EUS-Guided Pancreatic Cyst Brushing: A Comparative Study in a Tertiary Referral Centre
Abstract
Context Fluid analysis obtained by EUS guided FNA is used to aid in diagnosis and management of cystic lesions in the pancreas. Complementing fluid aspiration with brushing of cyst wall may increase the cellular yield. Objective To compare cellular yield of pancreatic cyst FNA with and without wall brushing. Design Comparative study. Setting Tertiary referral centre. Patients Fifty-one patients with cystic pancreatic lesions referred for EUS-guided aspiration/sampling were included (median age 69 years; interquartile range: 49-77 years). Main outcome measures Comparing adequacy of cellular yield between EUS-guided aspiration alone vs. EUS-guided aspiration and cyst wall brushing. Intervention EUS-guided FNA and/or wall brushing (aspiration only: No. 27; brushing: No. 24). Results There was no significant difference in age (P=0.496) cyst size (P=0.084) or cyst location (P=0.227) between groups. Overall 29.5%; (15/51) of samples were acellular/insufficient with no significant difference between the two groups (22.2% in the aspiration only group vs. 37.5% in the brushing group; P=0.356). The remaining samples were adequate for cytological evaluation (77.8% vs. 62.5%; aspiration only vs. brushing groups). Seventeen cases were neoplastic (8 benign, 9 malignant). The diagnostic accuracy was 61.9% and 55.0% in aspiration only and brushing groups, respectively. Two out of 4 (50.0%) patents were diagnosed as having cancer in the brushings group compared to 1/5 (20.0%) in the FNA only group (P=0.524). Limitations Non-randomised series. Conclusions The cellular yield was similar in FNA and brushing group. Greater proportion of patients with malignant cystic pancreatic lesions diagnosed by EUS sampling was in the brushing group, but this did not reach statistical significance.
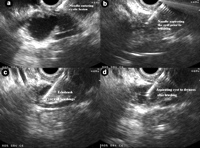
Image: Linear endoscopic ultrasound showing EUS-guided brushing of a cystic pancreatic lesion.
Downloads
References
Fernandez-del Castillo C, Warshaw AL. Cystic tumours of the pancreas. Surg Clin North Am 1995; 75:1001-16. [PMID 7660245]
Le Borgne J. Cystic tumours of the pancreas. Br J Surg 1998; 85:577-9. [PMID 9635798] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/102523570/PDFSTART)
Brugge WR, Lauwers GY, Sahani D, Fernandez-Del Castillo C, Warshaw AL. Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. N Engl J Med 2004; 351:1218-26. [PMID 15371579] (FULL TEXT: http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/351/12/1218)
Friedman AC, Lichtenstein JE, Dachman AH. Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Radiological-pathological correlation. Radiology 1983; 149:45-50. [PMID 6611949] (FULL TEXT: http://radiology.rsna.org/content/149/1/45.long)
Itoh S, Ishiguchi T, Ishigaki T, Sakuma S, Maruyama K, Senda K. Mucin-producing pancreatic tumor: CT findings and histopathologic correlation. Radiology 1992; 183:81-6. [PMID 1312735] (FULL TEXT: http://radiology.rsna.org/content/183/1/81.long)
Wiersema MJ, Vilmann P, Giovannini M, Chang KJ, Wiersema LM. Endosonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy: diagnostic accuracy and complication assessment. Gastroenterology 1997; 112:1087-95. [PMID 9097990]
van der Waaij LA, van Dullemen HM, Porte RJ. Cyst fluid analysis in the differential diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions: a pooled analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2005; 62:383-9. [PMID 16111956] (FULL TEXT: http://www.giejournal.org/article/PIIS0016510705015816/fulltext)
Sedlack R, Affi A, Vazquez-Sequeiros E, Norton ID, Clain JE, Wiersema MJ. Utility of EUS in the evaluation of cystic pancreatic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 2002; 56:543-7. [PMID 12297771] (FULL TEXT: http://www.giejournal.org/article/S0016-5107(02)70440-9/fulltext)
Guidelines of the Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology for fine-needle aspiration procedure and reporting. The Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology Task Force on Standards of Practice. Mod Pathol 1997; 10:739-47. [PMID 9237187]
Buchan I. Arcus QuickStat Biomedical Windows User Manual. Pearson Longman , Harlow, Essex, United Kingdom, 1997. [ISBN 9780582945678]
Song MH, Lee SK, Kim MH, Lee HJ, Kim KP, Kim HJ, et al. EUS in the evaluation of pancreatic cystic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 2003; 57:891-6. [PMID 12776038] (FULL TEXT: http://www.giejournal.org/article/S0016-5107(03)70026-1/fulltext)
Ahmad NA, Kochman ML, Brensinger C, Brugge WR, Faigel DO, Gress FG, et al. Interobserver agreement among endosonographers for the diagnosis of neoplastic versus non-neoplastic pancreatic cystic lesions. Gastrointest Endosc 2003; 58:59-64. [PMID 12838222] (FULL TEXT: http://www.giejournal.org/article/PIIS0016510703013099/fulltext)
Linder JD, Geenen JE, Catalano MF. Cyst fluid analysis obtained by EUS-guided FNA in the evaluation of discrete cystic neoplasms of the pancreas: a prospective single-center experience. Gastrointest Endosc 2006, 64:697-702. [PMID 17055859] (FULL TEXT: http://www.giejournal.org/article/PIIS0016510706002768/fulltext)
Brandwein SL, Farrell JJ, Centeno BA, Brugge WR. Detection and tumor staging of malignancy in cystic, intraductal, and solid tumors of the pancreas by EUS. Gastrointest Endosc 2001; 53:722-7. [PMID 11375578] (FULL TEXT: http://www.giejournal.org/article/PIIS0016510701809883/fulltext)
Frossard JL, Amouyal P, Amouyal G, Palazzo L, Amaris J, Soldan M, et al. Performance of endosonography-guided fine needle aspiration and biopsy in the diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions. Am J Gastroenterol 2003; 98:1516-24. [PMID 12873573] (FULL TEXT: http://www.nature.com/ajg/journal/v98/n7/full/ajg2003355a.html)
Attasaranya S, Pais S, LeBlanc J, McHenry L, Sherman S, DeWitt JM. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration and cyst fluid analysis for pancreatic cysts. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2007; 8:553-63. [PMID 17873459] (FULL TEXT: http://www.joplink.net/prev/200709/06.html)
Moparty B, Logroño R, Nealon WH, Waxman I, Raju GS, Pasricha PJ, Bhutani MS. The role of endoscopic ultrasound and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration in distinguishing pancreatic cystic lesions. Diagn Cytopathol 2007; 35:18-25. [PMID 17173300] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/113523322/PDFSTART)
Alsibai KD, Denis B, Bottlaender J, Kleinclaus I, Straub P, Fabre M. Impact of cytopathologist expert on diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic lesions in current clinical practice. A series of 106 endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspirations. Cytopathology 2006; 17:18-26. [PMID 16417561] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/118604543/HTMLSTART)
Al-Haddad M, Raimondo M, Woodward T, Krishna M, Pungpapong S, Noh K, Wallace MB. Safety and efficacy of cytology brushings versus standard FNA in evaluating cystic lesions of the pancreas: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc 2007; 65:894-8. [PMID 17210151] (FULL TEXT: http://www.giejournal.org/article/PIIS0016510706028185/fulltext)
Lee LS, Saltzman JR, Bounds BC, Poneros JM, Brugge WR, Thompson CC. EUS-guided fine needle aspiration of pancreatic cysts: a retrospective analysis of complications and their predictors. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005; 3:231-6. [PMID 15765442] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B7GGW-4FNTCBY-F&_user=839424&_coverDate=03%2F31%2F2005&_rdoc=1&_fmt=full&_orig=search&_cdi=20161&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000045367&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=839424&md5=8373b47b4f4640c1bd9f2b68d56ab49d)
Varadarajgulu S, Eloubeidi MA. Frequency and significance of acute intracystic hemorrhage during EUS-FNA of cystic lesions of the pancreas. Gastrointest Endosc 2004; 60:631-5. [PMID 15472697] (FULL TEXT: http://www.giejournal.org/article/PIIS0016510704018917/fulltext)
Copyright (c) 2010 Titus Thomas, James Bebb, Jayan Mannath, Krish Ragunath, Phillip V Kaye, Guruprasad P Aithal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.