Tensegrity Model Hypothesis: May This Paradigm Be Useful to Explain Hepatic and Pancreatic Carcinogenesis in Patients with Persistent Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C Virus Infection?
Abstract
Context Hepatitis B (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) possess well-known oncogenic properties and may promote carcinogenesis in liver. However antigens and replicative sequences of HBV/HCV have been also detected in different extra-hepatic tissues, including the pancreas. Although epidemiological studies and meta-analyses have recently suggested that HBV/HCV may be also risk factors for pancreatic cancer and several researches have investigated the possible mechanisms and intra-/extra-cellular paths involved in pancreatic and hepatic carcinogenesis, to date, these complex processes remain largely unexplained. Objectives In our paper, we aimed to propose a comprehensive and qualitative hypothetical model, describing how HBV/HCV may exert their oncogenic role. Methods We performed a systematic research of scientific literature, by searching MEDLINE, the Cochrane Library and EMBASE databases. The used keywords were: “chronic HBV/HCV”, “pancreatic cancer”, “liver carcinoma”, “carcinogenesis mechanisms”, “tensional integrity”, “cytoskeleton”, and “extracellular matrix”. Results Taking advantage from available studies, we suggest an unifying hypothesis based on results and data, obtained from different areas of research. In particular we considered the well-defined model of tensional integrity and correlated it to changes induced by HBV/HCV in viscoelastic properties/stiffness of cellular/extracellular microenvironments. These events perturb the tightly-regulated feedback loop, which usually couples the intracellular-generated forces to substrate rigidity of extracellular compartments. Therefore, such a change strongly affects intracellular functions and cellular fate, by promoting a substantial deregulation of critical intracellular biochemical activities and genome expression. Conclusions Our hypothesis might provide for the first time a reliable system, which correlates tensional integrity model with intra-/extra-cellular modifications, occurring in liver and pancreas during HBV/HCV-induced carcinogenesis. This approach might improve our understanding of pathogenetic mechanisms involved in the development of pancreatic and hepatic carcinogenesis , enhancing the possibility of their treatment. Furthermore, should the usefulness of this model be definitively confirmed, it might be also helpful to extend its field of application to other viruses-related cancers.
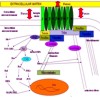
Image: Signaling pathways (Figure 1)
Downloads
References
El-Serag. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012; 142 (6): 1264-73. e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.12.061. [PMID: 22537432]
Bialek SR, Terrault NA. The changing epidemiology and natural history of hepatitis C virus infection. Clin Liver Dis 2006; 10: 697-715. [PMID: 17164113]
Dandri M, Locarnini S. New insight in the pathobiology of hepatitis B virus infection. Gut 2012; 2012;61 Suppl 1:i6-17. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302056. [PMID: 22504921]
Poynard T, Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Goodman Z, McHutchison J, Albrecht J. Rates and risk factors of liver fibrosis progression in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 2001; 34: 730-9. [PMID: 11434620]
Fiorino S, Lorenzini S, Masetti M, Deleonardi G, Grondona AG, Silvestri T et al. Hepatitis B and C virus infections as possible risk factor for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Med Hypotheses. 2012;79(5):678-97. [PMID: 22959312]
Hassan MM, Li D, El-Deeb AS, Wolff RA, Bondy ML, Davila M et al. Association between hepatitis B virus and pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26:4557-62. [PMID: 18824707]
Iloeje UH, Yang HI, Jen CL, Su J, Wang LY, You SL, et al. Risk of pancreatic cancer in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: data from the REVEAL-HBV cohort study Liver Int, 2010; 30 (3): 423–429. [PMID 19840258]
Wang DS, Chen DL, Ren C, Wang ZQ, Qiu MZ, Luo HY, et al. ABO blood group, hepatitis B viral infection and risk of pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(2):461-8. [PMID: 21858814]
Ben Q, Li Z, Liu C, Cai Q, Yuan Y, Wang K, et al. Hepatitis B virus status and risk of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a case-control study from China. Pancreas. 2012; 41(3):435-40. [PMID: 22422136]
El-Serag HB, Engels EA, Landgren O, Chiao E, Henderson L, Amaratunge HC et al. Risk of hepatobiliary and pancreatic cancers after hepatitis C virus infection: A population-based study of U.S. veterans. Hepatology 2009;49:116-23. [PMID: 19085911]
Wang Y, Yang S, Song F, Cao S, Yin X, Xie J et al. Hepatitis B virus status and the risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2013;22(4):328-34. doi: 10.1097/ CEJ.0b013e32835b6a21. [PMID: 23165286]
Luo G, Hao NB, Hu CJ, Yong X, Lü MH, Cheng BJ et al. HBV infection increases the risk of pancreatic cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control. 2013; 24 (3): 529-37. [PMID: 23306552]
Fiorino S, Chili E, Bacchi-Reggiani L, Masetti M, Deleonardi G, Grondona AG et al. Association between hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus infection and risk of pancreatic adenocarcinoma development: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pancreatology 2013; 147-60. [PMID 23561973]
Jin Y, Gao H, Chen H, Wang J, Chen M, Li G et al. Identification and impact of hepatitis B virus DNA and antigens in pancreatic cancer tissues and adjacent non-cancerous tissues. Cancer Lett. 2013. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.03.001. [PMID: 23499889]
Jackson L, Evers BM. Chronic inflammation and pathogenesis of GI and pancreatic cancers. Cancer Treat Res 2006;130:39–65. [PMID: 16610702]
Schottenfeld D, Beebe-Dimmer J. Chronic inflammation: a common and important factor in the pathogenesis of neoplasia. CA Cancer J Clin 2006;56(2):69–83. [PMID: 16514135]
Hussain SP, Harris CC. Inflammation and cancer: an ancient link with novel potentials. Int J Cancer 2007;121(11):2373–80. [PMID: 17893866]
Kuo JC. Mechanotransduction at focal adhesions: integrating cytoskeletal mechanics in migrating cells. Cell Mol Med. 2013. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12054. [PMID: 23551528]
Miyoshi J, Takai Y. Molecular perspective on tight-junction assembly and epithelial polarity. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005; 57(6):815-55. [PMID: 15820555]
Vignaud T, Blanchoin L, Théry M. Directed cytoskeleton self-organization. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22(12):671-82. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2012.08.012. [PMID: 23026031]
Berrier AL, Yamada KM. Cell-matrix adhesion. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213(3):565-73. [PMID: 17680633]
Ingber DE. Tensegrity I. Cell structure and hierarchical systems biology. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 7):1157-73. [PMID: 12615960]
Hynes RO. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 2002;110(6):673-87. [PMID: 12297042]
Calderwood DA, Shattil SJ, Ginsberg MH. Integrins and actin filaments: reciprocal regulation of cell adhesion and signaling. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(30):22607-10. [PMID: 10801899]
Wehrle-Haller B. Assembly and disassembly of cell matrix adhesions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24(5):569-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.06.010. [PMID:22819514]
Wehrle-Haller B. Structure and function of focal adhesions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24(1):116-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2011.11.001. [PMID: 22138388]
Horwitz A, Duggan K, Buck C, Beckerle MC, Burridge K. Interaction of plasma membrane fibronectin receptor with talin-a transmembrane linkage. Nature. 1986; 320(6062):531-3. [PMID: 2938015]
Burridge K, Turner CE, Romer LH. Tyrosine phosphorylation of paxillin and pp125FAK accompanies cell adhesion to extracellular matrix: a role in cytoskeletal assembly. J Cell Biol. 1992;119(4):893-903. [PMID: 1385444]
Humphries JD, Wang P, Streuli C, Geiger B, Humphries MJ, Ballestrem C. Vinculin controls focal adhesion formation by direct interactions with talin and actin. J Cell Biol. 2007;179(5):1043-57. [PMID: 18056416]
Nagano M, Hoshino D, Koshikawa N, Akizawa T, Seiki M. Turnover of focal adhesions and cancer cell migration. Int J Cell Biol. 2012;2012:310616. doi: 10.1155/2012/310616. [PMID: 22319531]
Roca-Cusachs P, Del Rio A, Puklin-Faucher E, Gauthier NC, Biais N, Sheetz MP. Integrin-dependent force transmission to the extracellular matrix by α-actinin triggers adhesion maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(15):E1361-70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1220723110. [PMID: 23515331]
Spiering D, Hodgson L. Dynamics of the Rho-family small GTPases in actin regulation and motility. Cell Adh Migr. 2011;5(2):170-80. [PMID: 21178402]
Huveneers S, Danen EH. Adhesion signaling - crosstalk between integrins, Src and Rho. J Cell Sci. 2009;122(Pt 8):1059-69. doi: 10.1242/jcs.039446. [PMID: 19339545]
Fey EG, Wan KM, Penman S. Epithelial cytoskeletal framework and nuclear matrix-intermediate filament scaffold: three-dimensional organization and protein composition. J Cell Biol. 1984;98(6):1973-84. [PMID:6202700]
Douglas T, Heinemann S, Bierbaum S, Scharnweber D, Worch H. Fibrillogenesis of collagen types I, II, and III with small leucine-rich proteoglycans decorin and biglycan. Biomacromolecules. 2006;7(8):2388-93. [PMID: 16903686]
Raspanti M, Viola M, Forlino A, Tenni R, Gruppi C, Tira ME. Glycosaminoglycans show a specific periodic interaction with type I collagen fibrils. J Struct Biol. 2008;164(1):134-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2008.07.001. [PMID: 18664384]
Theocharis AD, Skandalis SS, Tzanakakis GN, Karamanos NK. Proteoglycans in health and disease: novel roles for proteoglycans in malignancy and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 2010; 277(19):3904-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07800.x. [PMID: 20840587]
Couchman JR, Pataki CA. An introduction to proteoglycans and their localization. J Histochem Cytochem. 2012;60(12):885-97. doi: 10.1369/0022155412464638. [PMID: 23019015]
Nelson CM, Bissell MJ. Of extracellular matrix, scaffolds, and signaling: tissue architecture regulates development, homeostasis, and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:287-309. [PMID: 16824016]
Ingber DE. Cellular mechanotransduction: putting all the pieces together again. FASEB J. 2006;20(7):811-27. [PMID: 16675838]
Liedl T, Högberg B, Tytell J, Ingber DE, Shih WM. Self-assembly of three-dimensional prestressed tensegrity structures from DNA. Nat Nanotechnol. 2010 Jul;5(7):520-4. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2010.107. [PMID: 20562873]
Ingber DE. Tensegrity II. How structural networks influence cellular information processing networks. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 7):1397-408. [PMID: 12640025]
Fuller B. Tensegrity. Portfolio Artnews Annual. 1961; 4: 112-127.]
Snelson K. Snelson on the tensegrity invention. Int J Space Struct 1996; 11: 43-48.
Ingber DE. Tensegrity-based mechanosensing from macro to micro. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2008;97(2-3):163-79. [PMID: 18406455]
Discher DE, Janmey P, Wang YL. Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate. Science. 2005;310(5751):1139-43. [PMID: 16293750]
Buxboim A, Ivanovska IL, Discher DE. Matrix elasticity, cytoskeletal forces and physics of the nucleus: how deeply do cells 'feel' outside and in? J Cell Sci. 2010;123(Pt 3):297-308. doi: 10.1242/jcs.041186. [PMID: 20130138]
Mammoto A, Mammoto T, Ingber DE. Mechanosensitive mechanisms in transcriptional regulation. J Cell Sci. 2012;125 (Pt 13):3061-73. doi: 10.1242/jcs.093005. [PMID: 22797927]
Ingber DE. Mechanobiology and diseases of mechanotransduction. Ann Med. 2003;35(8):564-77. [PMID: 14708967]
Ingber D. Integrins as mechanochemical transducers. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991;3(5):841-8. [PMID: 1931084]
Raimondi S, Lowenfels AB, Morselli-Labate AM, Maisonneuve P, Pezzilli R. Pancreatic cancer in chronic pancreatitis; aetiology, incidence, and early detection. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2010;24(3):349-58.
Yue J, Zhang K, Chen J. Role of integrins in regulating proteases to mediate extracellular matrix remodeling. Cancer Microenviron. 2012;5(3):275-83. doi: 10.1007/s12307-012-0101-3.
Paszek MJ, Zahir N, Johnson KR, Lakins JN, Rozenberg GI, Gefen A et al. Tensional homeostasis and the malignant phenotype. Cancer Cell. 2005; 8(3):241-54.
Buchholz M, Kestler HA, Holzmann K, Ellenrieder V, Schneiderhan W, Siech M, et al. Transcriptome analysis of human hepatic and pancreatic stellate cells: organ-specific variations of a common transcriptional phenotype. J Mol Med (Berl). 2005;83(10):795-805. [PMID: 15976918]
Erkan M, Weis N, Pan Z, Schwager C, Samkharadze T, Jiang X et al. Organ-, inflammation- and cancer specific transcriptional fingerprints of pancreatic and hepatic stellate cells. Mol Cancer 2010;9:88 doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-88. [PMID: 20416094]
Zhang DY, Friedman SL. Fibrosis-dependent mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 2012;56(2):769-75 doi: 10.1002/hep.25670. [PMID: 22378017]
Patsenker E, Stickel F. Role of integrins in fibrosing liver diseases. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2011;301(3):G425-34. [PMID: 21659620]
Luo G, Long J, Zhang B, Liu C, Xu J, Ni Q et al. Stroma and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: An interaction loop. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012;1826(1):170-8. [PMID: 22521638]
Riener MO, Fritzsche FR, Soll C, Pestalozzi BC, Probst-Hensch N, Clavien PA et al. Expression of the extracellular matrix protein periostin in liver tumors and bile duct carcinomas. Histopathology. 2010;56(5):600-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2010.03527.x. [PMID: 20459570]
Baril P, Gangeswaran R, Mahon PC, Caulee K, Kocher HM, Harada T et al. Periostin promotes invasiveness and resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to hypoxia-induced cell death: role of the beta4 integrin and the PI3k pathway. Oncogene. 2007;26(14):2082-94. [PMID: 17043657]
Lv Y, Wang W, Jia WD, Sun QK, Li JS, Ma JL et al. High-level expression of periostin is closely related to metastatic potential and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 2013;30(1):385. doi: 10.1007/s12032-012-0385-7. [PMID: 23275141]
Tilman G, Mattiussi M, Brasseur F, van Baren N, Decottignies A. Human periostin gene expression in normal tissues, tumors and melanoma: evidences for periostin production by both stromal and melanoma cells. Mol Cancer. 2007;6:80. [PMID: 18086302]
Erkan M, Kleeff J, Gorbachevski A, Reiser C, Mitkus T, Esposito I et al. Periostin creates a tumor-supportive microenvironment in the pancreas by sustaining fibrogenic stellate cell activity. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(4):1447-64. [PMID: 17408641]
Imamura T, Iguchi H, Manabe T, Ohshio G, Yoshimura T, Wang ZH et al. Quantitative analysis of collagen and collagen subtypes I, III, and V in human pancreatic cancer, tumor-associated chronic pancreatitis, and alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas. 1995;11(4):357-64. [PMID: 8532652]
Armstrong T, Packham G, Murphy LB, Bateman AC, Conti JA, Fine DR et al. Type I collagen promotes the malignant phenotype of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(21):7427-37. [PMID: 15534120]
Koenig A, Mueller C, Hasel C, Adler G, Menke A. Collagen type I induces disruption of E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell contacts and promotes proliferation of pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(9):4662-71. [PMID: 16651417]
Takayama G, Arima K, Kanaji T, Toda S, Tanaka H, Shoji S et al. Periostin: a novel component of subepithelial fibrosis of bronchial asthma downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 signals. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118(1):98-104. [PMID: 16815144]
Norris RA, Damon B, Mironov V, Kasyanov V, Ramamurthi A, Moreno-Rodriguez R et al. Periostin regulates collagen fibrillogenesis and the biomechanical properties of connective tissues. J Cell Biochem. 2007;101(3):695-711. [PMID: 17226767]
Ward BM. The taking of the cytoskeleton one two three: how viruses utilize the cytoskeleton during egress. Virology. 2011;411(2):244-50. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2010.12.024. [PMID: 21241997]
Sun Q, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Liu F, Cheng X, Hou N et al. Expression profiling reveals dysregulation of cellular cytoskeletal genes in HBx-induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007;6(5):668-74. [PMID: 17873514]
Cross JC, Wen P, Rutter WJ. Transactivation by hepatitis B virus X protein is promiscuous and dependent on mitogen-activated cellular serine/threonine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1993; 90: 8078-82. [PMID: 8367466]
Benn J, Schneider R. Hepatitis B virus HBx protein activates Ras-GPT complex formation and establishes a Ras, Raf, MAP kinase signaling cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1994; 91: 10350-54. [PMID 7937954]
Klein NP, Schneider RJ Activation of Src family kinases by hepatitis B virus HBx protein and coupled signaling to Ras. Molec and Cell Biol 1997; 17: 6427-36. [PMID 9343405]
Bouchard MJ, Wang L, Schneider RJ. Activation of focal adhesion kinase by hepatitis B virus HBx protein: multiple functions in viral replication. J Virol. 2006;80(9):4406-14. [PMID: 16611900]
Zhao J, Guan JL. Signal transduction by focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009;28(1-2):35-49. doi: 10.1007/s10555-008-9165-4. [PMID: 19169797]
Izaguirre G, Aguirre L, Hu YP, Lee HY, Schlaepfer DD, Aneskievich BJ et al. The cytoskeletal/non-muscle isoform of alpha-actinin is phosphorylated on its actin-binding domain by the focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(31):28676-85. [PMID: 11369769]
Lara-Pezzi E, Serrador JM, Montoya MC, Zamora D, Yáñez-Mó M, Carretero M et al. The hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx) induces a migratory phenotype in a CD44-dependent manner: possible role of HBx in invasion and metastasis. Hepatology. 2001;33(5):1270-81. [PMID: 11343256]
Steed E, Balda MS, Matter K. Dynamics and functions of tight junctions. Trends Cell Biol. 2010;20(3):142-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.12.002. [PMID: 20061152]
Tian X, Liu Z, Niu B, Zhang J, Tan TK, Lee SR et al. E-cadherin/β-catenin complex and the epithelial barrier. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:567305. doi: 10.1155/2011/567305. [PMID: 22007144]
Desai R, Sarpal R, Ishiyama N, Pellikka M, Ikura M, Tepass U. Monomeric α-catenin links cadherin to the actin cytoskeleton. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15(3):261-73. doi: 10.1038/ncb2685. [PMID: 23417122]
Lara-Pezzi E, Roche S, Andrisani OM, Sánchez-Madrid F, López-Cabrera M. The hepatitis B virus HBx protein induces adherens junction disruption in a src-dependent manner. Oncogene. 2001; 20(26):3323-31. [PMID: 10074921]
Chen L, Hu L, Li L, Liu Y, Tu QQ, Chang YX et al. Dysregulation of β-catenin by hepatitis B virus X protein in HBV-infected human hepatocellular carcinomas. Front Med China. 2010;4(4):399-411. doi: 10.1007/s11684-010-0170-y. [PMID: 21107751]
Menke A, Philippi C, Vogelmann R, Seidel B, Lutz MP, Adler G et al. Down-regulation of E-cadherin gene expression by collagen type I and type III in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2001;61(8):3508-17. [PMID: 11309315]
Lara-Pezzi E, Majano PL, Yáñez-Mó M, Gómez-Gonzalo M, Carretero M, Moreno-Otero R et al. Effect of the hepatitis B virus HBx protein on integrin-mediated adhesion to and migration on extracellular matrix. J Hepatol. 2001; 34(3):409-15. [PMID: 11322202]
Tsukita S, Oishi K, Sato N, Sagara J, Kawai A, Tsukita S. ERM family members as molecular linkers between the cell surface glycoprotein CD44 and actin-based cytoskeletons. J Cell Biol. 1994;126(2):391-401. [PMID: 7518464]
Bost AG, Venable D, Liu L, Heinz BA. Cytoskeletal requirements for hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA synthesis in the HCV replicon cell culture system. J Virol. 2003;77(7):4401-8. [PMID: 12634397]
Lai CK, Jeng KS, Machida K, Lai MM. Association of hepatitis C virus replication complexes with microtubules and actin filaments is dependent on the interaction of NS3 and NS5A. J Virol. 2008; 82(17):8838-48. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00398-08. [PMID: 18562541]
Alisi A, Arciello M, Petrini S, Conti B, Missale G, Balsano C. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) mediates the induction of pro-oncogenic and fibrogenic phenotypes in hepatitis C virus (HCV)-infected cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44147. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044147. [PMID: 22937161]
Lan S, Wang H, Jiang H, Mao H, Liu X, Zhang X et al. Direct interaction between alpha-actinin and hepatitis C virus NS5B. FEBS Lett. 2003;554(3):289-94. [PMID: 14623081]
Nakashima K, Takeuchi K, Chihara K, Horiguchi T, Sun X, Deng L et al. HCV NS5A protein containing potential ligands for both Src homology 2 and 3 domains enhances autophosphorylation of Src family kinase Fyn in B cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e46634. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046634. [PMID: 23077515]
Benedicto I, Molina-Jiménez F, Barreiro O, Maldonado-Rodríguez A, Prieto J, Moreno-Otero R et al. Hepatitis C virus envelope components alter localization of hepatocyte tight junction-associated proteins and promote occludin retention in the endoplasmic reticulum. Hepatology. 2008;48(4):1044-53. doi: 10.1002/hep.22465. [PMID: 18802961]
Matter K, Balda MS. Epithelial tight junctions, gene expression and nucleo-junctional interplay. J Cell Sci. 2007;120(Pt 9):1505-11. [PMID: 17452622]
Aijaz S, Balda MS, Matter K. Tight junctions: molecular architecture and function. Int Rev Cytol. 2006;248:261-98. [PMID: 16487793]
Tan TL, Feng Z, Lu YW, Chan V, Chen WN. Adhesion contact kinetics of HepG2 cells during Hepatitis B virus replication: Involvement of SH3-binding motif in HBX. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1762(8):755-66. [PMID: 19339545]
Huveneers S, Danen EH. Adhesion signaling - crosstalk between integrins, Src and Rho. J Cell Sci. 2009;122(Pt 8):1059-69. doi: 10.1242/jcs.039446. [PMID: 19339545]
Zhao G, Cui J, Qin Q, Zhang J, Liu L, Deng S et al. Mechanical stiffness of liver tissues in relation to integrin β1 expression may influence the development of hepatic cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Surg Oncol. 2010;102(5):482-9. doi: 10.1002/jso.21613. [PMID: 20872952]
Popov Y, Patsenker E, Stickel F, Zaks J, Bhaskar KR, Niedobitek G et al. Integrin alphavbeta6 is a marker of the progression of biliary and portal liver fibrosis and a novel target for antifibrotic therapies. J Hepatol. 2008;48(3):453-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.11.021. [PMID: 18221819]
Nejjari M, Couvelard A, Mosnier JF, Moreau A, Feldmann G, Degott C et al. Integrin up-regulation in chronic liver disease: relationship with inflammation and fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. J Pathol. 2001;195(4):473-81. [PMID: 11745680]
Martín-Vílchez S, Sanz-Cameno P, Rodríguez-Muñoz Y, Majano PL, Molina-Jiménez F, López-Cabrera M et al. The hepatitis B virus X protein induces paracrine activation of human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2008;47(6):1872-83. [PMID: 18449922]
Watanabe N, Aizaki H, Matsuura T, Kojima S, Wakita T, Suzuki T. Hepatitis C virus RNA replication in human stellate cells regulates gene expression of extracellular matrix-related molecules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;407(1):135-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.02.125. [PMID: 21371436]
Liu X, Zhu ST, You H, Cong M, Liu TH, Wang BE et al. Hepatitis B virus infects hepatic stellate cells and affects their proliferation and expression of collagen type I. Chin Med J (Engl). 2009;122(12):1455-61. [PMID: 19567171]
Schulze-Krebs A, Preimel D, Popov Y, Bartenschlager R, Lohmann V, Pinzani M et al. Hepatitis C virus-replicating hepatocytes induce fibrogenic activation of hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology 2005;129(1):246-58. [PMID: 16012951]
Schulze A, Gripon P, Urban S. Hepatitis B virus infection initiates with a large surface protein-dependent binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Hepatology. 2007;46(6):1759-68. [PMID: 18046710]
Sureau C, Salisse J. A conformational heparan sulfate binding site essential to infectivity overlaps with the conserved hepatitis B virus a-determinant. Hepatology. 2013;57(3):985-94. doi: 10.1002/hep.26125. [PMID: 23161433]
Barth H, Schnober EK, Zhang F, Linhardt RJ, Depla E Boson B et al. Viral and cellular determinants of the hepatitis C virus envelope-heparan sulfate interaction. J Virol 2006; 80: 10579-10590. [PMID: 16928753]
Fung J, Lai CL, Seto WK, Wong DK, Yuen MF. Prognostic significance of liver stiffness for hepatocellular carcinoma and mortality in HBeAg-negative chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat. 2011;18(10):738-44.doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2010.01355.x. [PMID: 20659306]
Vergniol J, Foucher J, Terrebonne E, Bernard PH, le Bail B, Merrouche W et al. Noninvasive tests for fibrosis and liver stiffness predict 5-year outcomes of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(7):1970-9, 1979.e1-3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.058. [PMID: 21376047]
Copyright (c) 2014 Sirio Fiorino, Letizia Bacchi-Reggiani, Laura Pontoriero, Claudio Gallo, Elisabetta Chili, Michele Masetti, Nicola Zanini, Ana Grondona, Tania Silvestri, Gaia Deleonardi, Adele Fornelli, Arrigo Bondi, Dario de Biase, Paola Baccarini, Giovanni Tallini, Antonio Tropeano, Valeria Quartuccio, Andrea Cuppini, Gastone Castellani, Elio Jovine

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.