Regulation Mechanisms of the Hedgehog Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer: A Review
Abstract
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is the fourth most common cause of death from cancer. Its 5-year survival rate is less than 5%. This poor prognosis is mostly due to the cancer’s early invasion and metastasis formation, leading to an initial diagnosis at an advanced incurable stage in the majority of patients. The only potentially curative treatment is radical surgical resection. The effect of current chemotherapeutics or radiotherapy is limited. Novel therapeutic strategies are therefore much needed. One of the hallmarks of PDAC is its abundant desmoplastic (stromal) reaction. The Hedgehog (Hh) signaling pathway is critical for embryologic development of the pancreas. Aberrant Hh signaling promotes pancreatic carcinogenesis, the maintenance of the tumor microenvironment and stromal growth. The canonical Hh-pathway in the tumor stroma has been targeted widely but has not yet lead to hopeful clinical results. Targeting both the tumor and its surrounding stroma through Hh pathway inhibition by also targeting non-canonical pathways as apparent in the tumor cell may therefore be a novel treatment strategy for PDAC.
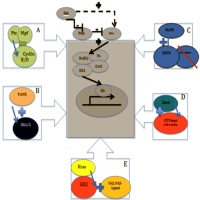
Image: The non-canonical Hedgehog pathway.
Downloads
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. Jan 2013; 63(1): 11-30. [PMID:23335087]
Kocher HM and Alrawashdeh W. Pancreatic cancer. Clin Evid (Online). 2010; 2010. [PMID:21729338]
Hariharan D, Saied A and Kocher HM. Analysis of mortality rates for pancreatic cancer across the world. HPB (Oxford). 2008; 10(1): 58-62. [PMID:18695761]
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. Sep-Oct 2010; 60(5):277-300. [PMID: 20610543]
Schneider G, Siveke JT, Eckel F and Schmid RM. Pancreatic cancer: basic and clinical aspects. Gastroenterology. May 2005; 128(6): 1606-1625. [PMID: 15887154]
Hruban RH, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J, Compton C, Garrett ES, Goodman SN, et al. Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: a new nomenclature and classification system for pancreatic duct lesions. Am J Surg Pathol. May 2001; 25(5): 579-586. [PMID: 11342768]
Hruban RH and Fukushima N. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: update on the surgical pathology of carcinomas of ductal origin and PanINs. Mod Pathol. Feb 2007; 20 Suppl 1: S61-70. [PMID: 17486053]
Breast Cancer Linkage C. Cancer risks in BRCA2 mutation carriers. J Natl Cancer Inst. Aug 4 1999; 91(15): 1310-1316. [PMID:10433620]
Goldstein AM, Fraser MC, Struewing JP, Hussussian CJ, Ranade K, Zametkin DP, et al. Increased risk of pancreatic cancer in melanoma-prone kindreds with p16INK4 mutations. N Engl J Med. Oct 12 1995;333(15):970-974. [PMID:7666916]
Morris JPt, Wang SC and Hebrok M. KRAS, Hedgehog, Wnt and the twisted developmental biology of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Nat Rev Cancer. Oct 2010; 10(10): 683-695. [PMID: 20814421]
Pellegata NS, Sessa F, Renault B, Bonato M, Leone BE, Solcia E, et al. K-ras and p53 gene mutations in pancreatic cancer: ductal and nonductal tumors progress through different genetic lesions. Cancer Res. Mar 15 1994; 54(6): 1556-1560. [PMID: 8137263]
Lewis EB. A gene complex controlling segmentation in Drosophila. Nature. Dec 7 1978; 276(5688): 565-570. [PMID: 103000]
Nusslein-Volhard C and Wieschaus E. Mutations affecting segment number and polarity in Drosophila. Nature. Oct 30 1980; 287(5785): 795-801. [PMID: 6776413]
Perrimon N. Hedgehog and beyond. Cell. Feb 24 1995; 80(4): 517-520. [PMID: 7867057]
Vortkamp A, Lee K, Lanske B, Segre GV, Kronenberg HM and Tabin CJ. Regulation of rate of cartilage differentiation by Indian hedgehog and PTH-related protein. Science. Aug 2 1996; 273(5275): 613-622. [PMID: 8662546]
Bitgood MJ and McMahon AP. Hedgehog and Bmp genes are coexpressed at many diverse sites of cell-cell interaction in the mouse embryo. Dev Biol. Nov 1995; 172(1): 126-138. [PMID: 7589793]
Parmantier E, Lynn B, Lawson D, Turmaine M, Namini SS, Chakrabarti L, et al. Schwann cell-derived Desert hedgehog controls the development of peripheral nerve sheaths. Neuron. Aug 1999; 23(4): 713-724. [PMID: 10482238]
Smith JC. Hedgehog, the floor plate, and the zone of polarizing activity. Cell. Jan 28 1994; 76(2): 193-196. [PMID: 8293455]
Tekki-Kessaris N, Woodruff R, Hall AC, Gaffield W, Kimura S, Stiles CD, et al. Hedgehog-dependent oligodendrocyte lineage specification in the telencephalon. Development. Jul 2001; 128(13): 2545-2554. [PMID: 11493571]
Kim HJ, Rice DP, Kettunen PJ and Thesleff I. FGF-, BMP- and Shh-mediated signalling pathways in the regulation of cranial suture morphogenesis and calvarial bone development. Development. Apr 1998; 125(7): 1241-1251. [PMID: 9477322]
Ekker SC, Ungar AR, Greenstein P, von Kessler DP, Porter JA, Moon RT, et al. Patterning activities of vertebrate hedgehog proteins in the developing eye and brain. Curr Biol. Aug 1 1995; 5(8): 944-955. [PMID: 7583153]
Ramalho-Santos M, Melton DA and McMahon AP. Hedgehog signals regulate multiple aspects of gastrointestinal development. Development. Jun 2000; 127(12): 2763-2772. [PMID: 10821773]
Motoyama J, Liu J, Mo R, Ding Q, Post M and Hui CC. Essential function of Gli2 and Gli3 in the formation of lung, trachea and oesophagus. Nat Genet. Sep 1998; 20(1): 54-57. [PMID: 9731531]
Kawahira H, Scheel DW, Smith SB, German MS and Hebrok M. Hedgehog signaling regulates expansion of pancreatic epithelial cells. Dev Biol. Apr 1 2005; 280(1): 111-121. [PMID: 15766752]
Roberts DJ, Smith DM, Goff DJ and Tabin CJ. Epithelial-mesenchymal signaling during the regionalization of the chick gut. Development. Aug 1998; 125(15): 2791-2801. [PMID: 9655802]
Marigo V and Tabin CJ. Regulation of patched by sonic hedgehog in the developing neural tube. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Sep 3 1996; 93(18): 9346-9351. [PMID: 8790332]
Kayed H, Kleeff J, Osman T, Keleg S, Buchler MW and Friess H. Hedgehog signaling in the normal and diseased pancreas. Pancreas. Mar 2006; 32(2): 119-129. [PMID: 16552330]
Grindley JC, Bellusci S, Perkins D and Hogan BL. Evidence for the involvement of the Gli gene family in embryonic mouse lung development. Dev Biol. Aug 15 1997; 188(2): 337-348. [PMID: 9268579]
Fendrich V, Oh E, Bang S, Karikari C, Ottenhof N, Bisht S, et al. Ectopic overexpression of Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) induces stromal expansion and metaplasia in the adult murine pancreas. Neoplasia. Oct 2011; 13(10): 923-930. [PMID: 22028618]
Bailey JM, Mohr AM and Hollingsworth MA. Sonic hedgehog paracrine signaling regulates metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. Oct 8 2009; 28(40): 3513-3525. [PMID: 19633682]
Tian H, Callahan CA, DuPree KJ, Darbonne WC, Ahn CP, Scales SJ, et al. Hedgehog signaling is restricted to the stromal compartment during pancreatic carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Mar 17 2009; 106(11): 4254-4259. [PMID: 19246386]
Yauch RL, Gould SE, Scales SJ, Tang T, Tian H, Ahn CP, et al. A paracrine requirement for hedgehog signalling in cancer. Nature. Sep 18 2008; 455(7211): 406-410. [PMID: 18754008]
Lee JJ, Perera RM, Wang H, Wu DC, Liu XS, Han S, et al. Stromal response to Hedgehog signaling restrains pancreatic cancer progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Jul 29 2014; 111(30): E3091-3100. [PMID: 25024225]
Marini KD, Payne BJ, Watkins DN and Martelotto LG. Mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling in cancer. Growth Factors. Dec 2011; 29(6): 221-234. [PMID: 21875383]
Hwang RF, Moore TT, Hattersley MM, Scarpitti M, Yang B, Devereaux E, et al. Inhibition of the hedgehog pathway targets the tumor-associated stroma in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Res. Sep 2012; 10(9): 1147-1157. [PMID: 22859707]
Li KK, Lau KM and Ng HK. Signaling pathway and molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013; 6(7): 1211-1222. [PMID: 23826403]
Nakashima H, Nakamura M, Yamaguchi H, Yamanaka N, Akiyoshi T, Koga K, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to hedgehog signaling pathway activation through sonic hedgehog induction in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. Jul 15 2006; 66(14): 7041-7049. [PMID: 16849549]
Rajurkar M, De Jesus-Monge WE, Driscoll DR, Appleman VA, Huang H, Cotton JL, et al. The activity of Gli transcription factors is essential for Kras-induced pancreatic tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Apr 24 2012; 109(17): E1038-1047. [PMID: 22493246]
Athar M, Li C, Tang X, Chi S, Zhang X, Kim AL, et al. Inhibition of smoothened signaling prevents ultraviolet B-induced basal cell carcinomas through regulation of Fas expression and apoptosis. Cancer Res. Oct 15 2004; 64(20): 7545-7552. [PMID: 15492281]
Lee SW, Moskowitz MA and Sims JR. Sonic hedgehog inversely regulates the expression of angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 in fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med. Mar 2007; 19(3): 445-451. [PMID: 17273793]
Adolphe C, Hetherington R, Ellis T and Wainwright B. Patched1 functions as a gatekeeper by promoting cell cycle progression. Cancer Res. Feb 15 2006; 66(4): 2081-2088. [PMID: 16489008]
Bian YH, Huang SH, Yang L, Ma XL, Xie JW and Zhang HW. Sonic hedgehog-Gli1 pathway in colorectal adenocarcinomas. World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21 2007; 13(11): 1659-1665. [PMID: 17461467]
Ma J, Tian L, Cheng J, Chen Z, Xu B, Wang L, et al. Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway supports cancer cell growth during cancer radiotherapy. PLoS One. 2013; 8(6): e65032. [PMID: 23762282]
Shahi MH, Rey JA and Castresana JS. The sonic hedgehog-GLI1 signaling pathway in brain tumor development. Expert Opin Ther Targets. Dec 2012; 16(12): 1227-1238. [PMID: 22992192]
Rohatgi R, Milenkovic L and Scott MP. Patched1 regulates hedgehog signaling at the primary cilium. Science. Jul 20 2007; 317(5836): 372-376. [PMID: 17641202]
Bijlsma MF, Spek CA, Zivkovic D, van de Water S, Rezaee F and Peppelenbosch MP. Repression of smoothened by patched-dependent (pro-)vitamin D3 secretion. PLoS Biol. Jul 2006; 4(8): e232. [PMID: 16895439]
Cheng SY and Yue S. Role and regulation of human tumor suppressor SUFU in Hedgehog signaling. Adv Cancer Res. 2008; 101:29-43. [PMID: 19055941]
Stone DM, Murone M, Luoh S, Ye W, Armanini MP, Gurney A, et al. Characterization of the human suppressor of fused, a negative regulator of the zinc-finger transcription factor Gli. J Cell Sci. Dec 1999; 112 ( Pt 23): 4437-4448. [PMID: 10564661]
Meng X, Poon R, Zhang X, Cheah A, Ding Q, Hui CC, et al. Suppressor of fused negatively regulates beta-catenin signaling. J Biol Chem. Oct 26 2001; 276(43): 40113-40119. [PMID: 11477086]
Kogerman P, Grimm T, Kogerman L, Krause D, Unden AB, Sandstedt B, et al. Mammalian suppressor-of-fused modulates nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of Gli-1. Nat Cell Biol. Sep 1999; 1(5): 312-319. [PMID: 10559945]
Ding Q, Fukami S, Meng X, Nishizaki Y, Zhang X, Sasaki H, et al. Mouse suppressor of fused is a negative regulator of sonic hedgehog signaling and alters the subcellular distribution of Gli1. Curr Biol. Oct 7 1999; 9(19): 1119-1122. [PMID: 10531011]
Yue S, Chen Y and Cheng SY. Hedgehog signaling promotes the degradation of tumor suppressor Sufu through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Oncogene. Jan 29 2009; 28(4): 492-499. [PMID: 18997815]
Strand MF, Wilson SR, Dembinski JL, Holsworth DD, Khvat A, Okun I, et al. A novel synthetic smoothened antagonist transiently inhibits pancreatic adenocarcinoma xenografts in a mouse model. PLoS One. 2011; 6(6): e19904. [PMID: 21698280]
Kelleher FC and McDermott R. Aberrations and therapeutics involving the developmental pathway Hedgehog in pancreatic cancer. Vitam Horm. 2012; 88: 355-378. [PMID: 22391312]
Lum L and Beachy PA. The Hedgehog response network: sensors, switches, and routers. Science. Jun 18 2004; 304(5678): 1755-1759. [PMID: 15205520]
Ingham PW and McMahon AP. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. Dec 1 2001; 15(23): 3059-3087. [PMID: 11731473]
Kinzler KW, Bigner SH, Bigner DD, Trent JM, Law ML, O'Brien SJ, et al. Identification of an amplified, highly expressed gene in a human glioma. Science. Apr 3 1987; 236(4797): 70-73. [PMID: 3563490]
Orenic TV, Slusarski DC, Kroll KL and Holmgren RA. Cloning and characterization of the segment polarity gene cubitus interruptus Dominant of Drosophila. Genes Dev. Jun 1990; 4(6): 1053-1067. [PMID: 2166702]
Matise MP and Joyner AL. Gli genes in development and cancer. Oncogene. Dec 20 1999; 18(55): 7852-7859. [PMID: 10630638]
Chuang PT and McMahon AP. Vertebrate Hedgehog signalling modulated by induction of a Hedgehog-binding protein. Nature. Feb 18 1999; 397(6720): 617-621. [PMID: 10050855]
Hebrok M. Hedgehog signaling in pancreas development. Mech Dev. Jan 2003; 120(1): 45-57. [PMID: 12490295]
Olsen CL, Hsu PP, Glienke J, Rubanyi GM and Brooks AR. Hedgehog-interacting protein is highly expressed in endothelial cells but down-regulated during angiogenesis and in several human tumors. BMC Cancer. Aug 4 2004; 4: 43. [PMID: 15294024]
Martin ST, Sato N, Dhara S, Chang R, Hustinx SR, Abe T, et al. Aberrant methylation of the Human Hedgehog interacting protein (HHIP) gene in pancreatic neoplasms. Cancer Biol Ther. Jul 2005; 4(7): 728-733. [PMID: 15970691]
Kayed H, Kleeff J, Esposito I, Giese T, Keleg S, Giese N, et al. Localization of the human hedgehog-interacting protein (Hip) in the normal and diseased pancreas. Mol Carcinog. Apr 2005; 42(4): 183-192. [PMID: 15754313]
Jenkins D. Hedgehog signalling: emerging evidence for non-canonical pathways. Cell Signal. Jul 2009; 21(7): 1023-1034. [PMID: 19399989]
Ito M. Factors controlling cyclin B expression. Plant Mol Biol. Aug 2000; 43(5-6): 677-690. [PMID: 11089869]
Barnes EA, Kong M, Ollendorff V and Donoghue DJ. Patched1 interacts with cyclin B1 to regulate cell cycle progression. EMBO J. May 1 2001; 20(9): 2214-2223. [PMID: 11331587]
Katoh Y and Katoh M. Hedgehog target genes: mechanisms of carcinogenesis induced by aberrant hedgehog signaling activation. Curr Mol Med. Sep 2009; 9(7): 873-886. [PMID: 19860666]
Ulloa F, Itasaki N and Briscoe J. Inhibitory Gli3 activity negatively regulates Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Curr Biol. Mar 20 2007; 17(6): 545-550. [PMID: 17331723]
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW, Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY, et al. Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature. Oct 23 2003; 425(6960): 851-856. [PMID: 14520413]
Berman DM, Karhadkar SS, Maitra A, Montes De Oca R, Gerstenblith MR, Briggs K, et al. Widespread requirement for Hedgehog ligand stimulation in growth of digestive tract tumours. Nature. Oct 23 2003; 425(6960): 846-851. [PMID: 14520411]
Pasca di Magliano M, Sekine S, Ermilov A, Ferris J, Dlugosz AA and Hebrok M. Hedgehog/Ras interactions regulate early stages of pancreatic cancer. Genes Dev. Nov 15 2006; 20(22): 3161-3173. [PMID: 17114586]
Merchant A, Joseph G, Wang Q, Brennan S and Matsui W. Gli1 regulates the proliferation and differentiation of HSCs and myeloid progenitors. Blood. Mar 25 2010; 115(12): 2391-2396. [PMID: 20107231]
Vokes SA, Ji H, McCuine S, Tenzen T, Giles S, Zhong S, et al. Genomic characterization of Gli-activator targets in sonic hedgehog-mediated neural patterning. Development. May 2007; 134(10): 1977-1989. [PMID: 17442700]
Evangelista M, Tian H and de Sauvage FJ. The hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. Oct 15 2006; 12(20 Pt 1): 5924-5928. [PMID: 17062662]
Ji Z, Mei FC, Xie J and Cheng X. Oncogenic KRAS activates hedgehog signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem. May 11 2007; 282(19): 14048-14055. [PMID: 17353198]
Mills LD, Zhang Y, Marler RJ, Herreros-Villanueva M, Zhang L, Almada LL, et al. Loss of the transcription factor GLI1 identifies a signaling network in the tumor microenvironment mediating KRAS oncogene-induced transformation. J Biol Chem. Apr 26 2013; 288(17): 11786-11794. [PMID: 23482563]
Johnson RW, Nguyen MP, Padalecki SS, Grubbs BG, Merkel AR, Oyajobi BO, et al. TGF-beta promotion of Gli2-induced expression of parathyroid hormone-related protein, an important osteolytic factor in bone metastasis, is independent of canonical Hedgehog signaling. Cancer Res. Feb 1 2011; 71(3): 822-831. [PMID: 21189326]
Katoh Y and Katoh M. Integrative genomic analyses on GLI1: positive regulation of GLI1 by Hedgehog-GLI, TGFbeta-Smads, and RTK-PI3K-AKT signals, and negative regulation of GLI1 by Notch-CSL-HES/HEY, and GPCR-Gs-PKA signals. Int J Oncol. Jul 2009; 35(1): 187-192. [PMID: 19513567]
Mills LD, Zhang L, Marler R, Svingen P, Fernandez-Barrena MG, Dave M, et al. Inactivation of the transcription factor GLI1 accelerates pancreatic cancer progression. J Biol Chem. Jun 6 2014; 289(23): 16516-16525. [PMID: 24737325]
Kubo M, Nakamura M, Tasaki A, Yamanaka N, Nakashima H, Nomura M, et al. Hedgehog signaling pathway is a new therapeutic target for patients with breast cancer. Cancer Res. Sep 1 2004; 64(17): 6071-6074. [PMID: 15342389]
Polizio AH, Chinchilla P, Chen X, Kim S, Manning DR and Riobo NA. Heterotrimeric Gi proteins link Hedgehog signaling to activation of Rho small GTPases to promote fibroblast migration. J Biol Chem. Jun 3 2011; 286(22): 19589-19596. [PMID: 21474452]
Guimaraes AR, Rakhlin E, Weissleder R and Thayer SP. Magnetic resonance imaging monitors physiological changes with antihedgehog therapy in pancreatic adenocarcinoma xenograft model. Pancreas. Nov 2008; 37(4): 440-444. [PMID: 18953259]
Xu FG, Ma QY and Wang Z. Blockade of hedgehog signaling pathway as a therapeutic strategy for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. Oct 8 2009; 283(2): 119-124. [PMID: 19232458]
Lauth M, Bergstrom A, Shimokawa T and Toftgard R. Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. May 15 2007; 104(20): 8455-8460. [PMID: 17494766]
Petrova E, Matevossian A and Resh MD. Hedgehog acyltransferase as a target in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. Jan 27 2014. [PMID: 24469057]
Petrova E, Rios-Esteves J, Ouerfelli O, Glickman JF and Resh MD. Inhibitors of Hedgehog acyltransferase block Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Nat Chem Biol. Apr 2013; 9(4): 247-249. [PMID: 23416332]
Agyeman A, Jha BK, Mazumdar T and Houghton JA. Mode and specificity of binding of the small molecule GANT61 to GLI determines inhibition of GLI-DNA binding. Oncotarget. Jun 30 2014; 5(12): 4492-4503. [PMID: 24962990]
Fu J, Rodova M, Roy SK, Sharma J, Singh KP, Srivastava RK, et al. GANT-61 inhibits pancreatic cancer stem cell growth in vitro and in NOD/SCID/IL2R gamma null mice xenograft. Cancer Lett. Mar 1 2013; 330(1): 22-32. [PMID: 23200667]
Guo J, Gao J, Li Z, Gong Y, Man X, Jin J, et al. Adenovirus vector-mediated Gli1 siRNA induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer with Smo-dependent or Smo-independent Hh pathway activation in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. Oct 10 2013; 339(2): 185-194. [PMID: 23791879]
Huntzicker EG, Estay IS, Zhen H, Lokteva LA, Jackson PK and Oro AE. Dual degradation signals control Gli protein stability and tumor formation. Genes Dev. Feb 1 2006; 20(3): 276-281. [PMID: 16421275]
Olive KP, Jacobetz MA, Davidson CJ, Gopinathan A, McIntyre D, Honess D, et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Science. Jun 12 2009; 324(5933): 1457-1461. [PMID: 19460966]
Kleger A, Perkhofer L and Seufferlein T. Smarter drugs emerging in pancreatic cancer therapy. Ann Oncol. Mar 14 2014. [PMID: 24631947]
LoRusso PM, Rudin CM, Reddy JC, Tibes R, Weiss GJ, Borad MJ, et al. Phase I trial of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449) in patients with refractory, locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. Apr 15 2011; 17(8): 2502-2511. [PMID: 21300762]
Von Hoff DD, Ervin T, Arena FP, Chiorean EG, Infante J, Moore M, et al. Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine. N Engl J Med. Oct 31 2013; 369(18): 1691-1703. [PMID: 24131140]
Jesus-Acosta D. A Phase II study of vismodegib, a hedgehog (Hh) pathway inhibitor, combined with gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel (nab-P) in patients with untreated metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA). J Clin Oncol. 2014; 32:257.
Copyright (c) 2015 Kim Christin Honselmann, Moritz Pross, Carlo Maria Felix Jung, Ulrich Friedrich Wellner, Steffen Deichmann, Tobias Keck, Dirk Bausch

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.