Glucococorticoid-Induced Death of Pancreatic Beta Cells: An Organized Chaos
Abstract
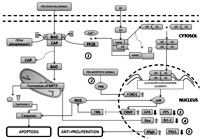
Glucocorticoids (GC) are renowned for their pleiotropic effects in all organ systems, their ubiquitous use in numerous clinical settings, and the abundant adverse effects they may exert, particularly in the endocrine-metabolic sphere. Although hyperglycemia and insulin resistance are well-defined GC-induced diabetogenic phenomena, an added component of direct injury to pancreatic β cells (PBC) may also participate in this scenario. Indeed, the apoptotic capacity of GC is widely recognized, and PBC do not escape this situation. No unified pathway has been characterized regarding GC-induced cell death; instead, it appears to depend on the specific machinery of each cell type, determining a great heterogeneity in GC-dependent apoptotic mechanisms among different tissues. In PBC, GC can induce the expression or activation of pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax, BAD, p38), repress anti-apoptotic proteins (Bcl-2), deactivate pro-survival mechanisms (cAMP-PKA signaling) and sensitize the cell to death induced by oxidative stress, fatty acids, hyperglycemia and cytokines. Although proliferative pathways (TGF-β, H-ras) are activated simultaneously – and an increase in PBC mass may be observed initially – pro-apoptotic and anti-proliferative mechanisms appear to eventually overcome their pro-survival counterparts, due to their synergic and aggregative action. Key molecules such as p38 and the cAMP-PKA system may be promising therapeutic targets in the prevention of GC-induced cell death.
Image: Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced death in pancreatic β cells.
Downloads
References
Pujols L, Mullol J, Roca-Ferrer J, Torrego A, Xaubet A, Cidlowski JA, et al. Expression of glucocorticoid receptor alpha- and beta-isoforms in human cells and tissues. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002; 283: C1324-31. [PMID: 12225995]
Zanchi NE, Filho MA, Felitti V, Nicastro H, Lorenzeti FM, Lancha AH Jr. Glucocorticoids: extensive physiological actions modulated through multiple mechanisms of gene regulation. J Cell Physiol. 2010; 224: 311-5. [PMID: 20432441]
Coutinho AE, Chapman KE. The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011 15; 335: 2-13. [PMC: 3047790]
Strehl C, Spies CM, Buttgereit F. Pharmacodynamics of glucocorticoids. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2011; 29: S13-8. [PMID: 22018178]
Kwon S, Hermayer KL. Glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia. Am J Med Sci 2013; 345: 274-7. [PMID: 23531958]
Ferris HA, Kahn CR. New mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced insulin resistance: make no bones about it. J Clin Invest 2012; 122: 3854-7. [PMID: 23093783]
Jörns A, Sennholz C, Naujok O, Lenzen S. Beta cell mass regulation in the rat pancreas through glucocorticoids and thyroid hormones. Pancreas 2010; 39: 1167-72. [PMID: 20683219]
Volgi JR, Baldwin D Jr. Glucocorticoid therapy and diabetes management. Nurs Clin North Am 2001; 36: 333-9. [PMID: 11382567]
Clore JN, Thurby-Hay L. Glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia. Endocr Pract 2009; 15: 469-74. [PMID: 19454391]
Schlossmacher G, Platt E, Davies A, Meredith S, White A. Glucocorticoid receptor-mediated apoptosis in small-cell lung cancer requires interaction with BCL2. Endocr Relat Cancer 2013 14; 20: 785-95. [PMID: 24036132]
Gross KL, Oakley RH, Scoltock AB, Jewell CM, Cidlowski JA. Glucocorticoid receptor alpha isoform-selective regulation of antiapoptotic genes in osteosarcoma cells: a new mechanism for glucocorticoid resistance. Mol Endocrinol 2011; 25: 1087-99. [PMID: 21527497]
Greenstein S, Ghias K, Krett NL, Rosen ST. Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-mediated apoptosis in hematological malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 2002; 8: 1681-94. [PMID: 12060604]
McClenaghan NH. Physiological regulation of the pancreatic {beta}-cell: functional insights for understanding and therapy of diabetes. Exp Physiol 2007; 92: 481-96. [PMID: 17272356]
Newton R. Molecular mechanisms of glucocorticoid action: what is important? Thorax. 2000; 55: 603-13. [PMID: 10856322]
Stahn C, Buttgereit F. Genomic and nongenomic effects of glucocorticoids. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2008; 4: 525-33. [PMID: 18762788]
Hebbar PB, Archer TK. Chromatin remodeling by nuclear receptors. Chromosoma 2003; 111: 495-504. [PMID: 12743713]
De Bosscher K, Vanden Berghe W, Haegeman G. The interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and nuclear factor-kappaB or activator protein-1: molecular mechanisms for gene repression. Endocr Rev 2003; 24: 488-522. [PMID: 12920152]
Oakley RH, Sar M, Cidlowski JA. The human glucocorticoid receptor beta isoform. Expression, biochemical properties, and putative function. J Biol Chem 1996 19; 271: 9550-9. [PMID: 8621628]
Lu NZ, Cidlowski JA. The origin and functions of multiple human glucocorticoid receptor isoforms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004; 1024: 102-23. [PMID: 15265776]
Koga Y, Matsuzaki A, Suminoe A, Hattori H, Kanemitsu S, Hara T. Differential mRNA expression of glucocorticoid receptor alpha and beta is associated with glucocorticoid sensitivity of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2005; 45: 121-7. [PMID: 15704223]
Lu NZ, Collins JB, Grissom SF, Cidlowski JA. Selective regulation of bone cell apoptosis by translational isoforms of the glucocorticoid receptor. Mol Cell Biol 2007; 27: 7143-60. [PMID: 17682054]
Liles WC, Dale DC, Klebanoff SJ. Glucocorticoids inhibit apoptosis of human neutrophils. Blood. 1995; 86: 3181-8. [PMID: 7579413]
Sasson R, Tajima K, Amsterdam A. Glucocorticoids protect against apoptosis induced by serum deprivation, cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and p53 activation in immortalized human granulosa cells: involvement of Bcl-2. Endocrinology. 2001; 142: 802-11. [PMID: 11159853]
Planey SL, Abrams MT, Robertson NM, Litwack G. Role of apical caspases and glucocorticoid-regulated genes in glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis of pre-B leukemic cells. Cancer Res 2003; 63: 172-8. [PMID: 12517795]
Herold MJ, McPherson KG, Reichardt HM. Glucocorticoids in T cell apoptosis and function. Cell Mol Life Sci 2006; 63: 60-72. [PMID: 16314919]
Herr I, Gassler N, Friess H, Büchler MW. Regulation of differential pro- and anti-apoptotic signaling by glucocorticoids. Apoptosis 2007; 12: 271-91. [PMID: 17191112]
Jiang X, Wang X. Cytochrome C-mediated apoptosis. Annu Rev Biochem 2004; 73: 87-106. [PMID: 15189137]
Hala M, Hartmann BL, Böck G, Geley S, Kofler R. Glucocorticoid-receptor-gene defects and resistance to glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in human leukemic cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1996; 68: 663-8. [PMID: 8938150]
Tao Y, Gao L, Wu X, Wang H, Yang G, Zhan F, et al. Down-regulation of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 by bortezomib sensitizes Jurkat leukemia T cells against glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis 2013 24; 8: e67067. [PMID: 23826195]
Reichardt HM, Umland T, Bauer A, Kretz O, Schütz G. Mice with an increased glucocorticoid receptor gene dosage show enhanced resistance to stress and endotoxic shock. Mol Cell Biol 2000; 20: 9009-17. [PMC: 86554 ]
Pazirandeh A, Xue Y, Prestegaard T, Jondal M, Okret S. Effects of altered glucocorticoid sensitivity in the T cell lineage on thymocyte and T cell homeostasis. FASEB J 2002; 16: 727-9. [PMID: 11923224]
Wallace AD, Cidlowski JA. Proteasome-mediated glucocorticoid receptor degradation restricts transcriptional signaling by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 42714-21. [PMID: 11555652]
Schmidt S, Rainer J, Ploner C, Presul E, Riml S, Kofler R. Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis and glucocorticoid resistance: molecular mechanisms and clinical relevance. Cell Death Differ. 2004; 1: S45-55. [PMID: 15243581]
Wu I, Shin SC, Cao Y, Bender IK, Jafari N, Feng G, et al Selective glucocorticoid receptor translational isoforms reveal glucocorticoid-induced apoptotic transcriptomes. Cell Death Dis 2013; 4: e453. [PMID: 23303127]
Geley S, Fiegl M, Hartmann BL, Kofler R. Genes mediating glucocorticoid effects and mechanisms of their regulation. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 1996; 128: 1-97. [PMID: 8791720]
Sharma S, Lichtenstein A. Dexamethasone-induced apoptotic mechanisms in myeloma cells investigated by analysis of mutant glucocorticoid receptors. Blood 2008; 112: 1338-45. [PMID: 18515658]
Auphan N, DiDonato JA, Rosette C, Helmberg A, Karin M. Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-kappa B activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis Science 1995; 270: 286-90. [PMID: 7569976]
Ayroldi E, Migliorati G, Bruscoli S, Marchetti C, Zollo O, Cannarile L, et al. Modulation of T-cell activation by the glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper factor via inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B Blood 2001; 98: 743-53. [PMID: 11468175]
Li Z, Chen Y, Cao D, Wang Y, Chen G, Zhang S, et al. Glucocorticoid up-regulates transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) type II receptor and enhances TGF-beta signaling in human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Endocrinology 2006; 147: 5259-67. [PMID: 16887915]
Ligons DL, Tuncer C, Linowes BA, Akcay IM, Kurtulus S, Deniz E, et al. CD8 lineage-specific regulation of interleukin-7 receptor expression by the transcriptional repressor Gfi1. J Biol Chem 2012; 287: 34386-99. [PMID: 22865857]
Rhen T, Cidlowski JA. Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids--new mechanisms for old drugs. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 1711-23. [PMID: 16236742]
Tonko M, Ausserlechner MJ, Bernhard D, Helmberg A, Kofler R. Gene expression profiles of proliferating vs. G1/G0 arrested human leukemia cells suggest a mechanism for glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. FASEB J 2001; 15: 693-9. [PMID: 11259387]
Obexer P, Certa U, Kofler R, Helmberg A. Expression profiling of glucocorticoid-treated T-ALL cell lines: rapid repression of multiple genes involved in RNA-, protein- and nucleotide synthesis. Oncogene 2001; 20: 4324-36. [PMID: 11466613]
Wang Z, Rong YP, Malone MH, Davis MC, Zhong F, Distelhorst CW. Thioredoxin-interacting protein (txnip) is a glucocorticoid-regulated primary response gene involved in mediating glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2006; 25: 1903-13. [PMID: 16301999]
McColl KS, He H, Zhong H, Whitacre CM, Berger NA, Distelhorst CW. Apoptosis induction by the glucocorticoid hormone dexamethasone and the calcium-ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin involves Bc1-2 regulated caspase activation. Mol Cell Endocrinol 1998; 139: 229-38. [PMID: 9705090]
Matsuyama S, Reed JC. Mitochondria-dependent apoptosis and cellular pH regulation. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: 1155-65. [PMID: 11175252]
Gómez-Angelats M, Bortner CD, Cidlowski JA. Cell volume regulation in immune cell apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res 2000; 301: 33-42. [PMID: 10928279]
Roma LP, Souza KL, Carneiro EM, Boschero AC, Bosqueiro JR. Pancreatic islets from dexamethasone-treated rats show alterations in global gene expression and mitochondrial pathways. Gen Physiol Biophys 2012; 31: 65-76. [PMID: 22447832]
Ranta F, Avram D, Berchtold S, Düfer M, Drews G, Lang F, et al. Dexamethasone induces cell death in insulin-secreting cells, an effect reversed by exendin-4. Diabetes 2006; 55: 1380-90. [PMID: 16644695]
Rabinovitch A, Suarez-Pinzon W, Strynadka K, Ju Q, Edelstein D, Brownlee M, et al. Transfection of human pancreatic islets with an anti-apoptotic gene (bcl-2) protects beta-cells from cytokine-induced destruction. Diabetes 1999; 48: 1223-9. [PMID: 10342808]
Vien Tran V, Chen G, Newgard CB, Hohmeier HE. Discrete and Complementary Mechanisms of Protection of β-Cells Against Cytokine-Induced and Oxidative Damage Achieved by bcl-2 Overexpression and a Cytokine Selection Strategy. Diabetes 2003; 32: 1423-1432.
Masters SC, Yang H, Datta SR, Greenberg ME, Fu H. 14-3-3 inhibits Bad-induced cell death through interaction with serine-136. Mol Pharmacol 2001; 60: 1325-31. [PMID: 11723239]
Lizcano JM, Morrice N, Cohen P. Regulation of BAD by cAMP-dependent protein kinase is mediated via phosphorylation of a novel site, Ser155. Biochem J 2000; 349: 547-57. [PMID: 10880354]
Virdee K, Parone PA, Tolkovsky AM. Phosphorylation of the pro-apoptotic protein BAD on serine 155, a novel site, contributes to cell survival. Curr Biol 2000; 10: 1151-4. [PMID: 10996800]
Harada H, Andersen JS, Mann M, Terada N, Korsmeyer SJ. p70S6 kinase signals cell survival as well as growth, inactivating the pro-apoptotic molecule BAD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2001; 98: 9666-70. [PMID: 11493700]
Yu C, Minemoto Y, Zhang J, Liu J, Tang F, Bui TN, et al. JNK suppresses apoptosis via phosphorylation of the proapoptotic Bcl-2 family protein BAD. Mol Cell 2004; 13: 329-40. [PMID: 14967141]
Kanamaru Y, Sekine S, Ichijo H, Takeda K. The phosphorylation-dependent regulation of mitochondrial proteins in stress responses. J Signal Transduct 2012; 931215. [PMID: 22848813]
Rumi-Masante J, Rusinga FI, Lester TE, Dunlap TB, Williams TD, Dunker AK, et al. Structural basis for activation of calcineurin by calmodulin. J Mol Biol 2012; 415: 307-17. [PMID: 22100452]
Ranta F, Düfer M, Stork B, Wesselborg S, Drews G, Häring HU, et al. Regulation of calcineurin activity in insulin-secreting cells: stimulation by Hsp90 during glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis. Cell Signal 2008; 20: 1780-6. [PMID: 18611438]
Lambillotte C, Gilon P, Henquin JC. Direct glucocorticoid inhibition of insulin secretion. An in vitro study of dexamethasone effects in mouse islets. J Clin Invest 1997; 99: 414-23. [PMID: 9022074]
Chiang CW, Harris G, Ellig C, Masters SC, Subramanian R, Shenolikar S, et al. Protein phosphatase 2A activates the proapoptotic function of BAD in interleukin- 3-dependent lymphoid cells by a mechanism requiring 14-3-3 dissociation. Blood 2001; 97: 1289-97. [PMID: 11222372]
Ayllón V, Cayla X, García A, Roncal F, Fernández R, Albar JP, et al. Bcl-2 targets protein phosphatase 1 alpha to Bad. J Immunol 2001; 166: 7345-52. [PMID: 11390485]
Kaiser G, Gerst F, Michael D, Berchtold S, Friedrich B, Strutz-Seebohm N, et al. Regulation of forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) by protein kinase B and glucocorticoids: different mechanisms of induction of beta cell death in vitro. Diabetologia 2013; 56: 1587-95. [PMID: 23435785]
Kaneto H, Nakatani Y, Kawamori D, Miyatsuka T, Matsuoka T. Involvement of Oxidative Stress and the JNK Pathway in Glucose Toxicity. Rev Diabet Stud 2004; 1: 165–174. [PMC: 1783693]
Grunnet LG, Aikin R, Tonnesen MF, Paraskevas S, Blaabjerg L, Størling J, et al. Proinflammatory cytokines activate the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in beta-cells. Diabetes 2009; 58: 1807-15. [PMID: 19470609]
Fransson L, Rosengren V, Saha TK, Grankvist N, Islam T, Honkanen RE, et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinases and protein phosphatase 5 mediate glucocorticoid-induced cytotoxicity in pancreatic islets and β-cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2014; 383: 126-36. [PMID: 24361515]
Bruna A, Nicolàs M, Muñoz A, Kyriakis JM, Caelles C. Glucocorticoid receptor-JNK interaction mediates inhibition of the JNK pathway by glucocorticoids. EMBO J 2003; 22: 6035-44. [PMID: 14609950]
Abdelli S, Puyal J, Bielmann C, Buchillier V, Abderrahmani A, Clarke PG. JNK3 is abundant in insulin-secreting cells and protects against cytokine-induced apoptosis. Diabetologia 2009; 52: 1871-80. [PMID: 19609503]
Prause M, Christensen DP, Billestrup N, Mandrup-Poulsen T. JNK1 protects against glucolipotoxicity-mediated beta-cell apoptosis. PLoS One 2014; 9: e87067.
Klumpp S, Selke D, Krieglstein J. Protein phosphatase type 2C dephosphorylates BAD. Neurochem Int 2003; 42: 555-60. [PMID: 12590938]
Reich E, Tamary A, Vogt Sionov R, Melloul D. Involvement of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) in glucocorticoid-mediated beta cell death. Diabetologia 2012; 55: 1048-1057. [PMID: 22246375]
Hou N, Torii S, Saito N, Hosaka M, Takeuchi T. Reactive oxygen species-mediated pancreatic beta-cell death is regulated by interactions between stress-activated protein kinases, p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases. Endocrinology 2008; 149: 1654-65. [PMID: 18187551]
Yuan H, Zhang X, Huang X, Lu Y, Tang W, Man Y, et al. NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species mediate FFAs-induced dysfunction and apoptosis of β-cells via JNK, p38 MAPK and p53 pathways. PLoS One 2010; 5: e15726. [PMID: 21209957]
Maedler K, Schulthess FT, Bielman C, Berney T, Bonny C, Prentki M, et al. Glucose and leptin induce apoptosis in human beta-cells and impair glucose-stimulated insulin secretion through activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases. FASEB J 2008; 22: 1905-13. [PMID: 18263705]
Rafacho A, Cestari TM, Taboga SR, Boschero AC, Bosqueiro JR. High doses of dexamethasone induce increased beta-cell proliferation in pancreatic rat islets. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2009; 296: E681-9. [PMID: 19158320]
Colvin ES, Ma HY, Chen YC, Hernandez AM, Fueger PT. Glucocorticoid-induced suppression of β-cell proliferation is mediated by Mig6. Endocrinology 2013; 154: 1039-46. [PMID: 23384834]
Roma LP, Oliveira CA, Carneiro EM, Albuquerque GG, Boschero AC, Souza KL. N-acetylcysteine protects pancreatic islet against glucocorticoid toxicity. Redox Rep 2011; 16: 173-80. [PMID: 21888768]
El-Assaad W, Joly E, Barbeau A, Sladek R, Buteau J, Maestre I, et al. Glucolipotoxicity alters lipid partitioning and causes mitochondrial dysfunction, cholesterol, and ceramide deposition and reactive oxygen species production in INS832/13 ss-cells. Endocrinology 2010; 151: 3061-73. [PMID: 20444946]
Gesina E, Tronche F, Herrera P, Duchene B, Tales W, Czernichow P, Breant B. Dissecting the role of glucocorticoids on pancreas development. Diabetes 2004; 53: 2322-9. [PMID: 15331541]
Valtat B, Riveline JP, Zhang P, Singh-Estivalet A, Armanet M, Venteclef N, Besseiche A, Kelly DP, Tronche F, Ferré P, Gautier JF, Bréant B, Blondeau B. Fetal PGC-1α overexpression programs adult pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. Diabetes 2013; 62: 1206-16. [PMID: 23274887]
Matthews LC, Hanley NA. The stress of starvation: glucocorticoid restraint of beta cell development. Diabetologia 2011; 54: 223-6. [PMID: 21072627]
Gwathmey TM, Shaltout HA, Rose JC, Diz DI, Chappell MC. Glucocorticoid-induced fetal programming alters the functional complement of angiotensin receptor subtypes within the kidney. Hypertension 2011; 57: 620-6. [PMID: 21220702]
Gokulakrishnan G, Estrada IJ, Sosa HA, Fiorotto ML. In utero glucocorticoid exposure reduces fetal skeletal muscle mass in rats independent of effects on maternal nutrition. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2012; 302: R1143-52. [PMID: 22422665]
Rafacho A, Ortsäter H, Nadal A, Quesada I. Glucocorticoid treatment and endocrine pancreas function: implications for glucose homeostasis, insulin resistance and diabetes. J Endocrinol 2014; 223: R49-R62. [PMID: 25271217]
Barseghian G, Levine R. Effect of corticosterone on insulin and glucagon secretion by the isolated perfused rat pancreas. Endocrinology 1980; 106: 547-52. [PMID: 6986256]
Rafacho A, Gonçalves-Neto LM, Santos-Silva JC, Alonso-Magdalena P, Merino B, Taboga SR,et al. Pancreatic alpha-cell dysfunction contributes to the disruption of glucose homeostasis and compensatory insulin hypersecretion in glucocorticoid-treated rats. PLoS One 2014; 9: e93531. [PMID: 24705399]
Dumortier O, Theys N, Ahn MT, Remacle C, Reusens B. Impairment of rat fetal β-cell development by maternal exposure to dexamethasone during different time-windows. PLoS ONE 6 e25576. [PMID: 21991320]
Scherbaum WA. The role of amylin in the physiology of glycemic control. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 1998; 106: 97-102. [PMID: 9628238]
Pillay K, Govender P. Amylin uncovered: a review on the polypeptide responsible for type II diabetes. Biomed Res Int 2013; 826706. [PMID: 23607096]
Ludvik B, Clodi M, Kautzky-Willer A, Capek M, Hartter E, Pacini G, et al. Effect of dexamethasone on insulin sensitivity, islet amyloid polypeptide and insulin secretion in humans. Diabetologia 1993; 36: 84-7. [PMID: 8436259]
Hauge-Evans AC, King AJ, Carmignac D, Richardson CC, Robinson IC, Low MJ, et al. Somatostatin secreted by islet delta-cells fulfills multiple roles as a paracrine regulator of islet function. Diabetes 2009; 58: 403-11. [PMID: 18984743]
Papachristou DN, Liu JL, Patel YC. Glucocorticoids regulate somatostatin peptide and steady state messenger ribonucleic acid levels in normal rat tissues and in a somatostatin-producing islet tumor cell line (1027B2). Endocrinology 1994; 134: 2259-66. [PMID: 7908873]
Kojima M, Kangawa K. Ghrelin: from gene to physiological function. Results Probl Cell Differ 2010; 50: 185-205. [PMID: 19859676]
van Donkelaar EL, Vaessen KR, Pawluski J, Sierksma AS, Blokland A, Cañete R, Steinbusch HW. Long-Term Corticosterone Exposure Decreases Insulin Sensitivity and Induces Depressive-Like Behaviour in the C57BL/6NCrl Mouse. PLoS One 2014; 9: e106960. [PMID: 25310187]
Campbell JE, Peckett AJ, D'souza AM, Hawke TJ, Riddell MC. Adipogenic and lipolytic effects of chronic glucocorticoid exposure. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2011; 300: C198-209. [PMID: 20943959]
Guidotti G, Calabrese F, Anacker C, Racagni G, Pariante CM, Riva MA. Glucocorticoid receptor and FKBP5 expression is altered following exposure to chronic stress: modulation by antidepressant treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 2013; 38: 616-27. [PMID: 23169346]
Sominsky L, Spencer SJ. Eating behavior and stress: a pathway to obesity. Front Psychol 2014; 13; 5:434. [PMID: 24860541]
Alex Rafacho, Antonio C. Boschero and Henrik Ortsäter (2012). Functional and Molecular Aspects of Glucocorticoids in the Endocrine Pancreas and Glucose Homeostasis, State of the Art of Therapeutic Endocrinology, Dr. Sameh Magdeldin (Ed.), ISBN: 978-953-51-0772-9, InTech, DOI: 10.5772/50233. [PMID: ]
Rafacho A, Abrantes JL, Ribeiro DL, Paula FM, Pinto ME, Boschero AC, Bosqueiro JR Morphofunctional alterations in endocrine pancreas of short- and long-term dexamethasone-treated rats. Horm Metab Res 2011; 43: 275-81. [PMID: 21225543]
Weinhaus AJ, Bhagroo NV, Brelje TC, Sorenson RL. Dexamethasone counteracts the effect of prolactin on islet function: implications for islet regulation in late pregnancy. Endocrinology 2000; 141: 1384-93. [PMID: 10746642]
Ranta F, Avram D, Berchtold S, Düfer M, Drews G, Lang F, Ullrich S. Dexamethasone induces cell death in insulin-secreting cells, an effect reversed by exendin-4. Diabetes 2006; 55: 1380-90. [PMID: 16644695]
Protzek AO, Costa-Júnior JM, Rezende LF, Santos GJ, Araújo TG, Vettorazzi JF, Ortis F, Carneiro EM, Rafacho A, Boschero AC. Augmented β-Cell Function and Mass in Glucocorticoid-Treated Rodents Are Associated with Increased Islet Ir-β /AKT/mTOR and Decreased AMPK/ACC and AS160 Signaling. Int J Endocrinol 2014: 983453. [PMID: 25313308]
Roma LP, Oliveira CA, Carneiro EM, Albuquerque GG, Boschero AC, Souza KL. N-acetylcysteine protects pancreatic islet against glucocorticoid toxicity. Redox Rep 2011; 16: 173-80. [PMID: 21888768]
Kauh E, Mixson L, Malice MP, Mesens S, Ramael S, Burke J, Reynders T, Van Dyck K, Beals C, Rosenberg E, Ruddy M. Prednisone affects inflammation, glucose tolerance, and bone turnover within hours of treatment in healthy individuals. Eur J Endocrinol 2012; 166: 459-67. [PMID: 22180452]
Kauh EA, Mixson LA, Shankar S, McCarthy J, Maridakis V, Morrow L, Heinemann L, Ruddy MK, Herman GA, Kelley DE, Hompesch M. Short-term metabolic effects of prednisone administration in healthy subjects. Diabetes Obes Metab 2011; 13: 1001-7. [PMID: 21635675]
Pellacani A, Fornengo P, Bruno A, Ceruti C, Mioletti S, Curto M, Rinaudo MT, Pagano G, Cavallo-Perin P. Acute methylprednisolone administration induces a transient alteration of glucose tolerance and pyruvate dehydrogenase in humans. Eur J Clin Invest 1999; 29: 861-7. [PMID: 10583428]
Gonzalez-Gonzalez JG, Mireles-Zavala LG, Rodriguez-Gutierrez R, Gomez-Almaguer D, Lavalle-Gonzalez FJ, Tamez-Perez HE, Gonzalez-Saldivar G, Villarreal-Perez JZ. Hyperglycemia related to high-dose glucocorticoid use in noncritically ill patients. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2013; 5: 18. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-18. [PMID: 23557386]
Clore JN, Thurby-Hay L. Glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia. Endocr Pract 2009; 15: 469-74. [PMID: 19454391]
Henriksen JE, Alford F, Ward GM, Beck-Nielsen H. Risk and mechanism of dexamethasone-induced deterioration of glucose tolerance in non-diabetic first-degree relatives of NIDDM patients. Diabetologia 1997; 40: 1439-48. [PMID: 9447952]
Ezanno H, Pawlowski V, Abdelli A, Boutry R, Gmyr V, Kerr-Conte J, Bonny C, Pattou F, Abderrahmani A. JNK3 Is Required for the Cytoprotective Effect of Exendin 4. J Diabetes Res 2014; 814: 854. [PMID: 25025079]
Wang Q, Li L, Xu E, Wong V, Rhodes C, Brubaker PL. Glucagon-like peptide-1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis via activation of protein kinase B in pancreatic INS-1 beta cells. Diabetologia 2004; 47: 478-87. [PMID: 14762654]
Zhao R, Fuentes-Mattei E, Velazquez-Torres G, Su CH, Chen J, Lee MH, Yeung SC. Exenatide improves glucocorticoid-induced glucose intolerance in mice. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2011; 4: 61-5. [PMID: 21448323]
van Raalte DH, van Genugten RE, Linssen MM, Ouwens DM, Diamant M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist treatment prevents glucocorticoid-induced glucose intolerance and islet-cell dysfunction in humans. Diabetes Care 2011; 34: 412-7. [PMID: 21216851]
Fransson L, Dos Santos C, Wolbert P, Sjöholm A, Rafacho A, Ortsäter H. Liraglutide counteracts obesity and glucose intolerance in a mouse model of glucocorticoid-induced metabolic syndrome. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2014; 6: 3. [PMID: 24423471]
Garber AJ. Incretin effects on β-cell function, replication, and mass: the human perspective. Diabetes Care 2011; 34: S258-63. [PMID: 21525465]
Copyright (c) 2015 Joselyn Rojas, Mervin Chávez-Castillo, Mervin Chávez-Castillo, Mayela Cabrera, Mayela Cabrera, Valmore Bermúdez, Valmore Bermúdez

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.