: a case-referent study. Occup Environ Med 1994; 51:631-7. [PMID 7951796] (FULL TEXT: http://oem.bmj.com/content/51/9/631.full.pdf)
Jeppe CY, Smith MD. Transversal descriptive study of xenobiotic exposures in patients with chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2008; 9:235-9. [PMID 18326937] (FULL TEXT: http://www.joplink.net/prev/200803/04.html)
Braganza JM, John S, Padmalayam I, Mohan V, Viswanathan M, Chari S, Madanagopalan M. Xenobiotics and tropical chronic pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol 1990; 7:231-45. (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/x738006566676473/fulltext.pdf)
Acheson DW, Hunt LP, Rose P, Houston JB, Braganza JM. Factors contributing to the accelerated clearance of theophylline and antipyrine in adults with exocrine pancreatic disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 1989; 76:377-85. [PMID 2714050]
Foster JR, Idle JR, Hardwick JP, Bars R, Scott P, Braganza JM. Induction of drug-metabolizing enzymes in human pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis. J Pathol 1993;169:457-63. [PMID 8501544] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/110535579/PDFSTART)
Wacke R, Kirchner A, Prall F, Nizze H, Schmidt W, Fischer U, et al. Up-regulation of cytochrome P450 1A2, 2C9 and 2E1 in chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas 1998; 16:521-8. [PMID 9598815] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=1998&issue=05000&article=00011&type=abstract)
Standop J, Schneider M, Ulrich A, Büchler MW, Pour PM. Differences in immunohistochemical expression of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes between normal pancreas, chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Toxicol Pathol 2003; 31:506-13. [PMID 14692619] (FULL TEXT: http://tpx.sagepub.com/cgi/reprint/31/5/506)
Schoenberg MH, Büchler M, Pietrzyk C, Uhl W, Birk D, Eisele S, et al. Lipid peroxidation and glutathione metabolism in chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas 1995; 10:36-43. [PMID 7899458] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/toc/1995/01000)
Santini SA, Spada C, Bononi F, Foschia F, Mutignani M, Perri V, et al. Liver, pancreas and biliary tract enhanced lipoperoxidation products in pure pancreatic juice: evidence for organ-specific oxidative stress in chronic pancreatitis. Dig Liver Dis 2003; 35:888-92. [PMID 14703885] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B7582-49YD0YT-8-10&_cdi=12914&_user=839424&_pii=S159086580300519X&_orig=browse&_coverDate=12%2F31%2F2003&_sk=999649987&view=c&wchp=dGLzVtb-zSkWA&md5=3ebad1e990e95b10a83d92ca3893ce29&ie=/sdarticle.pdf)
Pai GC, Rao MNS. Evidence for oxidant stress in chronic pancreatitis. Indian J Gastroenterol 1999; 18:156-7. [PMID 10531717]
Gutteridge JMC. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidants as biomarkers of tissue damage. Clin Chem 1995; 41:1819-28. [PMID 7497639] (FULL TEXT: http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/reprint/41/12/1819)
Weber H, Merkord J, Jonas L, Wagner A, Schröder H, Käding U, et al. Oxygen radical generation and acute pancreatitis: effects of dibutyltin dichloride/ethanol and ethanol on rat pancreas. Pancreas 1995; 11:382-8. [PMID 8532655] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/toc/1995/11000)
Ulrich AB, Schmied BM, Matsuzaki H, Lawson TA, Freiss H, Andrén-Sandberg A, et al. Increased expression of glutathione S-transferase-pi in the islets of patients with primary chronic pancreatitis but not secondary chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas 2001; 22:388-94. [PMID 11345140] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2001&issue=05000&article=00009&type=abstract)
Ulrich AB, Schmied BM, Standop J, Schneider MB, Lawson TA, Friess H, et al. Differences in the expression of glutathione S-transferases in normal pancreas, chronic pancreatitis, secondary chronic pancreatitis, and pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2002; 24:291-7. [PMID 11893938] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2002&issue=04000&article=00013&type=abstract)
Hausmann DH, Porstmann T, Weber I, Hausmann S, Dummler W, Liebe S, Emmrich J. Cu/Zn-SOD in human pancreatic tissue and pancreatic juice. Int J Pancreatol 1997; 22:207-13. [PMID 9444552] (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/bhgp72251q4064p3/fulltext.pdf)
Cullen JJ, Mitros FA, Oberley LW. Expression of antioxidant enzymes in diseases of the human pancreas: another link between chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2003; 26:23-7. [PMID 12499913] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2003&issue=01000&article=00005&type=abstract)
Brown LA. Glutathione protects signal transduction in type II cells under oxidant stress. Am J Physiol 1994; 266: 172-7. [PMID 7511342] (FULL TEXT: http://ajplung.physiology.org/cgi/reprint/266/2/L172)
Longnecker DS. Abnormal methyl metabolism in pancreatic toxicity and diabetes. J Nutr 2002; 132:2373-6s. [PMID 12163695] (FULL TEXT: http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/content/full/132/8/2373S)
Mårtensson J, Bolin T. Sulfur amino acid metabolism in chronic relapsing pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 1986; 81:1179-84. [PMID 3788926]
Verlaan M, Roelofs HM, van-Schaik A, Wanten GJ, Jansen JB, Peters WH, Drenth JP. Assessment of oxidative stress in chronic pancreatitis patients. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12:5705-10. [PMID 17007026] (FULL TEXT: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/12/5705.asp)
Sajewicz W, Milnerowicz S, Nabzdyk S. Blood plasma antioxidant defense in patients with pancreatitis. Pancreas 2006; 32:139-44. [PMID 16552332] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2006&issue=03000&article=00003&type=abstract)
Schrader H, Menge BA, Belyaev O, Uhl W, Schmidt WE, Meier JJ. Amino acid metabolism in patients with chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma. Pancreas 2009; 38:416-21. [PMID 19169171] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2009&issue=05000&article=00010&type=abstract)
Syrota A, Dop-Ngassa M, Paraf A. 11C-L-methionine for evaluation of pancreatic exocrine function. Gut 1981; 22:907-15. [PMID 6171485] (FULL TEXT: http://gut.bmj.com/content/22/11/907.full.pdf)
Schemann M, Grundy D. Role of hydrogen sulfide in visceral nociception. Gut 2009; 58:744-6. [PMID 19433593] (FULL TEXT: http://gut.bmj.com/content/58/6/744.long)
Morselli-Labate AM, Fantini L, Pezzilli R. Hydrogen sulfide, nitric oxide and a molecular mass 66 u substance in the exhaled breath of chronic pancreatitis patients. Pancreatology 2007; 7:497-504. [PMID 17912017] (FULL TEXT: http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=000108967&Ausgabe=233825&ProduktNr=224334&filename=000108967.pdf)
Nishimura S, Fukushima O, Ishikura H, Takahashi T, Matsunami M, Tsujiuchi T, et al. Hydrogen sulfide as a novel mediator for pancreatic pain in rodents. Gut 2009; 58:762-70. [PMID 19201768] (FULL TEXT: http://gut.bmj.com/content/58/6/762.long)
Rahman SH, Nanny C, Ibrahim K, O'Reilly D, Larvin M, Kingsnorth AJ, McMahon MJ. Genetic polymorphisms of GSTT1, GSTM1, GSTP1, MnSOD, and catalase in nonhereditary chronic pancreatitis: evidence of xenobiotic stress and impaired antioxidant capacity. Dig Dis Sci 2005; 50:1376-83. [PMID 16047490] (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/w64151mkp3643tx3/fulltext.pdf)
Osterreicher CH, Schultheiss J, Wehler M, Homann N, Hellerbrand C, Künzli B, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of manganese-superoxide dismutase and glutathione-S-transferase in chronic alcoholic pancreatitis. Mutagenesis 2007; 22:305-10. [PMID 17548864] (FULL TEXT: http://mutage.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/22/5/305)
Verlaan M, Harbers EG, Pap A, Jansen JB, Peters WH, Drenth JP. Paraoxonase 1-192Q allele is a risk factor for idiopathic chronic pancreatitis. Mol Diagn 2005; 9:9-15. [PMID 16035730]
Uden S, Acheson DW, Reeves J, Worthington HV, Hunt LP, Brown S, Braganza JM. Antioxidants, enzyme induction, and chronic pancreatitis: a reappraisal following studies in patients on anticonvulsants. Eur J Clin Nutr 1988; 42:561-9. [PMID 3224602]
Braganza JM, Hewitt C, Day JP. Serum selenium concentration in chronic pancreatitis: lowest values during painful exacerbations. Trace Elem Med 1988; 5: 79-84.
Van Gossum A, Closset P, Noel E, Cremer M, Neve J. Deficiency in antioxidant factors in patients with alcohol-related chronic pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 1996; 41:1225-31. [PMID 8654156] (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/nx166k605407tl0r/fulltext.pdf)
Morris-Stiff GJ, Bowrey DJ, Oleesky D, Davies M, Clark GW, Puntis MC. The antioxidant profiles of patients with recurrent acute and chronic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 1999; 94:2135-40. [PMID 10445540] (FULL TEXT: http://www.nature.com/ajg/journal/v94/n8/full/ajg1999514a.html)
Vaona B, Stanzial AM, Talamini G, Bovo P, Corrocher R, Cavallini G. Serum selenium concentrations in chronic pancreatitis and controls. Dig Liver Dis 2005; 37:522-5. [PMID 15975540] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B7582-4FWSDNV-1&_user=839424&_coverDate=07%2F31%2F2005&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000045367&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=839424&md5=f774ceed75f6dccfa6b01f08e63f977a)
Schulz KF, Grimes DA. Sample size calculations in randomised trials: mandatory and mystical. Lancet 2005; 365:1348-53. [PMID 15823387] (FULL TEXT: http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(05)61034-3/fulltext)
Schofield D, Braganza JM. Shortcomings of an automated assay for total antioxidant status in biological fluids. Clin Chem 1996; 42:1712-14. [PMID 8855160] (FULL TEXT: http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/reprint/42/10/1712)
Benzie IFF, Strain JJ. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of "antioxidant power": the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 1996; 239:70-6. [PMID 8660627] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6W9V-45N4P63-78-1&_cdi=6692&_user=839424&_pii=S0003269796902924&_orig=browse&_coverDate=07%2F15%2F1996&_sk=997609998&view=c&wchp=dGLbVzz-zSkzV&md5=73ef7fed22117abd4052bb0bd8597332&ie=/sdarticle.pdf)
Braganza JM, Schofield D, Snehalatha C, Mohan V. Micronutrient antioxidant status in tropical compared with temperate-zone chronic pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 1993; 28: 1098-104. [PMID 8303214]
Scott PD, Knoop M, McMahon RFT, Braganza JM, Hutchinson IV. S-Adenosyl-L-Methionine protects against haemorrhagic pancreatitis in partially immunosuppressed pancreaticoduodenal transplant recipients. Drug Invest 1992; 4(Suppl 4):69-77.
de Las Heras-Castaño G, García-Unzueta MT, Domínguez-Diez A, Fernández-González MD, García-de la Paz AM, Mayorga-Fernández M, Fernández-Fernández F. Pancreatic fibrosis in rats and its response to antioxidant treatment. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2005; 6:316-24. [PMID 16006681] (FULL TEXT: http://www.joplink.net/prev/200507/03.html)
Nonaka A, Manabe T, Tobe T. Effect of a new synthetic ascorbic acid derivative as a free radical scavenger on the development of acute pancreatitis in mice. Gut 1991; 32:528-32. [PMID 1710198] (FULL TEXT: http://gut.bmj.com/content/32/5/528.full.pdf)
Nonaka A, Manabe T, Kyogoku T, Tamura K, Tobe T. Evidence for a role of free radicals by synthesized scavenger, 2-octadecylascorbic acid, in cerulein-induced mouse acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 1992; 37:274-9. [PMID 1370933] (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/t0620783q08756j4/fulltext.pdf)
Lu XL, Song YH, Fu YB, Si JM, Qian KD. Ascorbic acid alleviates pancreatic damage induced by dibutyltin dichloride (DBTC) in rats. Yonsei Med J 2007; 48:1028-34. [PMID 18159597] (FULL TEXT: http://www.eymj.org/search.php?where=aview&id=59465&code=0069YMJ&vmode=FULL)
Swiery JH, Mann GE. Role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol 1996; 31(Suppl 219):10-5. [PMID 8865464]
Arnold R, Fodov G, Mathelier H, Mohasci T, Szent-Györgyi A, Veltri RW. Recent aspects of the chemistry of vitamin C. In: McBrien DCH, Slater TF (eds). Protective Agents in Cancer London, UK :Academic Press 1983:197-213.
Sowell J, Frei B, Stevens JF. Vitamin C conjugates of genotoxic lipid peroxidation products: structural characterization and detection in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101:17964-9. [PMID 15608056] (FULL TEXT: http://www.pnas.org/content/101/52/17964.full)
Winkler BS. Unequivocal evidence in support of the nonenzymatic redox coupling between glutathione/glutathione disulfide and ascorbic acid/dehydroascorbic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta 1992, 1117:287-90. [PMID 1420278]
Mårtensson J, Han J, Griffith OW, Meister A. Glutathione ester delays the onset of scurvy in ascorbate-deficient guinea pigs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90:317-21. [PMID 8419936] (FULL TEXT: http://www.pnas.org/content/90/1/317.full.pdf+html)
Lieb JG 2nd, Forsmark CE. Review article: pain and chronic pancreatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2009; 29:706-19. [PMID 19284407] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/121637831/HTMLSTART)
Grimble RF. The effects of sulfur amino acid intake on immune function in humans. J Nutr 2006; 136:1660S-5s. [PMID 16702336] (FULL TEXT: http://jn.nutrition.org/cgi/content/full/136/6/1660S)
Zimnoch L, Szynaka B, Puchalski Z. Mast cells and pancreatic stellate cells in chronic pancreatitis with differently intensified fibrosis. Hepatogastroenterology 2002; 49:1135-8. [PMID 12143220]
Dib M, Zhao X, Wang X, Andersson R. Mast cells contribute to early pancreatitis-induced systemic endothelial barrier dysfunction. Pancreatology 2002; 2:396-401. [PMID 12138228] (FULL TEXT: http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=65087&Ausgabe=228598&ProduktNr=224334&filename=65087.pdf)
Hoogerwerf WA, Gondesen K, Xiao SY, Winston JH, Willis WD, Pasricha PJ. The role of mast cells in the pathogenesis of pain in chronic pancreatitis. BMC Gastroenterol 2005; 5:8. [PMID 15745445] (FULL TEXT: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-230X/5/8)
Salim AS. Role of oxygen-derived free radical scavengers in the treatment of recurrent pain produced by chronic pancreatitis. Arch Surg 1991; 126:1109-14. [PMID 1929842] (FULL TEXT: http://archsurg.ama-assn.org/cgi/reprint/126/9/1109)
Yoshida A, Yokono O, Oda T. Therapeutic effect of chlorophyll-A in the treatment of patients with chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterol Jpn 1980; 15:49-61. [PMID 6153629]
Banks PA, Hughes M, Ferrante M, Noordhoek EC, Ramagopal V, Slivka A. Does allopurinol reduce pain of chronic pancreatitis? Int J Pancreatol 1997; 22:171-6. [PMID 9444547] (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/l038585452vm3146/fulltext.pdf)
Durgaprasad S, Pai CG, Vasanthkumar, Alvres JF, Namitha S. A pilot study of the antioxidant effect of curcumin in tropical pancreatitis. Indian J Med Res 2005; 122:315-8. [PMID 16394323] (FULL TEXT: http://www.icmr.nic.in/ijmr/2005/october/1005.pdf)
Szuster-Ciesielska A, Daniluk J, Kandefer-Szerszeń M. Oxidative stress in blood of patients with alcohol-related pancreatitis. Pancreas 2001; 22:261-6. [PMID 11291927] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2001&issue=04000&article=00006&type=abstract)
Banerjee B, Bagchi D. Beneficial effects of a novel IH636 grape seed proanthocyanidin extract in the treatment of chronic pancreatitis. Digestion 2001; 63:203-6. [PMID 11351148] (FULL TEXT: http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=51890&Ausgabe=227805&ProduktNr=223838&filename=51890.pdf)
Leach FN, Braganza JM. Treatment of recurrent pancreatitis with antioxidants. Hosp Pharmacist 1997; 4:169-71.
Ghyczy M, Boros M. Electrophilic methyl groups present in the diet ameliorate pathological states induced by reductive and oxidative stress: a hypothesis. Br J Nutr 2001; 85:409-14. [PMID 11348555] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayFulltext?type=6&fid=889856&jid=&volumeId=&issueId=04&aid=889852&bodyId=&membershipNumber=&societyETOCSession=&fulltextType=RV&fileId=S0007114501000642)
Ghyczy M, Torday C, Boros M. Simultaneous generation of methane, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide from choline and ascorbic acid: a defensive mechanism against reductive stress? FASEB J 2003; 17:1124-6. [PMID 12692080] (FULL TEXT: http://www.fasebj.org/cgi/reprint/02-0918fjev1)
Chen JM, Férec C. Chronic pancreatitis: genetics and pathogenesis. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2009; 10:63-87. [PMID 19453252] (FULL TEXT: http://arjournals.annualreviews.org/doi/full/10.1146/annurev-genom-082908-150009?amp;searchHistoryKey=%24%7BsearchHistoryKey%7D)
Mahurkar S, Reddy DN, Rao GV, Chandak GR. Genetic mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of tropical calcific pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2009; 21:256-69. [PMID 19140225] (FULL TEXT: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/15/264.asp)
Steven FS, Al-Habib A. Inhibition of trypsin and chymotrypsin by thiols. Biphasic kinetics of reactivation and inhibition induced by sodium periodate addition. Biochim Biophys Acta 1979; 568:408-15. [PMID 226148]
Steven FS, Griffin MM. Studies on the molecular mechanism of mersalyl and 4-aminophenylmercuric acetate re-activation of trypsin-thiol complexes. Eur J Biochem 1980; 109:567-73. [PMID 7408902] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/120758796/PDFSTART)
Chauhan UP. Glutathione as inhibitor of trypsin induced proteolysis. Indian J Exp Biol 1989; 27:472-3. [PMID 2599558]
Mathew P, Wyllie R, Van Lente F, Steffen RM, Kay MH. Antioxidants in hereditary pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 1996; 91:1558-62. [PMID 8759661]
Georgelin T, Schnee M, Sagniez M, Bailly F, Naudot I, Soulard FM, Martin F. Antioxidant status in patients with hereditary chronic pancreatitis (HCP) and alcoholics. Gastroenterology 1998; 114: A461. (FULL TEXT: http://download.journals.elsevierhealth.com/pdfs/journals/0016-5085/PIIS0016508598818647.pdf)
Dodge JA. Paediatric and hereditary aspects of chronic pancreatitis. Digestion 1998; 59(Suppl 4):49-59. [PMID 9832635] (FULL TEXT: http://content.karger.com/ProdukteDB/produkte.asp?Aktion=ShowPDF&ArtikelNr=51442&Ausgabe=227780&ProduktNr=223838&filename=51442.pdf)
Sharer N, Schwarz M, Malone G, Howarth A, Painter J, Super M, Braganza J. Mutations of the cystic fibrosis gene in patients with chronic pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 1998; 339:645-52. [PMID 9725921] (FULL TEXT: http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/339/10/645)
Cohn JA, Friedman KJ, Noone PG, Knowles MR, Silverman LM, Jowell PS. Relation between mutations of the cystic fibrosis gene and idiopathic pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 1998; 339:653-8. [PMID 9725922] (FULL TEXT: http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/339/10/653)
Cohn JA. Reduced CFTR function and the pathobiology of idiopathic pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2005; 39:S70-7. [PMID 15758663] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/jcge/Fulltext/2005/04002/Reduced_CFTR_Function_and_the_Pathobiology_of.8.aspx)
Uden S, Bilton D, Guyan PM, Kay PM, Braganza JM. Rationale for antioxidant therapy in pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis. Adv Exp Med Biol 1990; 264:555-72. [PMID 2244539]
Tang S, Beharry S, Kent G, Durie PR. Synergistic effects of cAMP- and calcium-mediated amylase secretion in isolated pancreatic acini from cystic fibrosis mice. Pediatric Res 1999; 45:482-8. [PMID 10203138] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pedresearch/Fulltext/1999/04010/Synergistic_Effects_of_cAMP__and_Calcium_Mediated.5.aspx)
Zeng W, Lee MG, Yan M, Diaz J, Benjamin I, Marino CR, et al. Immuno and functional characterization of CFTR in submandibular and pancreatic acinar and duct cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 1997; 273:C442-5. [PMID 9277342] (FULL TEXT: http://ajpcell.physiology.org/cgi/reprint/273/2/C442)
Morris AP, Frizzell RA. Vesicle targeting and ion secretion in epithelial cells: implications for cystic fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol 1994; 56:371-97. [PMID 7516644] (FULL TEXT: http://arjournals.annualreviews.org/doi/pdf/10.1146/annurev.ph.56.030194.002103)
Quesnel LB, Jaran AS, Braganza JM. Antibiotic accumulation and membrane trafficking in cystic fibrosis cells. J Antimicrob Chemother 1998; 41:215-21. [PMID 9533463] (FULL TEXT: http://jac.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/reprint/41/2/215)
Scotet V, De Braekeleer M, Audrézet MP, Lodé L, Verlingue C, Quéré I, et al. Prevalence of CFTR mutations in hypertrypsinaemia detected through neonatal screening for cystic fibrosis. Clin Genet 2001; 59:42-7. [PMID 11168024] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/118969498/HTMLSTART)
Liu Q, Fischer H, Welch WJ, Harris HW. Cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis is more severe in mice heterozygous for the DF508 cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene mutation than wild-type controls. J Surg Res 2000; 93:317-8. (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6WM6-45CWS96-1K-1&_cdi=6926&_user=839424&_pii=S0022480400959894&_orig=browse&_coverDate=10%2F31%2F2000&_sk=999069997&view=c&wchp=dGLbVzW-zSkzk&md5=91e40a72994279801e9a122e43d9b8ca&ie=/sdarticle.pdf)
Lee YS, Chou YH. Antioxidant profiles in full term and preterm neonates. Chang Gung Med J 2005; 28:846-51. [PMID 16515018] (FULL TEXT: http://memo.cgu.edu.tw/cgmj/2812/281205.pdf)
Cantin AM, Hanrahan JW, Bilodeau G, Ellis L, Dupuis A, Liao J, et al. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator function is suppressed in cigarette smokers. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 2006; 173:1139-44. [PMID 16497995] (FULL TEXT: http://ajrccm.atsjournals.org/cgi/content/full/173/10/1139)
Schwarzer C, Fischer H, Kim EJ, Barber KJ, Mills AD, Kurth MJ, et al. Oxidative stress caused by pyocyanin impairs CFTR Cl(-) transport in human bronchial epithelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 2008; 45:1653-62. [PMID 18845244] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T38-4THC1CC-4&_user=839424&_coverDate=12%2F15%2F2008&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000045367&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=839424&md5=99fc009dc7e113ebe698050a54ee3b91)
Fischer H, Schwarzer C, Illek B. Vitamin C controls the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride channel. Proc National Acad Sci 2004; 101:3691-6. [PMID 14993613] (FULL TEXT: http://www.pnas.org/content/101/10/3691.long)
Köttgen M, Busch AE, Hug MJ, Greger R, Kunzelmann K. N-Acetyl-L-cysteine and its derivatives activate a Cl- conductance in epithelial cells. Pflugers Arch 1996; 431-549-55. [PMID 8596698]
Braganza JM. Cystic fibrosis: a casualty of 'detoxification'? Med Hypotheses 1986; 20:233-43. [PMID 3637621] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6WN2-4C6SX9D-DC-1&_cdi=6950&_user=839424&_pii=0306987786901295&_orig=search&_coverDate=06%2F30%2F1986&_sk=999799997&view=c&wchp=dGLzVzz-zSkWb&md5=91abbe617fcd590b72eed4d1e971ebb1&ie=/sdarticle.pdf)
Bank S, Marks IN, Novis B. Sweat electrolytes in chronic pancreatitis. Am J Dig Dis 1978; 23:178-81. [PMID 623082]
Geetha H, Shetty KT. Sweat osmolality in Down's syndrome and cystic fibrosis in an Indian population. Brit Med J 1987; 294:156. [PMID 2954606] (FULL TEXT: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1245166/?tool=pubmed)
Yigit H, Selimoglu MA, Altinkaynak S. Sweat test results in children with primary protein energy malnutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2003; 37:242-5. [PMID 12960643] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/jpgn/Fulltext/2003/09000/Sweat_Test_Results_in_Children_with_Primary.7.aspx)
Beck R, Durie PR, Hill JG, Levison H. Malnutrition: a cause of elevated sweat chloride concentration. Acta Paediatr Scand 1986; 75:639-44. [PMID 3751557]
Durie PR, Forstner GG, Gaskin KJ, Weizman Z, Kopelman HR, Ellis L, Largman C. Elevated serum immunoreactive pancreatic cationic trypsinogen in acute malnutrition: evidence of pancreatic damage. J Pediatr 1985; 106:233-8. [PMID 3968610] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6WKR-4JKJKVR-G-1&_cdi=6913&_user=839424&_pii=S0022347685802936&_orig=browse&_coverDate=02%2F28%2F1985&_sk=998939997&view=c&wchp=dGLzVzz-zSkWz&md5=0dfe281426e0284e2d6179e026f959e8&ie=/sdarticle.pdf)
Gelrud A, Sheth S, Banerjee S, Weed D, Shea J, Chuttani R, et al. Analysis of cystic fibrosis gener product (CFTR) function in patients with pancreas divisum and recurrent acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 2004; 99:1557-62. [PMID 15307877] (FULL TEXT: http://www.nature.com/ajg/journal/v99/n8/full/ajg2004306a.html)
Segal I, Yaakov Y, Adler S, Blau H, Broide E, Santo M, et al. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator ion channel function testing in recurrent acute pancreatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 2008; 42:810-4. [PMID 18360295] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/jcge/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2008&issue=08000&article=00009&type=abstract)
Quinton PM. Cystic fibrosis: impaired bicarbonate secretion and mucoviscidosis. Lancet 2008; 372:415-7. [PMID 18675692] (FULL TEXT: http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(08)61162-9/fulltext)
Ishiguro H, Steward MC, Naruse S, Ko SB, Goto H, Case RM, et al. CFTR functions as a bicarbonate channel in pancreatic duct cells. J Gen Physiol 2009; 133:315-26. [PMID 19204187] (FULL TEXT: http://jgp.rupress.org/cgi/content/full/133/3/315)
Hudson VM. New insights into the pathogenesis of cystic fibrosis: pivotal role of glutathione system dysfunction and implications for therapy. Treat Respir Med 2004; 3:353-63. [PMID 15658882] (FULL TEXT: http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/adis/trm/2004/00000003/00000006/art00003)
Freedman SD. New concepts in understanding the pathophysiology of chronic pancreatitis. Int J Pancreatol 1998; 24:1-8. [PMID 9746883] (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/6477735423234331/fulltext.pdf)
Zhang Q, Davenport JR, Croyle MJ, Haycraft CJ, Yoder BK. Disruption of IFT results in both exocrine and endocrine abnormalities in the pancreas of Tg737(orpk) mutant mice. Lab Invest 2005; 85:45-64. [PMID 15580285] (FULL TEXT: http://www.nature.com/labinvest/journal/v85/n1/full/3700207a.html)
Heaney AP, Sharer N, Rameh B, Braganza JM, Durrington PN. Prevention of recurrent pancreatitis in familial lipoprotein lipase deficiency with high-dose antioxidant therapy. J Clin Endocrin Metab 1999; 84:1203-5. [PMID 10199753] (FULL TEXT: http://jcem.endojournals.org/cgi/content/full/84/4/1203)
Chang YT, Chang MC, Su TC, Liang PC, Su YN, Kuo CH, et al. Association of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) mutation/variant/haplotype and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) promoter polymorphism in hyperlipidemic pancreatitis. Clin Chem 2008; 54:131-8. [PMID 17981921] (FULL TEXT: http://www.clinchem.org/cgi/content/full/54/1/131)
Felderbauer P, Karakas E, Fendrich V, Bulut K, Horn T, Lebert R, et al. Pancreatitis risk in primary hyperparathyroidism: relation to mutations in the SPINK1 trypsin inhibitor (N34S) and the cystic fibrosis gene. Am J Gastroenterol 2008; 103:368-74. [PMID 18076731] (FULL TEXT: http://www.nature.com/ajg/journal/v103/n2/full/ajg20085072a.html)
Sharer NM, Taylor PM, Linaker BD, Gutteridge JMC, Braganza JM. Safe and successful use of vitamin C to treat painful calcific chronic pancreatitis despite iron overload from primary haemochromatosis. Clin Drug Invest 1995;10:310-5.
Garg PK, Tandon RK. Survey on chronic pancreatitis in the Asia-Pacific region. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004; 19:998-1004. [PMID 15304116] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/118783244/HTMLSTART)
Yan MX, Li YQ. Gall stones and chronic pancreatitis: the black box in between. Postgrad Med j 2006; 82:254-8. [PMID 16597812] (FULL TEXT: http://pmj.bmj.com/content/82/966/254.long)
Lowenfels AB, Maisonneuve P, Grover H, Gerber E, Korsten MA, Antunes MT, et al. Racial factors and the risk of chronic pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 1999; 94: 790-4. [PMID 10086667] (FULL TEXT: http://www.nature.com/ajg/journal/v94/n3/full/ajg1999166a.html)
Segal I, Sharer NM, Kay PM, Gutteridge JM, Braganza JM. Iron, ascorbate and copper status of Sowetan Blacks with calcific chronic pancreatitis. QJM 1996; 89:49-53. [PMID 8730342] (FULL TEXT: http://qjmed.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/reprint/89/1/45)
Simon JA, Hudes ES. Serum ascorbic acid and gallbladder disease prevalence among US adults: the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). Arch Int Med 2000; 160:931-6. [PMID 10761957] (FULL TEXT: http://archinte.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/160/7/931)
Worthington HV, Hunt LP, McCloy RF, Ubbink JB, Braganza JM. Dietary antioxidant lack, impaired hepatic glutathione reserve, and cholesterol gallstones. Clin Chim Acta 2004; 349: 157-65. [PMID 15469869] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T57-4D8VRCR-2&_user=839424&_coverDate=11%2F01%2F2004&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000045367&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=839424&md5=e0db39f83d33d19e54de55ee7f260c03)
Johnson JA, Herring VL, Wolfe MS, Relling MV. CYP1A2 and CYP2D6 4-hydroxylate propranolol and both reactions exhibit racial differences. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2000; 294:1099-105. [PMID 10945865] (FULL TEXT: http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/content/294/3/1099.long)
Kadlubar S, Anderson JP, Sweeney C, Gross MD, Lang NP, Kadlubar FF, Anderson KE. Phenotypic CYP2A6 variation and the risk of pancreatic cancer. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2009; 10: 263-70. [PMID 19454817] (FULL TEXT: http://www.joplink.net/prev/200905/06.html)
Guyton KZ, Kenslev TW. Oxidative mechanisms in carcinogenesis. In: Cheeseman KH, Slater TF (eds). Free Radicals in Medicine. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone 1993: 523-44.
Larsson SC, Giovannucci E, Wolk A. Folate intake, MTHFR polymorphisms, and risk of esophageal, gastric, and pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2006; 131:1271-83. [PMID 17030196] (FULL TEXT: http://www.gastrojournal.org/article/PIIS0016508506017276/fulltext)
Copyright (c) 2010 Joan M Braganza, Thomas L Dormandy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.