Management of Skin Toxicities of Anti-EGFR Agents in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer and Other GI Tumors by Using Electronic Communication: Effective and Convenient
Abstract
Erlotinib has been FDA approved to be used in combination with gemcitabine as the first line treatment in advanced pancreatic cancer patients. Skin rash has been documented as one of the commonest adverse reactions in patients receiving erlotinib and other EGFR inhibitors. Draw back to this reaction leads to: 1) drug discontinuation or dose reduction; 2) impairs quality of life; and 3) Puts patients at risk of superinfection. Monitoring patients closely and initiating immediate skin care is recommended. However, patients forget how the rash started and when. No standard treatments exist secondary to the diversity of symptoms, variability and intermittent occurrence in relation to the cancer therapy. In addition, there is slow improvement with medical treatment. Also, patients need to make extra visits to doctor’s office for skin management when in needed in addition to chemotherapy appointments. Late presentation for medical attention leading to complications, such as sepsis. We here experience a novel way of assessing and managing the skin rash using the electronic media. We suggest that electronic communication is of crucial importance to detect early, diagnose and treat anti-EGFR related skin rash in order to continue the benefit of anti-EGFR.
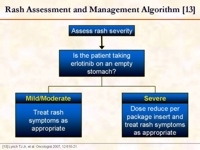
Image: Risk assessment and management algorithm.
Downloads
References
Li J, Peccerillo J, Kaley K, Saif MW. Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia related with erlotinib skin toxicity in a patient with pancreatic cancer. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2009; 10:338-40. [PMID 19454833] (FULL TEXT: http://www.joplink.net/prev/200905/22.html)
Agero AL, Dusza SW, Benvenuto-Andrade C, Busam KJ, Myskowski P, Halpern AC. Dermatologic side effects associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors. J Am Acad Dermatol 2006; 55:657-70. [PMID 17010747] (FULL TEXT: http://www.eblue.org/article/PIIS0190962205032408/fulltext)
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A, Hecht JR, Gallinger S, et al. Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25:1960-6. [PMID 17452677] (FULL TEXT: http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/content/full/25/15/1960)
Boeck S, Hausmann A, Reibke R, Schulz C, Heinemann V. Severe lung and skin toxicity during treatment with gemcitabine and erlotinib for metastatic pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2007; 18:1109-11. [PMID 17704662] (FULL TEXT: http://journals.lww.com/anti-cancerdrugs/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2007&issue=10000&article=00015&type=abstract)
Saif MW. Pancreatic cancer: highlights from the 42nd annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 2006. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2006; 7:337-48. [PMID 16832131] (FULL TEXT: http://www.joplink.net/prev/200607/02.html)
Gutzmer R, Werfel T, Kapp A, Elsner J. Cutaneous side effects of EGF-receptor inhibition and their management. Hautarzt 2006; 57:509-13. [PMID 16205868] (FULL TEXT: http://www.springerlink.com/content/y4706p1871226870/fulltext.html)
Giovannini M, Gregorc V, Belli C, Roca E, Lazzari C, Viganò MG, et al. Clinical significance of skin toxicity due to EGFR-targeted therapies. J Oncol 2009; 849051:1-8. [PMID 19584908] (FULL TEXT: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2699661/?tool=pubmed)
Pérez-Soler R, Delord JP, Halpern A, Kelly K, Krueger J, Sureda BM, et al. HER1/EGFR inhibitor-associated rash: future directions for management and investigation outcomes from the HER1/EGFR inhibitor rash management forum. Oncologist 2005; 10:345-56. [PMID 15851793] (FULL TEXT: http://theoncologist.alphamedpress.org/cgi/content/full/10/5/345)
Soulieres D, Senzer NN, Vokes EE, Hidalgo M, Agarwala SS, Siu LL. Multicenter phase II study of erlotinib, an oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with recurrent or metastatic squamous cell cancer of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22:77-85. [PMID 14701768] (FULL TEXT: http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/content/full/22/1/77)
Tan AR, Steinberg SM, Parr AL, Nguyen D, Yang SX. Markers in the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway and skin toxicity during erlotinib treatment. Ann Oncol 2008; 19:185-90. [PMID 17878175] (FULL TEXT: http://annonc.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/content/full/19/1/185)
National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v3.0 (CTCAE). CTEP: Cancer Therapy Evaluation Program. Publish date August 9, 2006 Accessed January 14, 2008. (FULL TEXT: http://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/ctcaev3.pdf)
Saif MW, Merikas I, Tsimboukis S, Syrigos K. Erlotinib-induced skin rash. Pathogenesis, clinical significance and management in pancreatic cancer patients. JOP. J Pancreas (Online) 2008; 9:267-74. [PMID 18469438] (FULL TEXT: http://www.joplink.net/prev/200805/01.html)
Lynch TJ Jr, Kim ES, Eaby B, Garey J, West DP, Lacouture ME. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor-associated cutaneous toxicities: an evolving paradigm in clinical management. Oncologist 2007; 12:610-21. [PMID 17522250] (FULL TEXT: http://theoncologist.alphamedpress.org/cgi/content/full/12/5/610)
Genentech. Inc. Tarceva®. Highlights of Prescribing Information. Accessed February 19, 2007. (FULL TEXT: http://www.gene.com/gene/products/information/pdf/tarceva-prescribing.pdf)
Saif MW, Kim R. Incidence and management of cutaneous toxicities associated with cetuximab. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2007; 6:175-82. [PMID 17367263] (FULL TEXT: http://informahealthcare.com/doi/full/10.1517/14740338.6.2.175)
Van Doorn R, Kirtschig G, Scheffer E, Stoof TJ, Giaccone G. Follicular and epidermal alterations in patients treated with ZD1839 (Iressa), an inhibitor of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Br J Dermatol 2002; 147:598-601. [PMID 12207609] (FULL TEXT: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/118938563/HTMLSTART)
Sipples R. Common side effects of anti-EGFR therapy: acneform rash. Semin Oncol Nurs 2006; 22(Suppl 1):28-34. [PMID 16616284] (FULL TEXT: http://www.seminarsoncologynursing.com/article/PIIS0749208106000362/fulltext)
Sapadin AN, Fleischmajer R. Tetracyclines: nonantibiotic properties and their clinical implications. J Am Acad Dermatol 2006; 54:258-65. [PMID 16443056] (FULL TEXT: http://www.eblue.org/article/PIIS0190962205032317/fulltext)
Lacouture ME, Mitchell EP, Piperdi B, Pillai MV, Shearer H, Iannotti N, et al. Skin toxicity evaluation protocol with panitumumab (STEPP), a phase II, open-label, randomized trial evaluating the impact of a pre-emptive skin treatment regimen on skin toxicities and quality of life in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2010 Feb 8. [PMID 20142600] (FULL TEXT: http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/reprint/JCO.2008.21.7828v1)
Saif MW, Cohenuram M. Role of panitumumab in the management of metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 2006; 6:118-24. [PMID 16945167] (FULL TEXT: http://cigjournals.metapress.com/content/b40383qphu01244t/fulltext.pdf)
Boland WK, Bebb G. Nimotuzumab: a novel anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody that retains anti-EGFR activity while minimizing skin toxicity. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2009; 9:1199-206. [PMID 19624281] (FULL TEXT: http://informahealthcare.com/doi/full/10.1517/14712590903110709)
Saltz LB, Meropol NJ, Loehrer PJ Sr, Needle MN, Kopit J, Mayer RJ. Phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with refractory colorectal cancer that expresses the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22:1201-8. [PMID 14993230] (FULL TEXT: http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/content/full/22/7/1201)
Saltz LB, Rubin M, Hochster H, et al. Cetuximab (IMC-225) plus irinotecan (CPT-11) is active in CPT-11-refractory colorectal cancer (CRC) that expresses epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 2001; 20:3a. Abstract 7.
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, et al. Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2004; 351:337-45. [PMID 15269313] (FULL TEXT: http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/351/4/337)
Wacker B, Nagrani T, Weinberg J, Witt K, Clark G, Cagnoni PJ. Correlation between development of rash and efficacy in patients treated with the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib in two large phase III studies. Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:3913-21. [PMID 17606725] (FULL TEXT: http://clincancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/13/13/3913.full)
Cedrés S, Prat A, Martínez P, Pallisa E, Sala G, Andreu J, et al. Clinical surrogate markers of survival in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with second-third line erlotinib. Lung Cancer 2009; 66:257-61. [PMID 19231023] (FULL TEXT: http://www.lungcancerjournal.info/article/PIIS0169500209000543/fulltext)
Xiong HQ, Rosenberg A, LoBuglio A, Schmidt W, Wolff RA, Deutsch J, et al. Cetuximab, a monoclonal antibody targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor, in combination with gemcitabine for advanced pancreatic cancer: a multicenter phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22:2610-6. [PMID 15226328] (FULL TEXT: http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/content/full/22/13/2610)
Kies M, Arquette MA, Nabell L, et al. Final report of the efficacy and safety of the anti-epidermal growth factor antibody Cetuximab (IMC-C225), in combination with cisplatin in patients with recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN) refractory to cisplatin containing chemotherapy. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 2002; Abstract 925.
Kane B, Sands DZ. White paper: guidelines for the clinical use of electronic mail with patients. J Am Med Inform Assoc 1998; 5:104-11. [PMID 9452989] (FULL TEXT: http://jamia.bmj.com/content/5/1/104.full)
Copyright (c) 2010 Muhammad Wasif Saif, Kristin Kaley, Lynne Lamb, Jennifer Pecerillo, Susan Hotchkiss, Lisa Steven, Marianne Brennan, Robin Penney, Carolyn Gillespie, Walid Shaib

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
As a member of Publisher International Linking Association, PILA, iMedPub Group’s JOP follows the Creative Commons Attribution License and Scholars Open Access publishing policies. Journal of the Pancreas is the Council Contributor Member of Council of Science Editors (CSE) and following the CSE slogan Education, Ethics, and Evidence for Editors.