Successful Endoscopic Transpapillary Management of Intrahepatic Pancreatic Pseudocyst
Abstract
Context Intrahepatic pancreatic pseudocyst extension is a rare but complex clinical entity requiring multimodality approach for management. There is no consensus regarding the optimal strategy for the treatment of intrahepatic pancreatic pseudocyst and the literature is limited to a few case reports. Most of the published cases were managed by surgical or percutaneous drainage. Case report We hereby report a case of intrahepatic pancreatic pseudocyst extension which failed to resolve by percutaneous drainage. Endoscopic transpapillary drainage was utilized which led to complete resolution of the intrahepatic pancreatic pseudocyst. Conclusion The excellent results obtained in our patient suggest that it should be considered as primary treatment and may obviate the need for more aggressive and potentially morbid procedures.
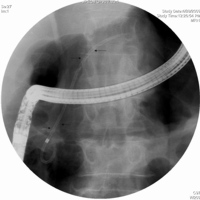
Image: ERCP showing the 7F, 10 cm long pancreatic stent traversing the main duct stricture extending to the tail.
Downloads
References
Hamm B, Franzen N. Atypically located pancreatic pseudocysts in the liver, spleen, stomach wall and mediastinum: their CT diagnosis. Rofo 1993; 159:522-7. [PMID 8298111] (FULL TEXT: http://www.thieme-connect.de/ejournals/pdf/roefo/doi/10.1055/s-2008-1032813.pdf)
Chahal P, Baron TH, Topazian MD, Levy MJ. EUS-guided diagnosis and successful endoscopic transpapillary management of an intrahepatic pancreatic pseudocyst masquerading as a metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 2009; 70:393-6. [PMID 19394005] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WFY-4W50JXM-3&_user=839424&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000045367&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=839424&md5=9ae0ac9f5c54aacbfb40cea2e4df644d)
Shibasaki M, Bandai Y, Ukai T. Pancreatic pseudocyst extending into the liver via the hepatoduodenal ligament: a case report. Hepatogastroenterology 2002; 49:1719-21. [PMID 12397775]
Okuda K, Sugita S, Tsukada E, Sakuma Y, Ohkubo K. Pancreatic pseudocyst in the left hepatic lobe: a report of two cases. Hepatology 1991; 13:359-63. [PMID 1995443] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/112180356/PDFSTART)
Mofredj A, Cadranel JF, Dautreaux M, Kazerouni F, Hadj-Nacer K, Deplaix P, et al. Pancreatic pseudocyst located in the liver: a case report and literature review. J Clin Gastroenterol 2000; 30:81-3. [PMID 10636217] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/jcge/Abstract/2000/01000/Pancreatic_Pseudocyst_Located_in_the_Liver__A_Case.16.aspx)
Wang SJ, Chen JJ, Changchien CS, Chiou SS, Tai DI, Lee CM, et al. Sequential invasions of pancreatic pseudocysts in pancreatic tail, hepatic left lobe, caudate lobe, and spleen. Pancreas 1993; 8:133-6. [PMID 8419901] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/pancreasjournal/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=1993&issue=01000&article=00024&type=abstract)
Aiza I, Barkin JS, Casillas VJ, Molina EG. Pancreatic pseudocysts involving both hepatic lobes. Am J Gastroenterol 1993; 88:1450-2. [PMID 8362849]
Ryu JK, Woo SM, Hwang JH, Jeong JB, Yoon YB, Park IA, et al. Cyst fluid analysis for the differential diagnosis of pancreatic cysts. Diagn Cytopathol 2004; 31:100-5. [PMID 15282721] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/109572610/PDFSTART)
Balzan S, Kianmanesh R, Farges O, Sauvanet A, O'toole D, Levy P, et al. Right intrahepatic pseudocyst following acute pancreatitis: an unusual location after acute pancreatitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 2005; 12:135-7. [PMID 15868077] (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/w51067130605655r/fulltext.pdf)
Atia A, Kalra S, Rogers M, Murthy R, Borthwick TR, Smalligan RD. A wayward cyst. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2009; 10:421-4. [PMID 19581748] (FULL TEXT: http://www.joplink.net/prev/200907/16.html)
Varadarajulu S, Noone TC, Tutuian R, Hawes RH, Cotton PB. Predictors of outcome in pancreatic duct disruption managed by endoscopic transpapillary stent placement. Gastrointest Endosc 2005; 61:568-75. [PMID 15812410] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WFY-4FVJ42V-P&_user=839424&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000045367&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=839424&md5=43b3b9ac43aa6fc0b2e48d84939103ef)
Telford JJ, Farrell JJ, Saltzman JR, Shields SJ, Banks PA, Lichtenstein DR, et al. Pancreatic stent placement for duct disruption. Gastrointest Endosc 2002; 56:18-24. [PMID 12085030] (FULL TEXT: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=MImg&_imagekey=B6WFY-467K1BN-3-1&_cdi=6807&_user=839424&_orig=search&_coverDate=07%2F31%2F2002&_sk=999439998&view=c&wchp=dGLbVlb-zSkWb&md5=360ba2b898a311e30e73c38705294016&ie=/sdarticle.pdf)
Copyright (c) 2010 Rizwan Kibria, Salma Akram, Syed A Ali

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.