Intrapancreatic Accessory Spleen: Investigative Dilemmas and Role of EUS-Guided FNA for Diagnostic Confirmation
Abstract
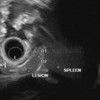
Context We submit a case of intrapancreatic accessory spleen. Case report A 33-year-old patient with history of dyspepsia underwent imaging studies suggestive of a neuroendocrine tumor. After referral to our institute, endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) confirmed diagnosis as intrapancreatic accessory spleen. Discussion An accessory spleen may develop from estranged mesenchymal cells due to fusion failure of the splenic anlage. The prevalence of an accessory spleen is 10-30% with 80% of them present at the splenic hilum and 17% in the pancreatic tail. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen is commonly misdiagnosed as a pancreatic tumor. Since, the differential diagnosis includes pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, additional investigation with EUS-FNA should be considered when radiological diagnosis is not definitive. Conclusion For diagnosis of intrapancreatic accessory spleen, radiographic imaging is useful, but lacks specificity without tissue diagnosis. Diagnosis can be safely and reliably established with EUS-FNA, leading to a benign prognosis and avoidance of unnecessary surgical intervention.
Downloads
References
Dodds WJ, Taylor AJ, Erickson SJ, Stewart ET, Lawson TL. Radiologic imaging of splenic anomalies. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1990; 155:805-10. [PMID 2119113]
Halpert B, Gyorkey F. Lesions observed in accessory spleens of 311 patients. Am J Clin Pathol 1959; 32:165-8. [PMID 13670140]
Kim SH, Lee JM, Han JK, Lee JY, Kim KW, Cho KC, et al. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: findings on MR Imaging, CT, US and scintigraphy, and the pathologic analysis. Korean J Radiol 2008; 9:162-74. [PMID 18385564]
Low G, Panu A, Millo N, Leen E. Multimodality imaging of neoplastic and nonneoplastic solid lesions of the pancreas. Radiographics 2011; 31:993-1015. [PMID 21768235]
Chung SY, Ryo UY, Pinsky S. Evaluation of a patient with splenosis by various imaging modalities. J Natl Med Assoc 1986; 78:458-9. [PMID 3519990]
Ota T, Tei M, Yoshioka A, Mizuno M, Watanabe S, Seki M, et al. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen diagnosed by technetium-99m heat-damaged red blood cell SPECT. J Nucl Med 1997; 38:494-5. [PMID 9074546]
Barawi M, Bekal P, Gress F. Accessory spleen: a potential cause of misdiagnosis at EUS. Gastrointest Endosc 2000; 52:769-72. [PMID 11115915]
Schreiner AM, Mansoor A, Faigel DO, Morgan TK. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen: mimic of pancreatic endocrine tumor diagnosed by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Diagn Cytopathol 2008; 36:262-5. [PMID 18335556]
Arkadopoulos N, Athanasopoulos P, Stafyla V, Karakatsanis A, Koutoulidis V, Theodosopoulos T, et al. Intrapancreatic accessory spleen issues: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2009; 10:400-5. [PMID 19581743]
Hutchinson CB, Canlas K, Evans JA, Obando JV, Waugh M. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy of the intrapancreatic accessory spleen: a report of 2 cases. Acta Cytol 2010; 54:337-40. [PMID 20518423]
Lin J, Jing X. Fine-needle aspiration of intrapancreatic accessory spleen, mimic of pancreatic neoplasms. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010; 134:1474-8. [PMID 20923303]
Pugh JL, Jhala NC, Eloubeidi MA, Chhieng DC, Eltoum IA, Crowe DR, et al. Diagnosis of deep-seated lymphoma and leukemia by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Am J Clin Pathol 2006; 125:703-9. [PMID 16707371]
Copyright (c) 2014 Somashekar G Krishna, Muhannad M Heif, Shree G Sharma, Tarun Pandey, Rayburn F Rego

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.