Wernicke Encephalopathy Presenting in a Patient with Severe Acute Pancreatitis
Abstract
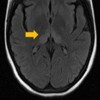
Context Acute pancreatitis can lead to prolonged fasting and malnutrition. Many metabolic changes, including thiamine deficiency, may lead to the well know pancreatic encephalopathy. In this condition however the thiamine deficiency is rarely suspected. Case report We report the case of a 17-year-old woman with severe acute pancreatitis who developed mental status changes and ophthalmoplegia. A magnetic resonance image showed hyperintensive signals in periventricular areas, medial thalamus, and mammillary bodies, findings consistent with the diagnosis of Wernicke encephalopathy. Thiamine treatment reversed neurological complications. Conclusion Wernicke encephalopathy secondary to thiamine deficiency should be considered as a possible cause of acute mental status changes in patients with acute pancreatitis and malnutrition. Prophylactic doses of thiamine could be considered in susceptible patients.
Downloads
References
Sechi G, Serra A. Wernicke's encephalopathy: new clinical settings and recent advances in diagnosis and management. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:442-55. [PMID 17434099]
Rufa A, Rosini F, Cerase A, et al. Wernicke encephalopathy after gastrointestinal surgery for cancer: causes of diagnostic failure or delay. Int J Neurosci. 2011;121:201-8. [PMID 21244301]
Sullivan EV, Pfefferbaum A. Neuroimaging of the Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Alcohol Alcohol. 2009;44:155-65. [PMID 19066199]
Fei GQ, Zhong C, Jin L, et al. Clinical characteristics and MR imaging features of nonalcoholic Wernicke encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:164-9. [PMID 18192344]
Thomson AD, Cook CC, Guerrini I, Sheedy D, Harper C, Marshall EJ. Wernicke's encephalopathy: 'Plus ça change, plus c'est la mème chose'. Alcohol Alcohol. 2008;43:180-6. [PMID 17959615]
Martin PR, Singleton CK, Hiller-Sturmhöfel S. The role of thiamine deficiency in alcoholic brain disease. Alcohol Res Health. 2003;27:134-42. [PMID 15303623]
Zhang XP, Lu YQ, Huang WD. Wernicke encephalopathy following splenectomy in a patient with liver cirrhosis: a case report and review of the literature. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010;11(6):433-6. [PMID 20506574]
Thomson AD, Cook CC, Touquet R, Henry JA; Royal College of Physicians, London. The Royal College of Physicians report on alcohol: guidelines for managing Wernicke's encephalopathy in the accident and Emergency Department. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002;37:513-21. [PMID 12414541]
Zhang XP, Tian H. Pathogenesis of pancreatic encephalopathy in severe acute pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007;6:134-40. [PMID 17374570]
Sun GH, Yang YS, Liu QS, Cheng LF, Huang XS. Pancreatic encephalopathy and Wernicke encephalopathy in association with acute pancreatitis: a clinical study. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:4224-7. [PMID 16830380]
Chen L, Zhang X. Pancreatic encephalopathy and Wernicke encephalopathy. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2002;41:94-7. [PMID 11940303]
Copyright (c) 2014 Ana Cecilia Arana-Guajardo, Carlos Rodrigo Cámara-Lemarroy, Erick Joel Rendón- Ramírez, Joel Omar Jáquez-Quintana, Juan Fernando Góngora -Rivera, Dionicio Ángel Galarza-Delgado

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.